![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
294 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the airplane "maximum" ambient temperature limit? |
50 degrees C "or" ISA + 35 degrees (whichever is lower). |
|
|
What is the airplane "minimum" ambient temperature limit?
|
-54 degrees C. |
|
|
What is the maximum operating altitude?
|
25,000 feet |
|
|
What is the maximum operating altitude for takeoff?
|
10,000 feet
|
|
|
What is Horizon's Vfe speed for flaps 5 degrees?
|
195 kts
|
|
|
What is Horizon's Vfe speed for flaps 10 degrees?
|
175 kts
|
|
|
What is Horizon's Vfe speed for flaps 15 degrees?
|
165 kts
|
|
|
What is Horizon's Vfe speed for flaps 35 degrees?
|
155 kts
|
|
|
What is Horizon's Vlo speed?
|
195 kts
|
|
|
What is the Landing Gear Extended speed?
|
215 kts
185 kts following "Alternate gear extension" (gear doors remain open) |
|
|
What is the maximum airspeed for flight in severe turbulence?
|
210 kts
|
|
|
What is Va (Maneuvering Speed)?
|
204 kts
|
|
|
What is Vmin for flaps 0 degrees?
|
180 kts
|
|
|
What is Vmin for flaps 5 degrees?
|
160 kts
|
|
|
What is Vmin for flaps 10 degrees?
|
150 kts
|
|
|
What is Vmin for flaps 15 degrees?
|
Vref flaps 15 degrees
|
|
|
What is Vmin for flaps 35 degrees?
|
Vref flaps 35 degrees
|
|
|
What are the engine starter cranking limits?
|
1st Attempt: |
|
|
When are the engine intake bypass doors required to be open?
|
1. For flight in icing conditions |
|
|
Regarding the use of ice protection equipment, what is the definition of icing conditions?
|
Icing conditions exist when: |
|
|
What is the maximum crosswind component for takeoff or landing?
|
32 kts |
|
|
What is the maximum "inflight" fuel imbalance between the main fuel tanks?
|
600 lbs
|
|
|
When are the tank "AUX Pumps" required to be "ON"?
|
For all takeoffs and landings.
|
|
|
What is the maximum Main, AUX and Standby Battery load meter reading for takeoff?
|
.10 on all three batteries (10% load)
|
|
|
What is the minimum battery temperature for takeoff?
|
-20 degrees C
|
|
|
Under normal operations, what is the maximum altitude with the landing gear and/or flaps extended?
|
15,000 feet
|
|
|
Is in flight operation of the power levers aft of the flight idle gate allowed?
|
No
|
|
|
What is the maximum cabin pressure differential limit?
|
5.95 PSI
|
|
|
What is the maximum cabin pressure differential during takeoff and landing?
|
.5 PSI
|
|
|
When must the engine bleed air be "OFF" for takeoff?
|
1. Suspected windshear
2. Tailwind exceeds 10 kts 3. MTOP power is required |
|
|
When must the engine bleed air be "OFF" for landing?
|
1. OAT above 39 degrees C / 100 degrees F
2. Tailwind exceeds 10 kts. 3. Suspected windshear |
|
|
Is takeoff with the AHARS in "Basic" mode allowed?
|
No
|
|
|
Is takeoff with the AHARS in "DG" mode allowed?
|
No
|
|
|
If the forward and aft baggage compartments are not empty, how far can the airplane be operated from a "suitable" airport for landing?
|
60 minutes |
|
|
When using the flight deck speakers, how shall the hot mic switches be set on both ARCDUs?
|
Both hot mic switches must be selected to "OFF". |
|
|
How does the observers INT/RAD switch need to be set when using the flight deck speakers?
|
Centered
|
|
|
Can the APU be operated while inflight?
|
No
It must be shutdown prior to takeoff. |
|
|
May the APU be operated "unattended" with passengers on board?
|
No
|
|
|
May the APU be operated during gravity refueling?
|
No
|
|
|
May the APU be started during refueling?
|
No |
|
|
What is the APU "maximum" ambient temperature limitation?
|
50 degrees C "or" ISA + 35 degrees C, whichever is lower. |
|
|
What is the APU "minimum" ambient temperature limitation?
|
- 54 degrees C for operating.
-35 degrees C for starting unless the APU has been preheated. |
|
|
What are the APU starter cranking limits? |
60 seconds "ON" / 5 minutes "OFF" |
|
|
Can we operate the APU during de-icing of the aircraft?
|
Yes
... however the APU bleed air must be selected to "OFF". |
|
|
When is the Autopilot prohibited from being used? |
1. Below 1,000' AFE following takeoff. 7. AIII Approaches below 1,000 feet AFE 8. PRM Breakout maneuver |
|
|
The use of MTOP power for takeoff is limited to how many minutes?
|
10 minutes |
|
|
When are reduced NP landings prohibited? |
1. Landings are accomplished using the "solid bug" (Vref (ice)). 8. Short field landings are conducted (less than 5,000 feet). |
|
|
What flap settings are approved for approaches flown in AIII mode?
|
15 degrees |
|
|
For approaches flown in AIII mode, how must the aircraft be configured by the FAF? |
1. The ILS Approach must be flown with the flaps at 15 degrees. 2. The HGS must be in the AIII mode prior to the FAF with the gear and flaps in the landing configuration. 3. The autopilot must be disengaged prior to 1,000 feet AFE. 4. The glideslope angle is limited to 2.51 degrees to 3.0 degrees when in the AIII Mode. 5. "AIII" mode and "RO" must be displayed prior to the FAF.
|
|
|
What are the AIII wind limitations?
|
Headwind: 25 kts |
|
|
What is the "minimum" oil temperature to unfeather the prop?
|
-18 degrees C
|
|
|
What is the minimum oil temperature for takeoff?
|
0 degrees C 55 degrees C |
|
|
What is the minimum oil temperature for takeoff into "icing" conditions?
|
55 degrees C |
|
|
When do we fly "Solid Bug" on approach below 1,000' AFE?
|
1. Icing conditions exist below 1,000 feet. 2. Suspected windshear or wind gusts exceeding 10 kts. 3. Bank angles greater than 15 degrees are required. 4. "REF SPEEDS" switch is selected to "Increase". |
|
|
What are the Takeoff Abort memory items?
|
CAPTAIN
Call "Abort - My Airplane"
1. Power Levers - "FLT IDLE" then "DISC" 2. Apply Max braking (as required) 3. Apply reverse thrust as needed. 4. Stop the aircraft and clear the runway if practical. 5. Evaluate the situation. 6. Have the first officer request any emergency equipment needed. 7. Call for the "Takeoff Abort" checklist.
- Following the "Takeoff Abort Checklist" call for the appropriate "Emergency Checklist". - Evacuate the aircraft if necessary or inform the passengers to remain seated. ("Evacuate, Evacuate" x2). - Maintain directional control using rudder and nose wheel steering. - Consult the QRH for brake cooling times prior to a subsequent takeoff (minimum of 10 minutes).
FIRST OFFICER
- State: "Your Airplane" - Maintain wings level as appropriate to the wind. - Advise ATC. - Accomplish the appropriate checklist when requested. |
|
|
What events require a takeoff to be aborted prior to V1?
|
1. Takeoff torque not obtained on either engine.
Prior to 80 kts:
2. Failure of the "A/F ARM" message to appear on the ED. 3. HGS failure or "TO WARN" or loss of symbology when below 500 RVR and the runway centerline is not in sight.
