![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many pairs of legs do Crustacea have? Insecta? Arachnids? |
Crustacea = 5 or more pairs Insecta = 3 pairs Arachnids = 4 pairs |
|
|
What is the 'cuticle'? |
Chitinous (polysaccharide) skeleton of the arthropod |
|
|
Where are the muscles of an arthropod located and where does it attach to? |
Internal muscles Attach to the exoskeleton |
|
|
Describe the circulatory system of an arthropod. |
Open circulatory system blood is free in the haemocoel(=cavity where blood circulates between organs of the arthropod) |
|
|
What does an arthropods digestive system consist of? |
Mouth --> Gut --> Anus |
|
|
Describe the nervous system of an arthropod. What neurotransmitters do they have? |
Consists of brain surrounding the oesophagus with longitundinal nerves with a ganglion in each segment.
Have GABBA and ACh |
|
|
How does respiration occur in arthropods? |
O2 diffuses through cuticle or gills or tracheal system opening through spiracles/stigmata |
|
|
What are the 'stages' between moults called? |
instars |
|
|
Define ectoparasites |
Parasites that live on the outside of the host |
|
|
Define obligate parasites |
organisms that depend on the host for existence |
|
|
Define facultative parasites |
organism can live without a host but in some circumstances become parasitic (ie opportunistic) |
|
|
Define permanent parasites |
organism is on the host all the time |
|
|
Define intermittent parasites |
organism visits host periodically |
|
|
What does pathogenicity cause? |
Loss of production Act as Vectors Irritation Death Intermediates for nematodes, cestodes, trematodes |
|
|
What are the 9 types of Insecticides and Acaricides? |
Repellent Chlorinated Hydrocarbons Organophosphates Carbamates Formamidines Botanicals Growth Regulators Macrocytic Lactones Neonicotinoids |
|
|
Give 2 out of the 5 examples of repellents |
DEET, dimethyl phthlalate, dipropyl isocinchomeronate, piperonyl butoxide, citronella |
|
|
What are 4 examples of chlorinated hydrocarbons? |
DDT Lindane (gamma isomer of benzene hexachloride) Dieldrin Endrin |
|
|
How do chlorinated hydrocarbons work? |
Hyperexcitabiliy; interfering with ion transport across membranes of axons |
|
|
How do organophosphates work? |
Reversible binding to ACh-Esterase causing parasympathetic effects |
|
|
How do carbamates work? |
Reversible binding to ACh-Esterase affecting ganglia |
|
|
How do formamidines work? |
Inhibit mono-amine oxidase |
|
|
How do botanicals work? |
Disrupt Na+ and K+ fluxes in neurones |
|
|
How do growth regulators work? |
Interfere with growth and moulting |
|
|
Which drug works best against blood or tissue feeding parasites? |
macrocytic lactones |
|
|
How do Neonicotinoids work? |
affect nicotinic receptors |
|
|
What do growth regulators interfere with? |
growth/moulting/egg laying |
|
|
What are the three sub-classes of parasitic crustacea? |
Copepoda Isopoda Pentastomida |
|
|
What are Copepoda parasites of? |
ectoparasites of aquatic fish |
|
|
Lernea spp. (anchor worm) |
|

|
Argulus foliaceus |
|
|
What are Argulus foliaceus parasites of? |
Ectoparasites of aquatic fish |
|
|
Ourozuektes owenii |
|
|
Where are Ourozuektes owenii found? |
The body cavity of marine fish |
|

