![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Phidias - Athena Parthenos (Virgin)
-enormously tall makes you awe, overwhelm you -she's armed-- goddess of war -very streamlined, classical sculpture -not moving, very grounded -shield shows battles -faces East to attract light -pool in front >to preserve ivory >separates you from the statue >acts as a mirror, reflects light increases awe |
|
|
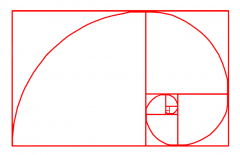
The Golden Section (ratio)
– first written about by Euclid in The Elements (300 BCE) * sides of squares in Fibonacci sequence |
|

|
Reconstruction Drawing of the Acropolis |
|
|
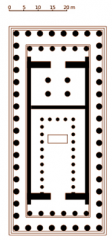
Iktinos & Kallikrates - Floor Plan of the Parthenon, Temple of Athena Parthenos
447-432 BCE * columns: N x (2N+1) |
|
|
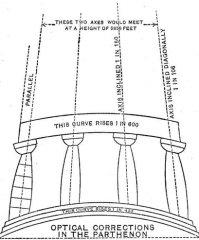
Exaggeration of the swelling of the stylobate on the Parthenon |
|

|
Erectheion, Acropolis
* ionic columns |
|
|
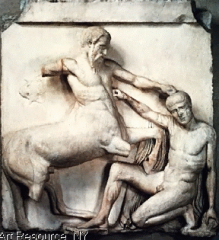
Metope: Lapiths versus the Centaurs -high up; not that easy to see -just scenes from battle; not telling narrative -starts looking at human body -relief sculpture -all were painted -Phidias
|
|

|
Parthenon Frieze: Horsemen marshal procession (West) and in procession (North) -dynamic sense of physical movement, tradition, culture -shading gives you a sense of muscle and of movement -put themselves on the same levels of Gods -bulges out further on top so you can physically view it -Athenian citizens are glorious; godlike qualitites -intense sense of realism, but idealized vision of the horse **MOVEMENT** |
|

|
Parthenon Frieze: Sacrificial animals and Unmounted Horsemen (North) - |
|

|
Parthenon Frieze: Maidens with incense and sacrificial vessels (North) |
|

|
Maidens bringing peplos (worn by gods) to chief priest: seated deities (Athena and Hephasitos) (East) |
|

|
Reconstructions of Eastern and Western Pediment -east: showed the origin story of Athena -explosion of energy -significantly more depth -much larger -back fully developed as front though noone was supposed to see it --> unique to Parthenon -trying to figure out human body |
|

|
West pediment: Ilissos, river God of Athens -cloth is clinging to arm shows wet environment
|
|

|
East Pediment: Hestia, Dione, and Aphrodite
-clothes reveal bodies; not conceal -gives you sensation of environment (water) --> anticipates next stage of sculpture -shows goddesses in a much more human way |
|

|
Kallikrates - Temple of Athena Nike, Acropolis, Athens |
|

|
Nike Adjusting her Sandal, from south side of the parapet of the Temple of Athena Nike, Acropolis
-awkward posture -garments cling tightly to body -drapery folds form intricate linear patterns |
|

|
Polykleitos - Doryphoros (Spear Bearer) -high Classical Period -emphasis on ideal man -naturalistic in musculature and pose -idealism; faces are generic with no emotion or individualized features while bodies are smooth, muscular, and proportionate -contrapposto >legs counterbalanced by arms -addressed mathematical questions presented by human form
|
|

|
Kouros -stands rigidly in an unnatural stance -shown nude |
|

|
Praxiteles - Hermes and Infant Dionysos -Late Classical Period -off-balanced stance -defined musculature, somewhat softer -sensuous and graceful appearance -humans were slenderer, softer, and taller >adjusting proportions of humans -gods were real and humanlike -less scientific cision -use of emotion >contrast with idealized and stoic works |
|

|
Lysippos - Apoxyomenos (The Scraper) -new rules of proportion -shorter torso; longer limbs -3d >right arms protrudes into viewing plane >spectator must circle the piece -physical interaction between viewer and image --> Hellenistic |
|

