![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Acropolis |
Origin: Greek Means "high city", site of the city's most important temples. |
|

Abstract Expressionism |
American Avant Garde Art Movement. Developed in the 1940s @ New York School. Two Types: Gestural (action painting) abstraction and chromatic abstraction. |
|

Gestural abstraction (Action Painting) |
Gestural movement of painting with emphasis on physical act. Paint is spontaneously dribbled, splashed or smeared onto the canvas, rather than being carefully applied. Famous Artists: Franz Kline and Jackson Pollock |
|

Chromatic Abstraction |
Characterized primarily by large flat, solid color across the canvas; creating areas of unbroken surface and a flat picture plane. The movement places less emphasis on gesture, brushstrokes and action in favor of an overall consistency of form and process. Famous Artists: Rothko and Barnet Newman |
|

Additive Sculpture |
Type of sculpture that material is added to. (All sculpture) |
|

Adobe |
A building material (clay) made from earth and often organic material. Most adobe buildings are similar to cob and rammed earth buildings. Adobe is among the earliest building materials, and is used throughout the world. |
|

Additive Light |
sum of all the colors in the spectrum. Natural light or sunlight. |
|

Agora |
Origin: Greek Was the center of athletic, artistic, spiritual and political life of the city. The Ancient Agora of Athens was the best-known example. |
|

Ahu |
The central stone part of a Marae ( sacred religious place) in much of Polynesia. |
|
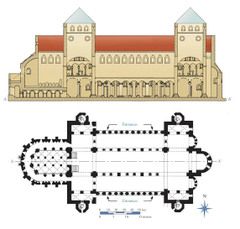
Alternative Support System |
The use of alternating wall support in the nave, usually piers and columns. |
|

Alter Pieces |
Pieces of art located behind the alter. |
|

Analytical Cubism |
Famous Artists: Braque and Picasso School of Cubism that focused on fracturing the form. |
|

Ampitheatre |
Roman building formed by joining two theaters. Used for bull fights, concerts, plays and other events. |
|

Arabesque |
Islamic art. Simple decorations based on rhythmic patterns. Ex.) Tiles |
|

Anamorphic Image |
Distorted image that must be viewed using a mirror or special lens. |
|

Apse |
Semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an Exedra in a Roman Basilica. |
|

Arcadian |
A category of art that consists of idyllic peaceful scenes. |
|

Bestiary |
A collection of descriptions or representations or real or imaginary animals. |
|

Art Brut |
Jean Dubuffet. Idea that art produced by children or mentally ill adults are the purest form of art. |
|

Black Figure Painting |
*Pottery* The silhouetting of dark figures on light background. |
|

Art Deco |
1920s to 1930s Movement in the decorative arts and architecture that features simple streamlined designs. An upgraded of industrial art often man made but could also be mass produced. Examples of materials used: plastic, jade, chrome, and ivory. |
|

Bodhisattra |
A potential buddha, common figures in Buddhist art. |
|

Art Nouveau |
1890 - 1910 Style of decorative art, architecture, and design prominent in western Europe and the US. Had by linear designs and flowing curves based on natural forms. |
|

Caduceus |
A staff (rod covered by serpents) carried by Hermes as a symbol of peace. |
|

Calligraphy |
Meaning: Beautiful writing in Greek. The art of script. |
|

Baroque |
1600s to 1750s Occurred before Rococo Famous Artists: Caravaggio and Rubens |
|
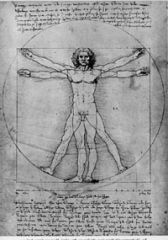
Canon |
A set of rules Ex.) Rules of proportions |
|

Calotype |
1830s A process of developing images on chemically treated paper. Early photographic process in which negatives were made using paper coated with silver iodide. |
|

Carytid |
A stone carving of a draped female figure, used as a pillar to support the entablature of a Greek or Greek-style building. |
|

Shutter Speed |
The time for which a shutter is open at a given setting. It is measured in seconds.
High shutter speeds = freeze action Low shutter speeds = motion |
|

ISO |
Level of sensitivity of your camera to available light. The lower the ISO number, the less sensitive it is to the light. (clean) Higher ISO number increases the sensitivity of your camera. (grainy / noisy) |
|

Aperture |
Is an opening / hole where light travels through. The aperture that you set impacts the size of that hole. Larger the hole (given smaller number)= more light but background is less focused Smaller the hole (bigger number) = less light but can see more of the background. |
|

White Balance |
Adjusting colors so that the image looks more natural. Most light sources (the sun, light bulbs, flashlights, etc) do not emit purely white color and have a certain “color temperature“. |

