![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Requirements For Participation |
Fitness - can be obtained, maintained or improved, assuming that basic health is present. Ability - confidence, skills & sufficient knowledge to participate. Resources - Physical equipment, sufficient amount of people & money to pay for court hire/facilities available. |
|
|
Concepts Of Recreation & Active Leisure |
Leisure - period of time spent out of work and essential domestic activity. Must be voluntarily & done for state of mind.
Recreation - use of time designed for a therapeutic refreshment of one's body/mind. |
|
|
Contemporary Concerns Definition |
A modern day issue that prevents one from participating in physical activity. |
|
|
Contemporary Concerns |
Obesity - % of fat above the accepted norm. CHD - build up of plaque in arteries. Cholesterol - Fatty deposits in arteries. Stress - weakens immune system. MTBS - combination of medical disorders risking CHD + diabetes |
|
|
Contemporary Concerns (pt 2) |
Sedentary lifestyles - A lifestyle lacking in physical activity Ageing pop. - Amount of people 65+ Opportunity - cultural factors preventing p's. Age/Gender/SC/Ability/Ethnicity Provision - resources to p's. Access - chance to take part in sport |
|
|
Health, Fitness & Exercise |
Health - complete state of physical & mental well -being & not merely the absence of disease
Fitness - being able to meet the demands of the environment without undue fatigue
Exercise - physical activity that produces a +ve physiological adaptation. |
|
|
Positive Benefits To Achieving Health/ Fitness |
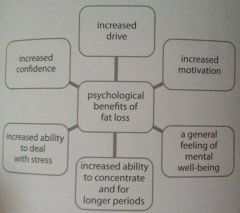
|
|
|
Health & fitness targets during fatloss |
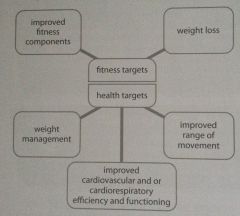
|
|
|
Energy Expenditure |
Energy in = energy out = body weight maintained
Energy in > energy out = gain weight
Energy in < energy out = lose weight |
|
|
Basal Metabolic Rate |
Rate at which calories are burnt.
Increases: Frequent meals, exercise, muscle mass, age (mid 20's), height, getting pregnant, environment, hormones, smoking. Decreases: Age (30's), fasting/starvation, hormones, sleep. |
|
|
Food Groups (energy providers) |
Carbohydrates - HI fuel source = fruit, pasta, wheat, cereal.
Fat - LI, insulation, insoluble/soluble = fish,animal & dairy products.
Proteins - Growth + repair, last resort, = meats, soya, dairy products |
|
|
Food Groups (non- energy providers)
|
Vitamins - Facilitate physio func, = animal /dairy, Fruits + veg Minerals - aid V absorption, structure for bones = Veg, fruits, fish, nuts Fibre - healthy bowel func, not digested = plant foods, fruits + veg, beans + oats Water - thermoregulation + transport = fruits + water |
|
|
Hunger + Appetite |
Hunger - physiological factor or response
Appetite - learned or psychological response of sight, smell or though of food, can be brought on by: boredom, anxiety, time of day & stress.
|
|
|
Water, Oxygen & Heat |
Water - essential for body to function
Oxygen - required to produce energy
Heat - essential for physiological function |
|
|
Role Of Water |
- Helps digest food in saliva + gastrointestinal - Transports nutrients + oxygen to cells in blood - Helps lubricate joints, cushions organs + tissue -Carries waste products out of blood in urine -Removes body heat during exercise in sweat |
|
|
Dehydration |
-First sign is thirst -Signs of headache + fatigue -Inc. HR, nausea, chills, inability to sweat -Cells start donate water to essential organs -Organs start to gradually shut down |
|
|
Electrolytes ,Thermoregulation & Viscosity |
Electrolytes - mineral soluble in body fluids, NA, K and CL.
Thermoregulation - process of keeping internal environment of body at an acceptable temp.
Viscosity - thickness or stickiness of blood. |
|
|
Muscle Fibres |
Type l - aerobic endurance, slow contraction, low intensity duration, continuous, fartlek
Type lla - middle - long distance, team games, use oxygen, fartlek, interval, circuit
Type llb - anaerobic end., HI intensity, short duration, 100m, no oxygen, interval, weight |
|
|
Cardiac output, Stroke volume, Bradycardia |
Q - blood pumped by heart per minute, SV x HR SV - volume of blood ejected into aorta per beat
Bradycardia - resting HR below 60 BPM |
|
|
Long-term Effects Of Anaerobic Training |
-Size of type ll fibres increase -Inc: force exerted by muscle + duration -Inc: tolerance of muscle to lactic acid -Inc: strength of connective tissue -Inc: stored potential energy in muscle -Type llb adopt characteristics of type lla |
|
|
Long-term Effects Of Aerobic Training |
-Inc: vascularisation of muscle -Inc: myoglobin within muscle -Inc: size + density of mitochondria in muscle -Inc: stores of muscle glycogen -Inc: efficiency at which fat is metabolised |

