![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sculpture in the Round
|
A sculpture or work of art that you can freely walk around.
|
|
|
High Relief Sculpture
|
Detail of the work prominently stick out.
|
|
|
Low Relief Sculpture
|
Details of the work are not very prominent or not protruding from the work.
|
|
|
Sunken Relief Sculpture
|
The details of the work look almost as if they were carved into the work.
|
|
|
Twisted Perspective
|
Technique an artist uses to try and show every aspect of a work of art.
|
|
|
Post and Lintel
|
A structure consisting of vertical beams (posts) supporting a horizontal beam (lintel)
STONEHENGE |
|
|
Henge
|
A circular area, often containing a circle of stones or sometimes wooden posts, dating back to the Neolithic and Bronze Ages.
|
|
|
Megaliths
|
A very large stone used in various prehistoric architectures.
|
|
|
Ziggurat
|
A temple tower of the ancient Assyrians and Babylonians, having the form of a terraced pyramid of successively receeding stories.
|
|
|
Bent-Axis Approach
|
Indirect access to prevent invaders from destroying artifacts and other things.
|
|
|
Hieratic Style
|
Using the size of a figure in a work of art to signify importance.
|
|
|
Cuneiform
|
One of the worlds first systems of writing, began in Sumeria.
|
|
|
Stele
|
Ancient burial stone.
|
|
|
Citadel
|
A wall or barrier surrounding a city or building.
|
|
|
Necropolis
|
A large ancient cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments.
|
|
|
Sarcophagus
|
A tomb or coffin used by the Egyptians and many others.
|
|
|
Mummification
|
An ancient Egyptian ritual of preserving the dead.
|
|
|
Stepped Pyramid
|
An artchitechtural structure of that uses flat platforms, or steps, receding from the ground up, to achieve a completed similar to a geometric pyramid.
|
|
|
Pyramid
|
An ancient tomb shaped similar to a geometric pyramid.
|
|
|
Rock Cut Tomb
|
A burial chamber that is the cut into the living rock usually alongside of a hill.
|
|
|
Pylon
|
Greek term for a monumental gateway of an Egyptian temple. It consists of two tapering towers, each surmounted by a cornice, joined by a less elevated section which enclosed the entrance between them.
|
|
|
Canon
|
Supported by the work itself.
|
|
|
Ka
|
Egyptian word for spirit of a dead person.
|
|
|
Hieroglyphs
|
Characters used in ancient Egypt as a form of writing.
|
|
|
Fresco-Secco
|
A fresco painting technique in which pigments ground in water are tempered using egg yolk or whole egg mixed with water which are applied to plaster, that has been moistened using the temper, to simulate fresh plaster.
|
|
|
Portico
|
A porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls.
|
|
|
Vestibule
|
An antechamber, hall, or lobby next to the outer door of a building.
|
|
|
Hypostyle Haul
|
A roof supported by columns on either side creating a hall like structure.
|
|
|
Caryatid
|
A stone carving of a draped female figure, used as a pillar to support the entablature of a Greek or Greek-style building.
|
|
|
Corbel Vault
|
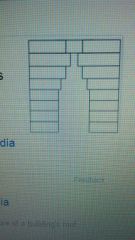
Uses this technique to support the superstructure of a buildings roof.
|
|
|
Repousse
|
Hammered into relief from the reverse side.
|
|
|
Megaron
|
Great hall of the Grecian palace complexes.
|
|
|
Tholos
|
A round building of classical Greek date and style.
A circular tomb or beehive shaped approached by a horizontal passage in the side of a hill. |
|
|
Dromos
|
An avenue or passage leading into an ancient Greek temple or tomb, especially one between rows of columns or statues.
|
|
|
Amphora
|
A tall ancient Greek jar with two handles and a narrow neck.
|
|
|
Amphora
|
A tall ancient Greek jar with two handles and a narrow neck.
|
|
|
Amphora
|
A tall ancient Greek jar with two handles and a narrow neck.
|
|
|
Krater
|
A jar or vase having a large round body and a wide mouth, used for mixing wine and water.
|
|
|
Lekythos
|
A type of Greek pottery used for storing olive oil. It had a narrow body and one handle attached to the neck of the vessel.
|
|
|
Contrsaposto
|
An asymmetrical arrangement of the human figure in which the line of the arms and shoulders contrasts with while balancing those of the hips and legs.
|
|
|
Cella
|
The inner area of an ancient temple, especially one housing the hidden cult image in a Greek or Roman temple.