|
Pantheon -Front looks like classical Greek temple, but opens up into huge space -cools you off; physically calms you -concrete covers the fact that the dome is being held up by pillars -makes square niches to make the walls thinner >allows for symmetry
|
|

|
Chartres, Cathedral
|
|

|
Essential Architectural Developments of the Gothic Style: -allows wall to be carved out to allow more light in
-light conveys life, spirituality, presence of God -every structure is focused on building light |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment -exterior anticipates height & how you travel through the building -entrance on west so when you walk in you face the light |
|

|
Manuscript Illumination: Celestial City from The Trinity Apocalypse -represents the geometrical basis of the plan of Ameins Cathedral, the double square high medieval European culture equated geometrical transformations and platonic shapes seen as perfect with a Christian notion of the divine |
|

|
Giotto - Lamentation -makes sure both hands are visible -she's not faing directly forward, towards the side towards Christ |
|

|
Masaccio - Tribute Money -variety in facial expression --> meant for now -building enhances depth -jornatta is visible -responding to everything Alberti said -gestures |
|

|
Masaccio - Trinity * the space can be worked out backwards from the depiction |
|

|
Leonardo - Virgin of the Rocks -shows Virgin, Christ, John the Baptist and mistress of Milan -pyramid structure -Mary's hand is hand of protection over Christ -interplay of hands -foreshadows John's Baptism (water in foreground) -deep interest w/ nature
|
|

|
Leonardo - The Last Supper -strong orthogonal lines -table=strongest transversal -source of light, windows in back , from the left, door -first time last supper is shown as line -13 figures; grouped in trios -Christ's form is as large as each group -He brings the groups together
-shows still life of food Gesture--> -showing figures in every direction (enhances narrative) -groups line up architectually
This is a HUMAN moment -has natural light the same as that in picture Expressive Content: - betrayal , forgiveness (first communion) |
|

|
Raphael - Marriage of the Virgin -looks back to Leonardo: -door, persepective, gestures, grouping of people -union is more important than marriage -ring is absolutely central-- |
|

|
Raphael - Madonna of the Meadow -pyramid from Leonardo -eyes create spiral within pyramid -unificiation |
|

|
Leonardo - Virgin and Saint Anne -pyramid structure |
|

|
Raphael - Madonna of the Goldfinch -pyramid structure |
|

|
Raphael - Sistine Madonna -pope is pointing at us (he's the intermediate between spiritual and human) |
|

|
Raphael - Maddalena Strozzi Doni -facing forward -deep interest in showing wealth -low horizon of the landscape-->assessment of the human figure by providing uniform light which defines surfaces and volumes -balanced picture |
|

|
Leonardo - Mona Lisa -main lines: crossing of hands, chin and light on chest, hands, forehead -background-- unusual place -right side is higher --> elevates eye and mouth -in natural setting -natural beauty -she's wearing a veil -first woman shown not in profile -eyes are window to the soul -sfrumatto--smoky -soft, diluted, hazy colors -heightens mystery |
|

|
Piero della Francesca - Duke and Duchess of Urbino (Battista Sforza and Federigo da Montefeltro) -unreality -landscape
|
|

|
Raphael - Baldassare Castiglione -pyramidal composition -sprezzatura, an ideal of efforless grace befitting a man of culture -limited shaeds to black, white, and gray -soft contours of clothing and rounded beard -humane sensitivity characteristc -shadow in back -High Renaissance |
|

|
Raphael - Pope Leo X with Cardinals Guilio de’ Medici and Luigi de’Rossi -highly saturated red--shows power -combination of past portraits -shown in realistic manner |
|

|
Raphael - Stanza della Segnatura |
|

|
Apollo Belvedere -influenced the David and the creation of adam -contrapposto -positioned in front and in profile |
|

|
Michelangelo - Pieta |
|

|
Michelangelo - David
- Marble (Carrare) * tradition of Davids in Florence * concetto of subtraction * head / hands disproportional * inspired by Belvedere torso & Spear Bearer |
|