|
Conodophilus imbricatus (tongue biters) |
|
|
Where are Conodophilus imbricatus found? |
in the mouth of marine fish |
|
|
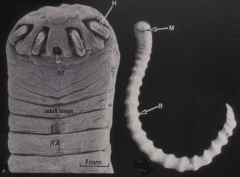
Pentastomida |
|
|
Where are pentastomes usually found on their host? |
respiratory system |
|
|
Describe the appearance of pentastomes. |
No appendages 2 hooks on either side of mouth |
|
|
Describe the appearance of the eggs of pentastomes |
contains an embryo |
|
|
Linguatula serrata |
|
|
Where do we find parasitic Linguatula serrata? |
nasal cavity of dogs |
|
|
What are the clinical signs of dogs with parasitic Linguatula serrata? How is it diagnosed? How is it treated? |
Nasal discharge, irritation diagnosis by testing faeces treated with ivermectin |
|
|
What acts as intermediate hosts for parasitic pentastomes of reptiles? |
small mammals or arthropods |
|
|
What are the features of Class Insecta? |
3 pairs of legs +/- wings head, thorax, abdomen antennae
|
|

|
Haematopinus asini |
|
|
What order do flies, midges, and mosquitoes belong to? |
Diptera |
|
|
What order do fleas belong to? |
Siphonaptera |
|
|
What order do lice belong to? |
Phthiraptera |
|
|
What are the 3 sub-orders of Diptera? |
Nematocera (midges & mosquitoes) Brachycera (March/horse flies) Cyclorrhapha (true flies:domestic, bush, blow, bot flies) |
|
|
Describe Nematocera |
small flies Long, segmented antennae pupae/larvae = aquatic females parasitic intermittent parasites not host specific irritation due to bites blood loss vectors for: bluetongue, ephemeral fever, anthrax, malaria, leishmaniasis, Dirofilaria, Onchocerca |
|
|
What are the families of Nematocera? |
Ceratopogonidae (biting midges) Simullidae (black flies) Psychodidae (sand flies) Culicidae (mosquitoes)
|
|
|
Describe Ceratopogonidae |
spotted wings larvae develop in mud, dung, sand, water Main genus: Culicoides |
|
|
What are the three groups of species of Culicoides? |
Maritime species: C. immaculatus, C. marmoratus
Native species: C. marksi
Introduced species: C. brevitarsis, C. wadai |
|
|
Describe the Maritime species of Culicoides |
C. immaculatus C. marmoratus
- breed in mangroves (saline waters) - twilight feeders (crepuscular) - not host specific - human nuisance |
|
|
Describe the Native species of Culicoides |
C. marksi
- breeds in fresh water - twilight feeders (crepuscular) - abundant in wet season of N. Aus - feed on legs and belly of cattle - vector for Onchocerca gibsoni
|
|
|
Describe the Introduced species of Culicoides |
C. brevitarsis, C. wadai
- breeds in cattle dung - twilight feeders (crepuscular) - bite on dorsal midline - cause Queensland itch - vector for bluetongue |
|

|
Simullidae Simulium/Austrosimulium |
|
|
Describe Simullidae |
- aquatic lifecycle - found around rivers - larvae are carnivorous - eggs survive in sand - emerge after flood - cause severe irritation on host - vector of Onchocerca gutturosa (cattle) and Onchocerca volvulus (human)
|
|
|
Major species of Simulium and Austrosimulium |
Simulium damnosum
Austrosimulium pestulins |
|

|
Psychodidae |
|
|
Describe Psychodidae |
- genus Phlebotomum - hairy wings - vector of protozoan, leishmaniasis - feed on reptiles |
|
|
Describe Culicidae |
- genus: Aedes, Anopheles, Culex - larvae aquatic - females = blood feed - males = non-parasitic - diurnal, nocturnal, or crepuscular - irritation and blood loss - act as vectors |
|
|
Culicidae |
|
|
What vectors do Culicidae carry? |
viruses: yellow fever, equine encephalitis, dengue, myxoma, Ross River, Barmah Forest, Murray Valley Encephalitis
protozoa: malaria
nematoda: Dirofilaria immitis |
|
|
Tabanidae Tabanus |
|
|
Describe Tabanidae |
- large - short antennae - painful bite - larval stages aquatic - found around coast and forests along creeks - cause irritation and blood loss - vectors for anthrax, trypanosomes, nematodes |