Prior to V1:
4. Engine Failure 5. Engine Fire 6. Any Master Warning 7. Takeoff warning horn 8. Windshear Warning 9. Exceeding an engine limitation |
|
|
What are the Engine Start Abort memory items?
|
1. ___ Condition Lever - "FUEL OFF" 2. Start Select Switch - "CENTER" 3. Call for the "Engine Start Abort" checklist.
Note: The captain calls for all checklist while on the ground! |
|
|
When shall an engine start be aborted by the pilot?
|
An engine start abort must be accomplished when:
1. Engine ITT exceeds 920 degrees C. 2. NH is not in the "green arc" within 70 seconds of selecting the Condition Lever to "Start & Feather". 3. The engine oil pressure fails to reach 44 psi by "Start Select Switch" reset. |
|
|
What are the "Pitch Control Jam" memory items?
|
1. Autopilot - "Disengage"
- Retain the flap setting and appropriate airspeed at the time of the jam.
If the controls are still jammed:
2. Both pilots attempt to control by applying force against the jam.
If unable to control the jam:
3. Control Column Pressure - "Relax" 4. Pitch Disconnect "T-Handle" - Pull and turn 90 degrees (pilot flying) 5. Control Column - Both pilots attempt pitch control. 6. Aircraft Control - Transfer to the pilot with the free control column. 7. Call for the "Pitch Control Jam" checklist! |
|
|
What are the "Roll Control Jam" memory items?
|
1. Autopilot - "Disengage"
If the controls are still jammed:
2. Roll Disconnect "T-Handle" - Pull and Turn 90 degrees (Pilot Flying) 3. Control Wheels Both pilots attempt roll control 4. Aircraft Control - Transfer to pilot with free controls. 5. Call for the "Roll Control Jam" checklist! |
|
|
What is the oxygen mask donning procedure?
|
State:
- "Smoke - Don Masks" or "Oxygen - Don Masks"
1. Headset - "Remove" 2. Oxygen Mask - "Don"
If smoke is present:
3. Regulator (if required) - "Emergency"
- This will pressurize the mask to prevent smoke from entering!
Establish Communications:
- Headset "ON" - Hot Mic "OFF" - Mask/Mic switch to "Mask"
4. Call for the appropriate checklist which caused the condition!
Notes: - If emergency has been selected on the regulator, the oxygen will be depleted at a rapid rate! - Always turn the "Hot Mic" switch OFF prior to turning the Mask/Mic switch to Mask so that you don't cause noise through the interphone system. - Use the interphone switch on the yoke for communication. |
|
|
What is the Missed Approach Procedure? |
2 Engine Missed Approach Procedure:
- Call "Missed Approach" and press the GA button. - The NFP automatically sets the flight guidance and states: "FLIGHT GUIDANCE SET" - Flying pilot states: "CHECKED" - If the NFP fails to set guidance then call: "SET FLIGHT GUIDANCE " - Climb at the "solid bug" Max 10 degrees pitch)
Single Engine Missed Approach Procedure:
- Call "Missed Approach" and press the GA button. Note: - The NFP automatically sets the flight guidance and states: "FLIGHT GUIDANCE SET" - Flying pilot states: "CHECKED" - If the NFP fails to set guidance then call: "SET FLIGHT GUIDANCE "
|
|
|
What is the appropriate pilot response to a "Too Low Gear" EGPWS alert? |
Accomplish the "Missed Approach" procedure.
Note: Occurs when within 500' AGL with the gear "UP" and below 190 kts.
|
|
|
What is the appropriate pilot response to a "Too Low Flaps" EGPWS alert?
|
Accomplish the "Missed Approach" procedure.
Note: Occurs when within 250' AGL with the gear "Down" and the flaps not in the EPWS landing configuration. |
|
|
If windshear is encountered on takeoff after V1, when shall rotation occur?
|
Normally Vr(W)
- If less than 2,000 feet of runway remains rotate normally, even if below Vr(W).
- Maintain the airspeed at V2+10 as a minimum.
- Maintain the current gear and flap setting until clear of the windshear encounter.
- Climb out at the "Solid Bug" (bottom bug).
|
|
|
What are the names of the passenger cabin doors?
|
Main Cabin Door (L1)
Aft Passenger Door (L2) |
|
|
Of the annunciated doors, how is an unsecured door annunciated on the flight deck?
|
"Master Warning" switchlight flashes and triple chime.
"Fuselage Doors" warning light flashes.
The MFD Door System page indicates any "open" door with a red "filled" rectangle. |
|
|
Which doors have a ditching dam?
|
Main Cabin Door (L1)
Type II/II Emergency Exit (R1) |
|
|
Explain the O2 mask's three modes of operation. |
NORMAL:
Provides mixed ambient air "on demand".
100%:
Provides 100% oxygen "on demand".
EMERGENCY:
Provides 100% oxygen under slight pressure. |
|
|
Where are the portable fire extinguishers located onboard the aircraft?
|
(1) is located behind the captain's seat.
(1) is in the Forward Emergency Stowage compartment.
(2) are in the Aft/Left Doghouse.
Note: There are a total of four (4) fire extinguishers on board the aircraft! |
|
|
How many portable oxygen bottles (POBs) are in the cabin of the aircraft?
|
6 total
- (2) for the flight attendants use during a rapid decompression.
- (4) for the passengers use during a rapid decompression.
- (1) for passenger "Therapeutic" oxygen. |
|
|
Where are the two flight attendant mobility oxygen bottles located?
|
- Forward LH overhead bin.
- Aft RH overhead bin. |
|
|
How are the emergency floor track lighting strips charged?
|
They are photo luminescent lighting strips charged by ambient light. |
|
|
How long must the emergency floor track strips be charged on the first flight of the day before boarding passengers?
|
A minimum of 15 minutes with the cabin lights "ON". |
|
|
How are the emergency lights powered?
|
By four (4) 6.4 volt Ni-Cad batteries.
Note: Batteries are installed in the cabin ceiling compartment above the forward and aft passenger doors.
Batteries are kept charged anytime that the Left Main DC Bus is powered! |
|
|
When will the emergency lights automatically activate?
|
- When the flight deck switch is selected to the "ARM" position and the "Left Main DC Bus" fails. |
|
|
How can the emergency lights be "manually" activated?
|
- By selecting the cockpit switch to the "ON" position.
"or"
- By selecting the flight attendants switch to the "ON" position. This will illuminate the emergency lights even if the cockpit switch is selected to "OFF". |
|
|
When is the flight deck emergency equipment on the "Preflight" checklist" required to be checked?
|
Anytime that the aircraft has been left unattended by the flight crew for any period of time a visual check must be made to ensure the emergency equipment has not been tampered with. Items to be checked are denoted with an "*" on the preflight checklist. |
|
|
If the temperature is _____ what is the minimum pressure required for a crew of two or three?
|
21 degrees C / 70 degrees F |
|
|
The PBE Provides oxygen for a minimum of how many minutes?
|
A minimum of 15 minutes!
Note: The PBE may last up to 60 minutes depending on conditions! |
|
|
What is the minimum landing gear strut extension?
|
The minimum strut extension is 1".
