![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The definition of articulation is:
|
The adjustments of the shape and acoustical properties of the vocal tract.
|
|
|
|
Articulators are:
|
The stretchers that allow the adjustment of the sound.
Another definition: the structures which mediate the adjustments (articulation). |
|
|
|
What two things make up the mechanism that allow for articulation?
|
the supportive framework (which is bone) and a muscular system.
|
|
|
|
The supportive framework is mostly made up by the facial skeleton which consists of:
|
1. Lower jaw (mandible)
2. Cervical vertebrae |
|
|
|
The two divisions of the skull are:
|
1. Cranium
2. Facial skeleton |
|
|
|
The cranium is:
|
Also known as the cranium case. This is what houses and protects the brain.
|
|
|
|
The facial skeleton forms :
|
The framework for organs of mastication (chewing) production of speech, respiration, and special senses and muscles used in facial expression.
|
|
|
|
How many bones are in the facial skeleton? How many are paired.
|
14 bones
All paired except two. |
|
|
|
Which bones of the facial skeleton are NOT paired?
|
The mandible and the vomer.
|
|
|
|
Name the bones of the facial skeleton.
|
mandible, maxillae, nasal, palatine, lacriminal, zygomatic, inferior concha, and vomer.
|
mandible, maxillae, nasal, palatine, lacriminal, zygomatic, inferior concha, and vomer.
Hint: Many Musicians Never Pack Last. Zylophones (are put) In Case (not) Valise. See third card for answer |
|
|
the symphysis, the alveolar process, the mental protuberance, the body, the ramus, the angle, the coronoid process, the mental spines and the condylar process. Look at answer card (for most of these) to see if you're right.
|
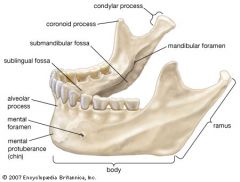
|
|
|
|
What is TMJ?
|
Abbreviation for temporomandibular joint.
The mandible articulates with the temporal bone here, with a hinge like movement and gliding action. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 ligaments that are attached to the mandible?
|
1. temporomandibular
2. spendomandibular 3. stylomandibular |
|
|
|
What is the maxilla?
|
It's the paired set of bones that form the entire upper jaw.
|
|
|
|
Picture the maxilla and the following parts: body, zygomatic process, frontal process, alveolar process, palatine process. Check answer card for "most" parts to see if you're right
|
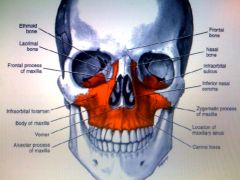
|
|
|
|
The zygomatic process on the maxillae articulates with what bone?
|
The zygomatic bone.
|
|
|
|
The frontal process of the maxillae articulates with what bone?
|
The frontal bone.
|
|
|
|
Where is the palatine process, since it's not seen from the anterior or lateral views of the maxilla?
|
It's part of the hard palate, which, the anterior three quarters of the hard palate. It can only be seen from the superior view.
|
|
|
|
Describe the nasal bones.
|
These are two small plates of bone. They are paired. This forms the bridge of the nose.
|
|
|
|
What is the shape of the palatine bones and where are they located?
|
They're two L shaped bones. The horizontal plates that come down contribute to the floor of the nasal cavity and the roof of the mouth.
|
|
|
|
What do the palatine bones articulate with?
|
The palatine process of the maxilla
|
|
|
|
Clarify the difference between where the palatine process is and the palatine bone.
|
Palatine bones are one quarter in the posterior back part of the hard palate. The palatine process of the maxilla is the is the anterior three quarters of the hard palate.
|
|
|
|
What bones are the smallest facial bones?
|
The lacrimal bones.
|
|
|
|
Where are the lacrimal bones found?
|
They form the medial wall of the orbital cavity. The orbital cavity is what some say the eye socket.
|
|
|
|
Picture the zygomatic bones and where to find the three processes, temporal, frontal and maxillary. Check picture on answer slide to see if you're right.
|
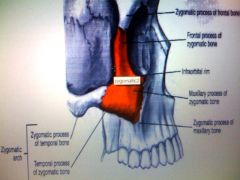
|
|
|
|
What bones have important muscles of matication and articulation on it?
|
The zygomatic bones
|
|
|
|
The inferior nasal conchae consists of three conchaes. What are they?
|
Superior, medial and inferior conchaes.
|
|
|
|
What bones make up the lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
|
Inferior nasal conchae.
|
|
|
|
Describe the vomer bone and it's location.
|
An unpaired thin quadrilateral plate. This makes up the inferior half of the bony nasal septum. This articulates inferiorly with the maxillae and the palatine bone. And superiorly with the ethmoid and sphenoid.
|
|
|
|
Name the 5 sutures in the skull.
|
1. coronal
2. sagittal 3. lambdoidal 4. squamosal 5. occipitomastoid |
|
|
|
What is a foramen?
|
A natural opening through the bone.
|
|
|
|
What is a fossa?
|
It is a pit, a depression, or concavity on a bone or formed from several bones.
|
|
|
|
Name the 8 bones of the cranium.
|
ethmoid, frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid
|
|
|
|
Which of the 8 cranial bones are paired?
|
Temporal and Parietal
|
|
|
|
Picture the three parts of the ehtmoid bone: cribriform plate, crista galli, and perpendicular plate. Check picture on the next slide to see if you're right.
|
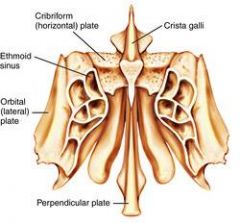
|
|
|
|
What bone forms the anterior part of the braincase?
|
The frontal bone.
|
|
|
|
What are the three important features of the frontal bone?
|
1. the zygomatic process
2. the coronal suture 3. the temporal line |
|
|
|
What are the four sutures found in the parietal bones?
|
1. Saggital
2. Coronal 3. Lambdoidal 4. Squamosal |
|
|
|
The important landmarks on the occipital bone are:
|
The magnum foramen, the occipital condyles, the lambdoidal suture, and the occipitomastoid suture.
|
|
|
|
What are the parts and landmarks of the temporal bone?
|
The external auditory meatus, which is the EAM, the articular fossa, the mastoid process, the styloid process, the zygomatic process, the squamous portion and suture, and the petrous portion.
|
|
|
|
Label parts of sphenoid bone in your mind: body, lesser and greater wings, medial and lateral pterygoid plates.
|
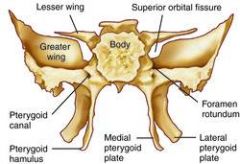
|
|
|
|
How many bones in the head are there (including auditory ossicles)?
|
29
|
|
|
|
Name the four paranasal sinuses.
|
Frontal
Maxillary Ethmoid Sphenoid |
|
|
|
Are mastoid air cells true sinues?
|
No, they are regarded as diverticulum of the tympanic antrum.
|
|