|
Belvedere Torso
- Marble |
|

|
Donatello - David |
|

|
Verrocchio - David
- Bronze |
|
|
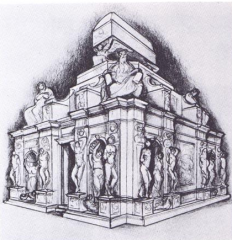
Michelangelo - Tomb of Pope Julius II
> reconstruction of the first plan 1505 > reconstruction of the second plan 1513 > completed tomb in S. Pietro in Vincoli, Rome |
|

|
Laocoon and his Sons |
|

|
Michelangelo - Captives
> The Dying Slave > Rebellious Slave - Marble * inspired by Laocoon and his sons |
|

|
Michelangelo - The Sistine Ceiling
- 1508-12 - fresco * neoplatonism * architecture (niches, structure etc.) painted! * contrast of light and shade * theme: Genesis |
|

|
Michelangelo - Libyan Sybil (Sistine) -open posture towards a book ACTIVE -intense light illuminating out of book -motioned to by jonah |
|

|
Michelangelo - Cumean Sybil (Sistine) -to the left of Eve -she can't see flipping her off -playing with form |
|

|
Michelangelo - Zechariah (Sistine) -1.) coming of christ in to Jerusalem -placed at entrace of temple speaks to notion of arrival -christ comes to jerusalem, you come to chapel 2.) building of temple -legitimizes the papcy -Julius II becomes rebuilder of Church |
|

|
Michelangelo - Jonah (Sistine) -at the end of the chapel -intense engagement with movement -the space concave, uses foreshortening to push figure into your space -first figure that pope sees -points up to go -guides your eyes -gesture of awe -sublime |
|

|
Michelangelo - Ezekiel (Sistine) -to the right of Eve |
|

|
Michelangelo - Jeremiah (Sistine) -closed posture -depressed, melancholic CONTEMPLATIVE -contemplative and active life together will take you to the divine place -pagan and christian together just like Raphael |
|

|
Michelangelo - Ignudi (Sistine) -ode to human body -working out different postures -ceiling is time of experimentation for him -holding acorns |
|

|
Michelangelo - The Flood (Sistine) -largest -too many figures present -ark in back -noah is waving goodby -confuses us |
|

|
Michelangelo - The Temptation (Sistine) -2 scenes in one : before and after -eve is picking fruit -but adam is going for it too -lust -fall eve is now ugly |
|

|
Michelangelo - The creation of Eve (Sistine) -at center -even is the counter part to mary who represent the church -god is portrayed as wise old man -not very dynamic - |
|

|
Michelangelo - Creation of Adam (Sistine) -god is flying through the air -not a natural pose -much more dynamic God -resembles Zeus -women is with God--someone who is going to become Eve -Adad looking at antique sculptures to make adam -God has new visual image -no evolution -space creates tension |
|

|
Michelangelo - Separation of Land and Water (Sistine)
- 1508-12 |
|

|
Michelangelo - Creation of the Sun, Moon and Plants (Sistine) |
|

|
Michelangelo - Separation of Light and Dark (Sistine)
- 1508-12 |
|

|
Michelangelo - Moses
- Marble |
|

|
Michelangelo - The Medici Tombs |
|

|
Michelangelo - Last Judgement (Sistine) |
|

|
Bernini - David -movement of action -captures determination -he fills the sapce more, but the viewer becomes a part of the space Baroque-- less sense of perfection models first--coming out of the block, not hugging it -more drama
1.) relationship between space 2.) rejects self-sufficiency -not a contained image -other tings are going in space 3.) invisible complement -goliath 4.) pictoral effect not possible in sculpture -drama, intense engagement, energy |
|

|
Bernini - The Martyrdom of St. Lawrence -conveys emotion in a way painting can't -sculpting fire -looks ast the virgin of m.a -willing to sacrifice for a cause |
|

|
Bernini - Portrait Bust of Cardinal Scipione Borghese |
|

|
Bernini - Apollo and Daphne -pictorialism-- a sculpture can look like an image and tell a story -shows climax -rape leaves -shows both sides of the story -transforms apollo belvedere >gives him movement >expression >makes drapery >intended for particular space
|
|