Main Gear: 1.5" to 4.5" Nose Gear: 1" to 3"
Note: Notify Maintenance Control if the strut extension is below 1". No maintenance write up is required unless the gear has "no chrome" showing or the nose gear bottoms out during taxi. |
|
|
What do the gear lights on the floor indicate?
|
The "Alternate Downlock Verification" system provides an alternate means of verifying the down and locked status of the landing gear. |
|
|
What does the Landing Gear "Inhibit" switch do?
|
It disables the electrical command from the gear selector lever to the landing gear solenoid valve. |
|
|
Is anti-skid available when using the "Emergency Brake"?
|
No
|
|
|
What is the minimum parking brake pressure for engine start?
|
Left Engine 1st: 1,000 psi
Right Engine 1st: 500 psi |
|
|
If sufficient parking brake pressure is not available for engine start, what can be done?
|
PROCEDURE 1 - Used if a pushback tug is to be used!
1. Attach the tug to the nose wheel to secure the aircraft from moving.
PROCEDURE 2 - Used if "no pushback" is available!
1. Brief the ground crew to remain clear of the gear doors.
PROCEDURE 3
- Brief the ground crew to chock both the "nose gear" and "left main gear".
1. Start the #2 engine to pressurize the #2 hydraulic system and brakes. |
|
|
Is nose wheel steering immediately available after selecting the steering switch to "ON"?
|
No |
|
|
Can we operate the Q-400 without nose wheel steering?
|
Only if it fails immediately after landing! You may taxi the aircraft to the gate using differential power and braking!
If the steering fails prior to takeoff it must be entered into the maintenance log and corrected prior to departure! |
|
|
Following gear selection what two indications should be verified?
|
1. Gear down indicator lights and Transit lights in gear selector handle.
2. Hydraulic pressures are "normal". |
|
|
Are brakes always immediately available upon landing touchdown?
|
No
The anti-skid system will disable the main brake system until:
1. Weight on wheels is detected. 2. Wheel speed is above 35 kts (canceled after 5 seconds). 3. Anti-skid is also disabled during taxi when below 10 kts. |
|
|
Following any gear extension/retraction, if you have an abnormal indication is it acceptable to re-cycle the gear?
|
No
Call for the "Abnormal Landing Gear Indication" checklist!
There could be an issue with a hydraulic sequence valve or proximity sensor in the gear system. |
|
|
What does the "LDG GEAR INOP" caution light indicate?
|
A failure of a hydraulic sequencing valve or proximity sensor on one of the gear doors. |
|
|
Who is responsible for verifying the landing gear position after gear selection?
|
Both Pilots! |
|
|
What components operate off the engine accessory gear box?
|
1. Fuel Metering Unit (FMU) 2. Oil Pump 3. DC Starter-Generator 4. Permanent Magnet Alternator (PMA)
Remember: FOD-P |
|
|
What components operate off the propeller reduction gear box?
|
1. Hydraulic Pump (Engine Driven) 2. AC Generator 3. Prop Control Unit (PCU) 4. Propeller Overspeed Governor (POG)
Remember: HAP-P |
|
|
What is the function of power uptrim? |
The "Automatic Takeoff Power Control System" uptrims the operating engine's power by 10% when an engine failure occurs.
Automatically "ARMS" when:
- Both power levers are at a high angle (60 degrees). "and" - The torque on both engines is above 50%.
Automatically "activates" when:
- The torque on the failed engine falls below 25% with the power levers in the "rating detent" and MTOP is not selected. "or" - When the Npt falls below 80% with the power levers in the "rating detent" and MTOP is not selected.
Note: - The torque loss must be confirmed by "both" torque sensors (each engine has two). - Uptrim may be cancelled by moving both power levers below the rating detent! |
|
|
What is the difference between "ENG FADEC" caution and "ENG FADEC FAIL" warning? |
ENG FADEC caution:
- It is a "cautionary fault"! Use caution when applying control inputs. You may have to re-position the power levers to maintain symmetrical torque.
ENG FADEC fail:
- It is a "critical" fault"! FADEC will automatically respond to a critical fault and may reduce power to flt Idle or completely shut the engine down. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the FADEC?
|
Full Authority Digital Electronic Control
- FADEC is a "dual channel" microprocessor controller. - Its primary function is to schedule fuel!
- Additional functions include: 1. Controls the engine bleed valves to prevent compressor stalls and surges. 2. Prevents engine overspeed at 108%. 3. Controls the engines automatic start sequence. 4. Powers the PEC. 5. Detects powerplant faults. |
|
|
How is the FADEC powered?
|
Below 20% Nh "or" PMA failure: Essential DC Bus
Above 20% Nh: Permanent Magnet Alternator (PMA) |
|
|
Does the autofeather need to be armed for uptrim to occur?
|
No
The autofeather and Automatic Takeoff Power Control System (ATPCS) are independent systems. |
|
|
What components control/regulate the propeller?
|
1. Propeller Electronic Control (PEC) 2. Pitch Control Unit (PCU) 3. Propeller Overspeed Governor (POG) 4. Auxiliary Feathering Pump 5. Automatic Propeller Synchrophase System |
|
|
By what methods can the propeller be feathered?
|
1. Autofeather system 2. Alternate feather system 3. Manual feathering
Autofeather will "arm" when:
1. Autofeather switch is selected.
"and"
2. Both engines torque exceeds 50%
"and"
3. Both power levers are advanced beyond 60 degree angle.
Autofeather will occur when:
1. System has armed itself
"and"
2. The torque on the failed engine drops below 25% for at least 3 seconds. |
|
|
When in the landing rollout may you use reverse? |
Only when:
1. The reported braking action is "POOR". 2. The anti-skid engages due to reduced braking action when braking is applied. 3. Contaminated Runways. 4. When the available landing distance is close to the required landing distance.
Only when above 60 kts! |
|
|
When is it appropriate to use reverse? |
1. Contaminated runways
2. Short runways (less than 5,000 feet) |
|
|
What is required after landing if reverse is used?
|
A "post-flight inspection" of the fuselage, propellers, and engine intake areas is required to ensure the aircraft was not damaged by FOD. |
|
|
What does the "monitoring pilot" look for during engine start? |
1. Observes the ground personnel and equipment for abnormal conditions which may require an engine shutdown.
2. Verifies that the oil pressure reaches 44 PSI and the "OIL PRESS" warning light extinguishes.
3. Verifies that the "ENG FUEL PRESS" and the "ENG HYD PUMP" caution lights extinguish.
REMEMBER: Check these caution/warning panel lights: 1. OIL PRESS |
|
|
After starter reset, when can you commence start of the other engine?
|
Following the Start Select switch resetting!
Wait until the "START" segment goes out (up to 15 seconds) prior to starting the second engine or you will not have fault protection!
Ensure that the "Main Battery" load is below .40!
"Bleed Air" annunciation does not have to be extinguished on the APU Control Panel, however the bleed air switch must be selected to off! |
|
|
Does the "APU BL AIR OPEN" light need to be extinguished prior to initiating engine start?
|
No
"Bleed Air" annunciation does not have to be extinguished on the APU Control Panel, however the bleed air switch must be selected to off! |
|
|
What does the asterisk (*) next to a flight director mode indicate?
|
The Flight Director is in the "capture" mode. |
|
|
Where can AFCS Failure or FD Abnormal messages be found?
|
- On the top of each PFD!
Note: Flashes "amber" for 5 seconds and then remains steady! These messages are "non-resetable". |
|
|
How can one differentiate between an automatic autopilot disengagement and a manual disengagement?
|
Automatic disengagement:
1. Aural tone sounds continuously until acknowledged by the flight crew. 2. The "A/P DISENG" warning lights illuminate on both sides of the glareshield until acknowledged by the flight crew. 3. An amber "AP DISENGAGED" message will annuciate on both PFD's.
Note: Acknowledge the disengagement by pressing either AP DISC button on the control yokes.
