![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Third style wall painting.
20-10 BC Pompeii |
|

|
Portrait bust of a Flavian woman
from Rome, Italy ca. 90 C.E. |
|

|
Portrait bust of Trajan Decius
from Rome, Italy ca. 249-251 C.E. |
|

|
Portrait of Constantine
from the Basilica Nova, Rome, Italy ca. 315-330 C.E. |
|

|
The Ampitheatre, Pompeii, Italy, ca. 70 BCE
- An early example of Roman concrete technology (a series of shallow concrete barrel vaults forms a retaining wall to hold the earth that the ampitheatre is built on) - Roman shows not like Greek shows (bloody and violent as opposed to intellectual displays) - "double theatre" (resembles two Greek theatres smushed into one) - mural painting in Pompeiian house detailing a vicious riot between the Pompeiians and the Nucerians during a gladitorial contest in 59 CE at ampitheatre. Mural shows what the ampitheatre looked like. |
|

|
Interior of the Pantheon, Rome, Italy, 118-125 CE
- coffered dome (sunken decorative panels) - light through oculus forms beam moving across the dome as sun moves across sky - marble veneer of walls, niches, floor - interior shows the Romans innovation from the original idea that an enclosed space was determined by the placement of solids - enclosed the space but did not 'imprison' the people |
|

|
Portraits of the Four Tetrarchs, from Constantinople, ca. 305 CE, porphyry (purple marble)
- Artists always depicted the four roman emperors together; no individual personalities portrayed. They are identically clad in cuirass and cloak. - large cubical heads on squat bodies - overt display of harmony (holding one another) - hands on swords shows readiness to protect - emotionless expressions - digressed once more from the greek human form. |
|

|
Vespasian/Titus
Colosseum ca. 70-80 AD -used for gladiatorial exhibitions and mock sea battles (though that theory has been contested as it seems rather hard to make the Colosseum water tight and the ships would have had much difficulty moving around); also used for executions and sometimes dramas based on Classical mythology |
|
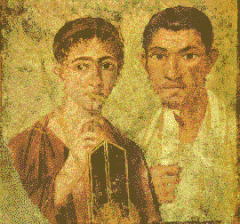
|
Pompeii, Italy
Portrait of a husband and wife ca. 70-79 CE |
|

|
Titus
Spoils of Jerusalem relief on the Arch of Titus ca. 81 CE -done in high relief, producing strong shadows -celebration Titus' conquest of Judaea -one of the soldiers is carrying a menorah, a Jewish candelabrum with religious significance -the soldiers are marching rapidly (suggested by the high energy of the soldiers) from Jerusalem back to Rome -only the heads are in low relief |
|

|
Capitoline Wolf
Rome, Italy ca. 500-480 BCE The wolf was made by the Etruscans, but the twins were added on in the 15th century. |
|

|
Temple of Portunus
Rome, Italy ca. 75 BCE |
|

|
Portrait of Augustus as a general
Primaporta, Italy ca. 20 BCE |
|

|
Portrait bust of Hadrian
Rome, Italy ca. 117-120 CE |
|

|
Dionysiac mystery frieze
Room 5, Villa of Mysteries Pompeii, Italy ca. 60-50 BCE |
|

|
Pont-du-Gard
Nimes, France ca. 16 BCE |
|

|
Frigidarium, Baths of Diocletian
Rome ca. 298-306 CE |
|

Hagia Sophia, Constantinople; built under Justinian, 532-537
|
- designed by Anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus
- Pendentive structure (to achieve a floating 'dome of Heaven') - the quality of the fall of light, creating the illusion of supporting the dome - exterior is plain and unobtrusive; a vast contrast to the interior, which is ornate and magnificent |
|

|
Ravenna, Italy
Christ the Good Shepherd (entrance wall of the Mausoleum of Galla Placidia) ca. 425 CE |