|
Bernini - Pluto and Persephone -rape -structural support= 3 headed dog -grasping of flesh TOO REAL -no romantic engagement -sculpted tears -space is redefined 0greater sense of infinity |
|

|
Bernini - Cornaro Chapel, Ecstasy of St. Theresa -orgasm -entirely painterly -clothes are vibrating -people on side are wathcing |
|
|
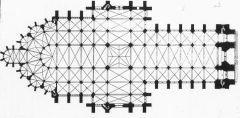
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment |
|
|
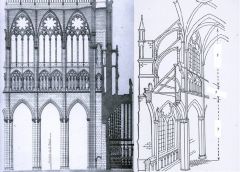
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment
- 1220-1269 - Triforium, Clerestory, and Arcade along with Elevation Drawing |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment
- 1220-1269 - High Altar with (7) Radiating Chapels |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment |
|
|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment
- 1220-1269 - Western Façade, Left Portal: > St. Firmin > The Invention and Procession of the Relics of St. Firmin |
|

|
Amiens Cathedral, Robert de Luzarches, Thomas de Corment, Renaud de Corment
- 1220-1269 - Western Façade, Right Portal: > Virgin Mary (standing on Adam & Eve) > The Dormition and Assumption of the Virgin (middle) > Coronation of the Virgin (top) |
|

|
Raphael Stanza della Segnatura |
|

|
Raphael Stanza della Segnatura -image of divine vision Heaven/ Earth -Primary Form: circle >halos >arch >holy spirit >clouds -main circle on Earth is the object that holds the wafer -wafer=vanishing point he uses figures to draw towards the center -figures are gestured toward the wafer -nephew on left- Albertian figure -most important figures are placed further away -4 of the founding members of the church -they're witness (they all hold books) the box ends the circle form -introduces 4 sides (earthly number) -continues on to the floor -circles create vertical line of symmetry -draws you up -aided by size of circles and figure pointing up -4 gospels held by angels--centered by holy spirit -the notion of circle and square= leonardo's man man is both divine and earthly
-crucified christ >wounds visible Mary and John the Baptist other men shown in the middle -in between gospel books and God -intermediaries -seen as saints/ holy figures but were once of this Earth -spacial/ temporal symmetry |
|

|
Raphael Stanza della Segnatura -vanishing point= Aristotle & Plato -Plato's finger guides you to arch >not wearing sandals, rejects the material world -harmony between pagan philosophy and christian theology >placed in a greek cross -a little sense of hiearchy -On right with Aristotle: (physical arts) >euclid -geometry guy seeing the light astronomy raphael -- painters are physical artists
Front Left: (divine type of engagement) -Pythagoreas-- ten -epicurus -socrates -apollo GREAT CHOREOGRAPHER
-guy on box disturbs thing michelagngelo (hericlitus) Aristotle with hand outwards engages and interats with you as viewer |
|

|
Raphael Stanza della Segnatura -under personification of poetry -claim poetry to divine origins -introduces nature -stuck with a door so he makes it a mountain -apollo in center >revelaed as Christ (clothing wise) -surrounded by muse -Homer, Dante, Virgil, Ovid -outside people frame the center >god of harmony; beauty; poetry Julius II sees himeself as following the tradition of using Apollo to git their own message -looking back at the notion of empires (using iconogrpahy to represent larger ideas) |
|

|
Michelangelo, Tomb of Pope Julius II
> reconstruction of the first plan > reconstruction of the second plan > completed tomb in S. Pietro in Vincoli, Rome * "Tragedy of the Tomb" * counter-reformation |
|

|
Michelangelo, Late Slaves
- Marble > The Young Slave > The Awakening Slave > Atlas (Prisoner) * escaping from the rock |
|

|
Michelangelo - The Medici Tombs -most active during day and very inactive during night
|
|

|
Michelangelo, The Medici Tombs -notions of time takes you closer to death -pensive during dusk and dawn -male dusk female dawn |
|

|
Michelangelo - Last Judgement (Sistine)
- fresco > Christ and Virgin Mary |
|

|
Michelangelo - Last Judgement (Sistine)
- fresco > The Damned Rowed by Charon |