Manual disengagement:
1. Manual disengagement is annunciated by an aural tone which sounds for 1.5 seconds.
|
|
|
Can the autopilot be engaged with the Yaw Damper inoperative?
|
No |
|
|
What is "Level One" automation?
|
Hand Flying (Raw Data) |
|
|
When can you not use "Level One" automation? |
Level One automation is a non-normal mode of operation and should only be used to maintain proficiency. Do not use Level One when:
1. Abnormal aircraft systems operations. 2. Poor visibility or strong crosswinds during takeoff, approach or landing. 3. Windshear |
|
|
When should you use "Level One" automation?
|
1. Unexpected response from automation. 2. Collision avoidance. 3. Terrain Avoidance 4. Aircraft upset. 5. PRM breakout maneuver. |
|
|
What is "Level Two" automation?
|
Use of the Flight Director (with or without the autopilot). |
|
|
When should you use "Level Two" automation?
|
During takeoff and when responding to ATC instructions in dynamic terminal environments. |
|
|
What is "Level Three" automation?
|
Use of the FMS (with or without the autopilot). |
|
|
When should you use "Level Three" automation? |
Normal enroute navigation.
Do not use level three automation when unexpected changes to the flight plan occurs and time constraints prevent the crew from properly completing the advanced planning necessary. |
|
|
The Flap Auto Trim feature operates between which flap settings?
|
15 and 35 degrees
Only functions when the following conditions exist: 1. Autopilot is disengaged. 2. Airspeed is below 200 kts. 3. Manual pitch trim is not being used. 4. Flaps are moving between 15 and 35 degrees. |
|
|
What battery switches must be "ON" in order to provide APU fire protection?
|
The Battery Master must be "ON"!
- This connects the batteries to the Essential buses! The "Right Essential Bus" must be powered to provide APU fire protection!
- Procedure is to leave the Battery Master and all three batteries to "ON"! |
|
|
After starting the APU, how long should you delay before selecting the "BL AIR" switch to "ON"?
|
2 Minutes |
|
|
After starting the APU, how long should you wait before starting an engine?
|
2 Minutes
|
|
|
What will happen if you conduct the "APU FIRE TEST" with the APU running?
|
The APU fuel shutoff valve will close causing the APU to shut down!
|
|
|
Where does the APU get its fuel?
|
From the left collector bay.
The fuel is gravity fed through a "rigid" fuel line to the APU firewall. |
|
|
How much fuel does the APU burn?
|
Bleeds Off: 130 lbs/hr
Bleeds ON: 260 lbs/hr |
|
|
After landing, when should the APU be "started" if needed? |
Only while at the gate with the parking brake set!
The APU may be used when no ground power is available "or" for passenger comfort. |
|
|
What kind of electrical power does the APU generator provide?
|
28 VDC power. |
|
|
When will the "WARN" segment of the APU GEN switchlight illuminate? |
1. The APU is operating with the APU Generator selected to "OFF". |
|
|
Under what conditions can the APU be used for engine starts even though a GPU is available?
|
1. Engine start will delay the boarding or deplaning of an adjacent aircraft.
2. An adjacent aircraft's boarding process will delay your pushback. |
|
|
What systems on the aircraft have fire protection?
|
1. Both engines 2. APU 3. Forward and aft baggage compartments 4. Lavatory |
|
|
What are the cockpit indications of an engine fire?
|
1. Master Warning 2. Check Fire Detect 3. (2) Engine Fire "Press to Reset" 4. T-Handle illuminates 5. Aural Fire warning tone. |
|
|
How do you determine which engine is on fire?
|
The respective "T-Handle" will illuminate red! |
|
|
What does the pulling of the Fire T-Handle accomplish?
|
1. Closes both the "Emergency Fuel Shutoff Valve" and the "Emergency Hydraulic Shutoff Valve". 2. Arms both bottles to fire into that engine. |
|
|
How is an engine fire extinguished?
|

By selecting the spring loaded switch to the "FWD" or "AFT" position to fire the respective bottle. |
|
|
After running the appropriate checklist what is the most direct indication of whether the engine fire has extinguished? |
- Both "ENGINE FIRE - PRESS TO RESET" warning lights extinguish.
- The "T-Handle" illumination extinguishes. |
|
|
The Q-400 has a fire warning tone in the event of an engine fire. How do you silence the tone? |
Press either "Engine Fire - Press to Reset" switchlight on either side of the glareshield. |
|
|
What does the "SMOKE" warning indicate?
|
That smoke has been sensed in either the FWD or AFT baggage compartments.
Check the fire protection panel to determine which compartments "SMOKE/EXTINGUISH" switchlight is illuminated. |
|
|
What indications are associated with a fire in the "FWD" cargo compartment? |

1. Master Warning and chime. 2. "SMOKE" warning. 3. "SMOKE/EXTINGUISH" switchlight illuminates. 4. "Bottle Arm" light illuminates.
Note: The bottle "ARM" light indicates that the "High Rate" bottle is armed to discharge. |
|
|
What indications are associated with a fire in the "AFT" cargo compartment?
|

1. Master Warning and chime. 2. "SMOKE" warning. 3. "SMOKE/EXTINGUISH" switchlight illuminates. 4. "Bottle Arm" light illuminates. 5. VENT INLET and VENT OTLT closed lights illuminate. |
|
|
How is a FWD/AFT cargo compartment fire extinguished?
|
By pushing the "SMOKE/EXTINGUISH" switchlight! AFT Cargo Compartment: |
|
|
What indications, if any, would you have for a fire in the lavatory?
|
- There are no cockpit indications of a fire in the lavatory other than you will hear the smoke detector!
- The smoke alarm will be heard through the PA system in the cabin and a red light will illuminate on all of the flight attendant overhead advisory panels. |
|
|
Is the APU fire protection system automatic or manual?
|
Automatic |
|
|
Can you manually extinguish an APU Fire?
|
Yes
If the automatic system fails to discharge the bottle after 7 seconds, then pressing the guarded "EXTG" switchlight will manually fire the bottle.
Failure of the automatic system to fire the bottle is indicated by the "BTL ARM" light remaining illuminated! |
|
|
To which yoke are the ailerons connected?
|
First Officer's yoke |
|
|
To which yoke are the spoilers connected?
|
Captain's yoke |
|
|
How are the flight controls powered?
|
Mechanically controlled and Hydraulically actuated. |
|
|
What controls are locked by the control lock?
|
1. Power levers |
|
|
What do the ground spoiler advisory lights, "ROLL OUTBD & ROLL INBD", indicate? |
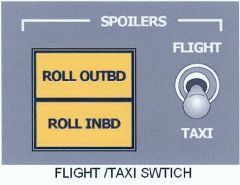
Located next to the "FLIGHT / TAXI" switch.
They will illuminate when the spoilers have "extended" while in the ground mode! |
|
|
What 3 conditions must be met on touchdown for the spoilers to extend? |
1. Flight/Taxi switch to "Flight" position. 2. Weight on wheels indicated from "both" mains. 3. Both power levers are at or aft of flight idle. |
|
|
What is the function of the powered flight control shutoff switchlights? |
Pressing the switch lights will remove hydraulic pressure to the PCU.
RUD1: Removes pressure to lower rudder PCU. RUD2: Removes pressure to the upper rudder PCU.
SPLR1: Removes pressure to the Inboard Roll Spoilers PCU. SPLR2: Removes pressure to the Outboard Roll Spoilers PCU. |
|
|
If the roll spoilers do not deploy or the props do not move into discing upon landing, should you increase or relax forward pressure on the control column? |
Relax forward pressure on the control column.
