![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Wavelength |
the distance between 2 successive points on a wave which are in phase with one another |
|
|
|
Amplitude |
the maximum displacement of the particle from its equilibrium position |
|
|
|
Displacement |
distance moved by the particle from its equilibrium position |
|
|
|
Period |
time taken for a particle on the wave to complete one oscillation |
|
|
|
Rarefraction |
a region where the particles are further apart. (Low pressure) |
|
|
|
Frequency |
the number of complete oscillations that pass through a given point in 1 second. Units: Hertz(Hz) |
|
|
|
Compression |
a region where particles are close to one another. (High pressure) |
|
|
|
Phase difference (φ) |
tells us how much a particle (or wave) is in front or behind another particle (or wave) |
|
|
|
Reflection |
the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated |
|
|
|
Refraction |
the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed |
|
|
|
Transverse wave |
the vibrations are perpendicular to the direction of the energy transfer |
|
|
|
Longitudinal waves |
the displacement of the medium is parallel to the propagation of the wave |
Along the direction if energy transfer |
|
|
Constructive interference |
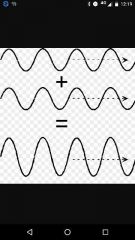
When two waves meet in such a way that their crests line up together |
|
|
|
Destructive interference |
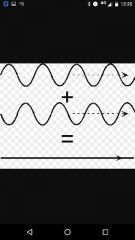
the crest of one wave meets the trough of another, and the result is a lower total amplitude |
|
|
|
Node |
a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude |
|
|
|
Antinode |
the position of maximum displacement in a standing wave system |
|
|
|
Standing wave |
The superposition of two progressive waves with the same frequency (wavelength), moving in opposite directions |
also known as stationary waves |
|
|
Fundamental frequency |
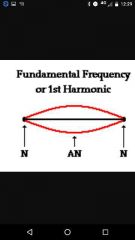
lowest possible frequency standing wave that can fit on the string |
1st harmonic |
|
|
1st overtone |
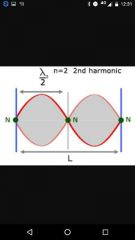
1st harmonic, 1 full wavelength |
|
|
|
Superposition |
When two waves meet they overlap and interact. Sometimes they add to make a wave bigger, sometimes they cancel each other out, and often it's a combination of both |
|
|
|
Polarisation |
the process by which the oscillations are made to occur in one plane only |
Can only happen for transverse waves |
|
|
Refractive index, n |
Measures how much a material slows down lift |
|
|
|
Critical angle |
the angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is 90° |
|
|
|
Angle of incidence |
the angle between an incident ray and the normal (perpendicular to the material) |
|
|
|
Angle of refraction |
The angle between a refracted ray and the normal. |
|
|
|
Phase |
A measurement of position of a certain point along the wave |
|
|
|
Diffraction |
The way waves spread it as they come through a narrow gap or go around obstacals |
|
|
|
Coherent |
two wave sources are perfectly coherent if they have a constant phase difference and the same frequency |
|
|
|
Monochromatic |
All the light has the same wavelength (and frequency) |
|
|
|
Fringe spacing |
The distance from the centre of one minimum to the centre of the next minimum (or max to max) |
|
|
|
Modal broadening |
Light rays enter at different angled so take different paths. Longer path= slower |
Modal dispersion, stopped by single mode fibre |
|
|
Material broadening |
Light consists of different wavelengths that travel at different speeds in the fibre |
Material dispersion, stopped by using monochromatic light |
|
|
Pulse broadening |
When the signal is sent down it becomes braided at the other end causing overlap and confuse the signal |
|
|
|
Absorption |
The signal is absorbed by the material causing a loss of amplitude so signal is reduced |
|
|
|
Optical fibre repeater |
boosts and regenerates signal which reduces degradation caused by absorption and dispersion |
|
|
|
Cladding |
Lowers refractive index in optical fibres and prevent scratches which let out light, allows total internal reflection |
|
|
|
Core |
Transmission medium for em waves to progress |
By total internal refraction |
|
|
Electromagnetic waves |
Transverse, travel in magnetic and electric fields, vibrations are perpendicular the direction of energy tansfere |
|
|
|
Central maximum |
Brightest part of the pattern |
In single slut light diffraction |
|
|
Intensity |
Power per unit area |
|
|
|
Fringe spacing |
The distance from the centre of one minimum to the next |
|
|
|
Incident ray |
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface |
|