|
|
|
Pronaos
|
A vestibule at the front of a classical temple, enclosed by a portico and projecting sidewalls.
|
|
|
Kouros
|
A Greek, archaic, standing, often naked statue of a young man.
|
|
|
Kore
|
A Greek, archaic, standing statue of a women clothed in loose long robes.
|
|
|
Doric
|
Relating to a classical order of architecture characterized by a sturdy fluted column and a thick square abacus resting on a rounded molding.
|
|
|
Ionic
|
Type of columns that has volutes at the capital. Comes after Doric columns.
|
|
|
Corinthian
|
Type of column. Comes after Ionic.
|
|
|
Pediment
|
The triangular upper part of the front of a building in classical style, typically summounting a portico of columns.
|
|
|
Triglyph
|
Vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze.
|
|
|
Metope
|
A square space between triglyphs in a Doric frieze.
|
|
|
Frieze
|
a broad horizontal band of sculpted or painted decoration, especially in a wall near a ceiling.
|
|
|
Entasis
|
A slight convex curve in the shaft of a column, introduced to correct the visual illusion of concavity produced by a straight shaft.
|
|
|
Column Capital
|
The topmost part of a column.
|
|
|
Column Shaft
|
The tall part of a column.
|
|
|
Column Base
|
The bottom of a column.
|
|
|
Volute
|
Spiral, scroll-like ornament that forms the basis of the Ionic order, found in the capital of the Ionic column.
|
|
|
Acropolis
|
City on a hill, usually protected by a citadel.
|
|
|
Acropolis
|
City on a hill, usually protected by a citadel.
|
|
|
Black-Figure
|
Style of vase painting in 6th and 7th centuries BC chiefly characterized by silhouetted figures painted in black slip on ah red clay body, details incised into the design, and a two-dimensional structure of form and space.
|
|
|
Red-Figure
|
Pertaining to or designating a style of vase painting developed in Greece in the latter part of the 6th and 5th centuries BC characterized chiefly by representations in red against a black-slip background, details painted in the design, and the introduction of three-dimensional illusion in the rendering of form and space.
|
|
|
White-ground Pottery
|
The vase is covered with a light or white slip of kaolinite.
|
|
|
Brahma
|
"The creator"
|
|
|
Vishnu
|
"The preserver"
|
|
|
Vishnu
|
"The preserver"
|
|
|
Shiva
|
"The destroyer"
|
|
|
Samsara
|
The process of coming into existence as a differentiated, mortal creature.
|
|
|
Buddhism
|
A religion originated in India by Buddha holding that life is full of suffering caused by desire and the way to end this suffering is through enlightenment that enables one to halt the endless sequence of births and deaths to which one is otherwise subject.
|
|
|
Stupa
|
A monumental pile of earth or other material, in memory of Buddha or a Buddhist saint, and commemorating some event or marking a sacred spot.
|
|
|
Mandala
|
A symbol representing the effort to reunify the self.
|
|
|
Yakshi
|
A class of generally benevolent nature spirits who are e the custodians of treasures that are hidden in the earth and in the roots of trees.
|
|
|
Ushnisha
|
Three dimensional oval at the top of the head of the Buddha. It symbolizes his attainment of reliance in the spiritual guide.
|
|
|
Urna
|
Spiral or circular dot placed on the forehead of Buddhist images as an auspicious mark.
|
|
|
Elongated Earlobes
|
A symbol of the heavy jewellery Buddha used to wear before h e achieved nirvanna
|
|
|
Mudras
|
Hand symbols of various Buddha statues
|
|
|
Bodhisattva
|
Enlightenment
|
|
|
Legal ism
|
Categorization of certain political-philosophical currents, reforms, persons, and writings from the Warring States, laws emphasized by the autocrat.
|
|
|
Legalism
|
Categorization of certain political-philosophical currents, reforms, persons, and writings from the Warring States, laws emphasized by the autocrat.
|
|
|
Legalism
|
Categorization of certain political-philosophical currents, reforms, persons, and writings from the Warring States, laws emphasized by the autocrat.
|
|
|
Daoism
|
A philosophical, ethical and religious tradition of Chinese origin that emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao
|
|
|
Confucianism
|
A system oh philosophical and ethical teachings founded by Confucius institute and developed by Mencius.
|
|
|
Silk Road
|
A series of trade and cultural Transmissions routes that were central to cultural interactions through regions of the Asian continent.
|
|
|
Pagoda
|
A hindhu or Buddhist temple or sacred building.
|