This will cause less stress on the nose wheel and increase brake effectiveness on the main gear. |
|
|
Above what speed are the outboard roll spoilers deactivated? |
170 kts
- Illumination of the "SPLR OUTBD" caution message indicates that either the spoilers did not deactivate above 170 kts "or" re-activate below 170 kts. |
|
|
Which spoilers deploy on the ground? |
Both the Inboard and Outboard Roll Spoilers! |
|
|
If the electric trim is in motion for more than 3 seconds, what happens? |
1. Aural clacker sounds.
Note: |
|
|
How could you disable a runaway pitch trim? |
By pressing the "Elevator Trim Shutoff" switchlight on either side of the glareshield!
This will deactivate the elevator trim system. |
|
|
When is an elevator trim test required? |
- The first officer completes the elevator trim test only after an aircraft "power-up"event.
- The captain may elect to conduct the elevator trim test when the "Takeoff Configuration" check indicates that something is out of parameters but the configuration appears to be appropriate. |
|
|
What needs to be verified before running the elevator trim test? |
Ensure that:
1. "Pitch Trim" caution light is extinguished. 2. "Elevator Feel" caution light is extinguished. |
|
|
Is it OK to complete a rudder check with the nose wheel steering "OFF", but with the tug still attached to the aircraft? |
No
Ensure all ground equipment is removed and personnel are clear! |
|
|
What is normal hydraulic system pressure? |
3,000 PSI |
|
|
What is the minimum hydraulic quantity for dispatch in each hydraulic system? |
40%
50% is recommended! |
|
|
What systems are powered by the #1 Main Hydraulic System? |
Flaps Inboard Roll Spoilers Brakes Anti-Skid Rudder PTU Elevator
Remember: FIBAR PE |
|
|
What backs up the #1 engine driven hydraulic pump? |
Standby Hydraulic Pump |
|
|
When will the "STBY HYD PUMP" turn on automatically? |
1. Failure of the #1 hydraulic system pressure.
2. Flaps are out of the 0 degree detent with the parking brake released. |
|
|
Will the green "ON" switchlight illuminate if the STBY HYD PUMP is automatically activated? |
No
The green switchlight will only illuminate if the pump is "manually" activated. |
|
|
What systems are powered by the #2 Main Hydraulic System? |
1. Landing Gear 2. Outboard Roll Spoilers 3. Steering 4. Elevator 5. Rudder 6. Emergency/Park Brake
Remember: LOSER E |
|
|
What backs up the #2 engine driven hydraulic pump? |
PTU |
|
|
What powers the PTU? |
#1 Main Hydraulic System
The PTU requires normal fluid quantity in the #2 hydraulic system to operate. |
|
|
Will the green "ON" switchlight illuminate if the PTU is automatically activated? |
Yes
The green light will illuminate anytime the PTU is either automatically or manually activated! |
|
|
When will the PTU automatically operate? |
Only when:
The flaps are out of the 0 degree position with the parking brake released!
While inflight the PTU must be "manually" selected to "ON" if the flaps are not out of the 0 degree position! |
|
|
How do you know if the PTU is automatically activated? |
The green "ON" switchlight will be illuminated! |
|
|
How are the hydraulic systems protected from fluid loss? |
Hydraulic System #1 and Hydraulic System #2 are protected by a "Isolation Valve" which will shuttoff flow to the EDP in the event of fluid loss. This occurs at a predetermined level!
If the Isolation valve closes then services will only be available to:
SYSTEM 1: - Rudder - Elevator - Flaps - PTU
SYSTEM 2:
- Rudder - Elevators |
|
|
If Hydraulic systems #1 and #2 fail, will braking be available? |
Normal braking will not be available (powered by Hyd System #1) |
|
|
What is the purpose of the #3 Hydraulic system? |
It provides backup pressure to the inboard PCU's on each elevator in the event that System #1 or System #2 were to fail. |
|
|
|
It is powered by a "gas charged" accumulator.
The accumulator is kept charged by a "DC Motor Pump" which automatically operates to keep the accumulator charged between 2,600 and 3,250 psi. |
|
|
When stating "HYD #3 ISO VLV CHKD" on the Before Start Checklist, what are you verifying has been checked? |
The "Hyd #3 ISO VLV" switchlight has been pressed and the "Hyd #3" fluid pressure has increased to between 2,600 and 3,250 psi. |
|
|
How would lightning in the airport vicinity affect ground operations? |
The use of headsets for communication with the ramp are not required if lightning is within 5 nm of the airport.
All ramp operations are suspended when lightning is within 3 nm of the airport. |
|
|
How far shall echoes/steep rainfall gradients be avoided in flight? |
Above 23,000 feet: - Avoid all echoes by 20 NM
Below 23,000 feet: - 0 degrees or colder: 10 NM - 0 degrees or warmer: 5 NM
- Clear all tops by 5,000 feet. - Increase distances by 50% for rapidly building cells. - When navigating between thunderstorms, use corridors that are reasonably straight. |
|
|
What is the maximum ground wind speed for operations? |
- 50 kts Steady |
|
|
What is the maximum tailwind allowed for takeoff? |
20 kts
If the tailwind exceeds 10 kts then the following restrictions apply:
- Nose wheel steering must be operative. - Anti-Skid must be operative. - Spoilers must be operative in both flight and ground modes. - Bleeds must be selected to "OFF".
In addition:
For Takeoff:
- Takeoff must be conducted with the flaps at 10 or 15 degrees. - NTop or MTop power is used. - Performance data is available.
For Landing:
- Flaps 35 degrees is used. - Props 1020 - Glidepath angle is less than 4 degrees. - Braking action is reported as "GOOD". - Performance data is available.
|
|
|
What is the maximum tailwind for landing? |
20 kts normally |
|
|
What adjustments shall be made due to reported windshear on takeoff? |
1. Bleeds Off 2. NTop Power 3. Use the appropriate flap setting from Takeoff Report. 4. Use "windshear" Vr(W) adjusted speeds from "IBal" program.
Note: Reduced Torque takeoffs are prohibited! |
|
|
What adjustments shall be made due to reported windshear on landing? |
1. Fly the "Solid Bug". 2. Bleeds "OFF" below 1,000' AFE. 3. Use normal flap setting from "Landing Report". 4. Arm "MTOP" for go-around. |
|
|
When shall intersection departures not be used? |
- Anytime that the departure end of the runway cannot be clearly visible.
- Performance data is "not available" for the intersection. |
|
|
After pushback on an icy ramp, when should you move the condition levers to "MAX"? |
Only when:
- The tug has been removed from the aircraft. - All equipment and personnel are clear! |
|
|
What is required if the runway is plowed less than 150 feet? |
The braking action must be reported as "Fair or Better" if the crosswind exceeds 10 kts.
The minimum plowed width is 100 feet! |
|
|
What are the taxiway clearing requirements? |
- Taxiways must be cleared to a minimum width of 50 feet.
- The maximum snow depth on the taxiways cannot exceed 4". |
|
|
What flap setting should be used when landing in windshear conditions? |
Use the appropriate flap setting from the "Takeoff Report". |
|
|
Where do you find the list of "Turbulence Airports? |
Flight Operations Manual (Weather Section). Turbulence Airports include: |
|
|
What are the departure/arrival turbulence procedures? |
Use when: - Moderate or greater turbulence is anticipated. - Operating "TO or FROM" Turbulence Airports.
1. Brief the flight attendants to remain seated until notified. 2. Make a PA to the passengers informing them that the flight attendants will remain seated during departure. 3. A Type I climb profile is the default, however a Type II climb may be used at the discretion of the flight crew. Notify ATC if using a Type II climb. Always use a Type II climb profile at RNO & MMH (notification to ATC is not required)! 4. Flight attendants must remain seated until 10,000 feet AFE (or higher if needed). 5. For arrival give the flight attendants a 10 minute warning prior to TOD so that they will be seated! 6. Conduct a "Seatbelt Sign Check"! |
|
|
What is the engine oil warming procedure? |
- Request a short delay on the runway from ATC. - If the wind is greater than 20 kts, align the nose within 30 degrees to the wind. - Set the parking brake. - Run up the engines between 20% to 40% torque until the engine oil warms to: 0 degrees: Normal 55 degrees: Icing below 1,000 feet. - Reduce power to Flight Idle. - Release the Parking Brake. |
|
|
What Condition Lever settings can be used for landing with "REF SPEEDS INCR"? |
1020 RPM |
|
|
What is the lowest allowable braking action for landing? |
Poor |
|
|
When are pilots required to call "Braking Action" reports to station operations? |
Anytime that "Field Reporting" is in effect.
Field Reporting is in effect when: 1. OAT is +5 degrees C or less. 2. There is visible or suspected contamination. 3. Braking action is "Less than Good". |
|
|
Is a field condition report required for legal dispatch release? |
Yes
- Stations with a 24-Hour control tower and year around temperate weather may be exempt from daily reporting! |
|
|
Part-time tower hours of operations can be found where? |
- Airport Information Charts in I-PAD.
- Back side of the "Low Altitude Enroute Charts". |
|
|
What are the recommended CTAF advisory announcements? |
OUTBOUND:
- Engine Start - Before Taxi - Before taxiing onto active runway - Departing traffic pattern
INBOUND:
- 10 miles out - Entering downwind, base and final - Clearing the runway
INSTRMENT APPROACH:
- FAF Inbound - Missed Approach - Approach completed or terminated. |
|
|
How long do pilot controlled lights stay illuminated? |
15 minutes from the last keying event. |
|
|
What are the ATC mandatory reports? |
1. Leaving an altitude. |
|
|
Are you required to follow the ODP (obstacle departure procedure) when issued a Vmc climb restriction on an IFR clearance? |
Yes
You are still required to follow the procedure unless you request a climb directly to a fix! |
|
|
What are the airspeed restrictions within Class "B", "C" or "D" airspace? |
Class "B" Airspace: No airspeed limit!
Class "C" Airspace: 250 kts below 10,000 feet msl
Class "D" Airspace: 200 kts surface to 2,500' AGL within 4 nm 250 kts below 10,000 ' msl |
|
|
When descending on a STAR and given a new altitude by ATC are you required to comply with the crossing restrictions on the STAR? Canada? US? |
Canada:
- All altitude constraints published on the STAR must be complied with!
US:
- A clearance to a new altitude overrides the altitudes published on the STAR. |
|
|
Arriving at an "uncontrolled" airport, can you cancel IFR and continue VFR? |
Yes
VFR Arrivals are allowed when:
- Weather is reported as 3,000'/5 miles - VFR cloud separation is maintained - Visual contact can be maintained with the runway "or" be within 10 nm. - Communications is established with a unicom or company remote.
Note: For night arrivals, the minimum altitude prior to landing is 1,000 feet above the highest obstacle within 5 sm of course or 2,000 feet in mountainous terrain. |
|
|
If you lose comm immediately after takeoff, what route would you fly? |
- If in VFR conditions or if VFR conditions are encountered, then maintain VFR and land as soon as practical.
- If in IFR conditions continue via the route in the last ATC clearance received "or" - If being radar vectored, by a direct route from the point of failure to the fix, route or airway specified in the vector clearance. "or" - In the absence of an assigned route by the route that ATC has advised could be expected or by the filed route. |
|
|
What is the standard holding pattern (direction, leg length)? |
Right Turns
Below 14,000 feet MSL:
Above 14,000 feet MSL: |
|
|
What is the "standard" traffic pattern? |
Traffic Pattern Altitude: |
|
|
Where do you find contamination levels? |
- Quick Reference Handbook on I-Pad.
- Performance Handbook on I-Pad
- Section 4 (performance) of Flight Standards Manual. |
|
|
When may you use MTOP power? |
1. Actual takeoff weight exceeds that for NTOP performance.
"and"
2. MTOP Performance is provided on the "Takeoff Report".
Note: MTOP Power is limited to 10 minutes! |
|
|
Based upon QNH, when does the TLR become "invalid"? |
Actual QNH is more than .10 below "planned" QNH. |
|
|
If the TLR is invalid (QNH is too low or temperature is too hot), how would you obtain takeoff performance data? |
Request updated performance data through dispatch
"or"
Use the performance charts on I-Pad. |
|
|
How is landing performance determined if the landing TLR is no longer valid or when diverting to an alternate airport? |
Request new landing data from dispatch
"or"
Use the general landing tables in the Performance Handbook (I-Pad). |
|
|
Be able to answer questions from a sample TLR! |
Review TLR report. |
|
|
If Flap Retract altitude is not specified, at what altitude above field elevation should the flaps be retracted? |
1,000 feet AFE unless a Special Turn Procedure (Simple Special or Complex Special) prescribes otherwise.
Some Complex Special turn procedures have it noted at the bottom of the Turn Procedure plate if 1-Engine and 2-Engine flap retract altitudes are different!
Dispatch Takeoff Reports list Flap Retraction Altitude as "FRA" and on paper charts as "FLAP RETRACT". |
|
|
How do you verify obstacle clearance when leaving the filed route and proceeding direct? |
The "Terrain Clearance" altitude is listed on the TLR. This will give you 1,000' of terrain separation within 5 sm of course if remaining on the filed course.
If proceeding "OFF COURSE":
1. Obtain the "Single-Engine Service Ceiling" from the performance section in the I-Pad, using the current ISA temperature and aircraft weight. 2. Compare this altitude to the "Grid MORA" altitudes listed on the Low Altitude Enroute charts. Grid MORA altitudes provide you with 2,000 feet terrain separation for obstructions above 5,000 feet and 1,000 feet terrain separation for altitudes below 5,000 feet. 3. For elevations above 5,000 feet subtract 1,000 feet from the grid MORA. This will give you the 1,000 feet terrain clearance as required by ZNTOL. 4. Compare this altitude with the Single Engine Service Ceiling altitude obtained from the performance charts! |
|
|
In general terms, explain the difference between "Terrain Clearance" and "Mountain Driftdown". |
Terrain Clearance guarantees:
- 1,000' terrain clearance within 5 sm either side of course. - A positive rate of climb at V2, single engine at 1,500' above the destination airport.
Mountain Driftdown guarantees:
- 2,000' terrain clearance within 5 sm either side of course. - A positive rate of climb at V2, single engine at 1,500' above the diversion airport.
|
|
|
If unable to maintain airspeed at your current altitude when operating single engine, when do you start descending? |
- Maintain altitude until the airspeed decays to Vse or Vse(ice) as appropriate. Driftdown at Vse!
- Use ice protection only when necessary. |
|
|
When is a takeoff alternate required? |
Anytime that the weather minimums is below the departure airport's landing minimums. |
|
|
When is a destination alternate required? |
- From 1 hour before to 1 hour after the flight's ETA the weather must be reported at least 2,000'/3 miles. 1. The airport must be served by an approved instrument approach procedure.
|
|
|
What does the weather need to be at the alternate to be legal? |
At the flights ETA the weather must be forecast to be:
1 Straight in approach or circling approach: - Add 400/1 to minimums.
2 straight in approaches: - Add 200 and 1/2 mile to the higher minimum. Note: The front course and back course of a localizer cannot be used as separate approaches.
Published CAT II or CAT III Approach: - CAT II: 300' HAT / 3/4 mile (4,000 RVR) - CAT III: 200' HAT / 1/2 mile (1,800 RVR) |
|
|
When are two destination alternates required? |
1. Anytime that the destination airport's weather has conditional language which could put it below landing minimums.
2. Anytime that the weather at the first alternate is marginal (at or near required minimums).
3. Based on "Single-Engine CAT II or CAT III" capability.
Note: Not authorized in Canada! |
|
|
May a flight be dispatched when the destination visibility is "or" is forecast to be below landing minimums? |
Yes provided:
1. Two alternates are listed on the dispatch release. 2. The weather is forecast to be:
Destination: 1/2 the required visibility minimum for the expected instrument approach.
1st Alternate: 1/2 the required visibility and ceiling.
2nd Alternate: Must meet normal alternate minimums! |
|
|
You were dispatched under a pre-planned amendment. The weather at your scheduled destination has improved but you are unable to contact dispatch. Can you land at your scheduled destination? |
No
If the weather improves at your scheduled destination you would have to contact dispatch via radio to amend the release to allow landing.
Even if the weather is still below minimums at the destination you must contact dispatch when within the vicinity to discuss options. |
|
|
To what portion of the weather report does Exemption 3585 provide relief? |
It allows dispatch to an airport when the weather reports indicate the destination or first alternate weather minimums could be below published minimums due to conditional language such as "PROB" or "TEMPO".
2 landing alternates are required! |
|
|
Where is the list of events that require dispatch notification found? |
Flight Operations Manual - Section 4 (Communications)
The following are required Dispatch Notification events: |
|
|
If the runway lights are inoperative, may a flight takeoff or land at that airport at night? |
No
If only a portion of the lights are inoperative, you may still takeoff and land provided that adequate visual reference is available to continuously identify the runway surface and maintain directional control. |
|
|
When is a "new" dispatch release required? |
1. Return to field 2. On ground for over 1 hour at intermediate stops. |
|
|
When does a "Hold-Over Time" begin? |
At the beginning of the final application of de-ice fluid. |
|
|
Where can you find hold-over times longer than those on the laminated worksheet? |
The Flight Operations Manual has holdover times published for the actual de-ice fluid types, which may increase your holdover time value. |
|
|
Following deicing/anti-icing how does the crew determine if all critical aircraft surfaces are free of frozen contamination? |
By conducting a "Post De-Ice Check".
This check is usually conducted by the De-Ice Coordinator following de-icing.
Conduct a Pre-Takeoff Contamination check prior to departure anytime that fluids have been applied to the aircraft. |
|
|
What are the represenative surfaces to conduct the "Pre-Takeoff Contamination Check"? |
Type I Fluid:
1. Visible portions of the windshield wiper blades. 2. Visible portions of the wing leading edges and spoilers.
Type IV Fluid:
1. Visible portions of the wing leading edges and spoilers only. |
|
|
ASOS is reporting 3/4 mile visibility, light snow, temperature -2C (daytime). What is your snowfall intensity? |
"Moderate"
Consult the "Snowfall Intensity" charts in the Flight Operations Manual (Section 13). |
|
|
ASOS is reporting 3/4 mile visibility, light snow and fog, temperature -2C (daytime). What is your snowfall intensity? |
"Light"
Use of the Snowfall Intensity chart is "not required" if there are other obscuring phenomena such as fog, smoke or haze. |
|
|
Where do you find airport specific deice pad procedures? |
- Flight Operations Manual (Section 13) - Airport Information Charts (I-Pad) |
|
|
When is a "Tactile Inspection" required? |
Anytime:
1. Ground icing conditions exist. 2. A clean wing cannot be visually verified. 3. Temperatures below 0C in visible precipitation. 4. Frost is observed on the underside of the wing. 5. Prior to anti-icing with type IV fluid unless hot type I fluid is used first. |
|
|
Can you depart if your holdover time has been exceeded? |
Not unless you are no longer in ground icing conditions!
If precipitation stops within the holdover time and ground icing conditions no longer exist, then the holdover time does not apply provided the OAT remains "above" the minimum temperature on which the holdover time was based. |
|
|
What is the definition of "Low Vis" operations? |
ATIS is broadcasting that Low Visibility Operations are in effect.
Usually below 1,200 RVR. |
|
|
Under what weather conditions would you expect to receive instructions from ATC to hold short of the ILS Critical Area? |
Anytime that "Low Visibility Operations" are in effect.
You must "always" observe the ILS critical areas for Canadian Operations! |
|
|
How do you differentiate between runway guard lights and stop bar lights? |
Guard lights are yellow and Stop Bar lights are red!
Runway Guard Lights:
- May be elevated "flashing" yellow lights installed in pairs at the runway entrance or in-pavement lights installed across the taxiway at runway hold short lines.
Stop Bar Lights:
- Controlled by ATC during Low Visibility Operations. - Red in color - May be either in-pavement or elevated lights. |
|
|
How can you determine if a runway has RVR? |
It is listed on the back of the 10-9 Airport Diagram plate. |
|
|
During low vis ops and following pushback, what must be ensured before you taxi? |
1. That you have the appropriate "Low Visibility" taxi chart. 2. The Low Visibility taxi chart allows for taxi with the reported visibility in effect. 3. Ensure that the ground crew has returned to the gate prior to requesting taxi clearance. 4. If visibility is not adequate, request assistance from ATC (Follow Me, Wing Walkers etc) 5. If it is not safe to continue then stop the aircraft and request assistance! |
|
|
Where may the aircraft exit the runway during low vis ops? |
Any runway with illuminated "Lead-Off Lights" is considered available unless ATC states otherwise. |
|
|
Where are takeoff minimums for an airport found? |
On the back of the Airport diagram (10-9 plate). |
|
|
KBIL is reporting 1/4 mile visibility, runway 10L RVR 1400. Can you depart runway 10L? 28R? |
10L: No ... RVR has precedence if available!
28R: No ... RVR has precedence if available! |
|
|
What is the lowest RVR the first officer can be "pilot flying" for takeoff? |
500/500/500 |
|
|
Where would you find guidance for proper aircraft configuration for a less than 500 RVR Takeoff? |
QRH on I-Pad |
|
|
How can the last 2,000 feet of an instrument runway be identified using runway edge lights? |
The runway edge lights turn "yellow" for the last 2,000 feet of runway. |
|
|
On a runway with centerline lighting, how can the last 3,000' of a runway be identified? |
- Centerline lights will alternate red and white from 3,000 feet to 1,000 feet from the runway end.
- The last 1,000 feet of runway will show "red" runway centerline lights. |
|
|
On a runway with centerline lighting, how can the last 1,000' of a runway be identified? |
The last 1,000 feet of runway will show "all red" runway centerline lights. |
|
|
Be prepared to identify various airport signage and markings. |
Review airport signage! |
|
|
What is the Type I climb profile? |
- 200 kts to 2,500' (airport traffic area)
- 240 kts to 10,000' msl
- 5 to 6 degree pitch to cruise altitude. |
|
|
What is the Type II climb profile? |
- 185 kts to FL250 or no longer required.
Note: Always advise ATC of the reduced speed during climb. |
|
|
What is the minimum altitude for turning after takeoff with two engines? |
Weather less than 1,000 / 3 miles: - 1,000' AGL unless a special departure procedure or SID prescribes otherwise.
Weather greater than 1,000 / 3 miles: - 400' AGL provided:
1. Both engines are operating at the time the turn is commenced. 2. Obstruction avoidance can be maintained visually. 3. In the event of engine failure and IMC conditions are encountered the aircraft can be maneuvered to intercept the Turn Procedure if an IFR protected altitude has not yet been reached. |
|
|
With an engine failure on departure when do you turn to follow the "VIA" block of the turn procedure? |
50' AGL |
|
|
Where are obstacle departure procedures found? |
On the front of the Airport Diagram chart (10-9). |
|
|
Following an engine failure on departure, how long must the turn procedure be followed? |
Standard Turn Procedure:
- 1,000 feet AGL
Simple Special Turn Procedure:
- 1,000 feet in VMC conditions - 3,000 feet in IMC conditions
Complex Special Turn Procedure:
- 3,000 feet in both VMC and IMC conditions. |
|
|
After takeoff, what is the maximum angle of bank? |
V2: 15 degrees
V2+10: 30 degrees |
|
|
When should terrain be displayed? |
During "Terminal" operations, unless limited by a specific aircraft procedure, the Terrain Display should be displayed for at least "one" pilot.
Note: Terminal operations are considered to be within 30 NM of the departure or arrival airport. |
|
|
Below what weather should the captain conduct the approach? |
Below 1,800 RVR |
|
|
The aircraft must be configured for landing above what altitude? |
Gear and Flaps:
Note: |
|
|
The aircraft must be stabilized on speed prior to what altitude? |
500 feet AFE |
|
|
Regarding stabilized approach, what is the maximum course deviation on an instrument approach? |
1 dot or less |
|
|
Regarding stabilized approach, what is the maximum glidepath deviation on an instrument approach with vertical guidance? |
1 dot above
1/2 dot below |
|
|
What is the maximum rate of descent on a stabilized approach between 2,000' AGL/RA and 1,000' AFE/RA? |
2,000 fpm |
|
|
What is the maximum rate of descent below 1,000' AFE? |
The rate as necessary to maintain the published glidepath.
If no published glidepath is available then not more than 1,000 fpm. |
|
|
What is the maximum airspeed deviation on a stabilized approach below 500' AFE? |
+10 kts / - 5 kts |
|
|
What is the maximum bank angle on a stabilized approach below 500 feet AFE? |
15 degrees |
|
|
At an uncontrolled airport, can you enter the pattern on final? |
Yes ... If joined at least 5 SM out. |
|
|
What is the minimum weather to conduct a circling approach? |
- The ceiling must be reported at least 1,000 feet or the published MDA, whichever is higher.
- The visibility must be 3 miles or the published visibility, whichever is higher. |
|
|
The reported weather is below published landing minimums. Can you begin the approach or continue the approach once inside the FAF? |
The weather must be at or above minimums prior to the FAF to initiate the approach. |
|
|
Can you descend below DA with only the approach lights visible? |
Yes ...
- Descent below DH/MDA using the approach light system as a visual reference is approved when using the Captain Monitored procedures "or" using the HGS only down to CAT I minimums. Note: |
|
|
As defined by FAR, what approach category is the Q400? |
Category "C"
Category "A": Less than 91 kts Category "B": 91 to 120 kts Category "C": 121 to 140 kts Category "D": 141 to 165 kts Category "E": Above 165 kts |
|
|
When on an RNP approach, are you required to use Cat "D" minimums? |
Only if CAT "D" speeds are used for any portion of an RF leg within the "final segment" of the approach. |
|
|
With the nose gear doors "open", should you connect to the tug? |
No
Once hydraulics are applied to the aircraft the doors could close with great force and possibly injure ground personnel! |
|
|
How many flight attendants are required to be on board: Boarding/Deplaning? Remain on board with passengers on a through flight? |
Boarding and Deplaning:
Both flight attendants are required!
Through Flights:
- At least on crew member must remain on board. This can be a pilot! The pilot must be identified to the passengers.
1. Aircraft engines must be shut down. 2. At least one floor level exit must remain open. |
|
|
How often does a company I-Pad need to be synced? |
Prior to the beginning of a trip.
Note: The minimum I-Pad battery charge is 50% to begin a flight segment. |
|
|
Are there any restrictions to where an I-Pad can be synced? |
The I-Pad may be synced from any Wi-Fi connection, however company sensitive information such as the I-Jaws program may only be synced from a company server at one of the pilot bases. |
|
|
What is the minimum I-Pad battery charge? |
50% prior to beginning a flight segment. |
|
|
Can you charge your I-Pad with the EFB if needed? |
No
Charging the I-Pad via the EFB is not authorized! |
|
|
Can both pilots simultaneously reference their I-Pad in flight? |
No |
|
|
What is the required flight crew equipment? |
1. Medical 2. Pilot License 3. Company ID (at start of trip) 4. Restricted Radio Telephone Operators permit 5. Passport (International Only) 6. Flashlight with 2 "D" cell batteries or equivalent 7. Jeppesen Airway Manual 8. Headset with boom mic 9. Company issued I-Pad 10. Manual dispatch release forms |
|
|
What is the standard takeoff briefing? |
"Call out 80, V1 and rotate" |
|
|
What is the maximum taxi speed? |
Good Braking / Good Visibility: 20 to 25 kts
Contaminated taxiways: 10 kts |
|
|
By what speed on takeoff do the power levers need to be set in the Rating Power detent? |
50 kts |
|
|
During the takeoff roll, what items are checked by the pilot monitoring? |
1. Roll Spoilers show retracted on the PFCS and the spoilers advisory lights are extinguished.
2. "AF ARM" message is displayed on the ED. |
|
|
What is the maximum pitch on takeoff until all wheels liftoff? |
8 degrees |
|
|
When are the flaps retracted on a two engine missed approach? |
At acceleration height (now 2,000 feet above approach minimums or first level off altitude, whichever is lower).
"and"
Airspeed at least V2+10 kts |
|
|
On initial climb out, when does the pilot monitoring complete the After Takeoff flow and checklist? |
When "Clear of the Traffic Area" and at least 2,500' AFE and 4 nm from the airport. |
|
|
What is the normal holding speed and configuration? |
200 kts
Gear and Flaps retracted |
|
|
On approach, when is the missed approach altitude set in the alerter? |
At the 1,000' chime or initiation of the missed approach, whichever occurs first. |
|
|
What is the maximum ground speed on the runway after landing? |
Good Visibility & Good Braking: 60 kts
25 kts when: - Braking action is less than good - Visibility is less than 1,000 RVR - Prior to reaching the last 1,000 feet of runway. |
|
|
How close may an aircraft be taxied to an object? |
Within 10' requires a wing walker.
We never taxi closer than 5' (even with a wing walker). |
|
|
What landing pitch attitude may induce a tail strike? |
Above 6 degrees |
|
|
If the pitch attitude reaches 6 degrees nose up or if an excessive sink rate develops on short final, the pilot flying should correct how? |
Increase power and lower the pitch 1 to 2 degrees. |
|
|
How would a tail strike be indicated? |
Master Warning / tripple chime
"Touched Runway" warning |

