![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ingredients to a Balanced Diet
|

Carbohydrates, Fats, Protein, Fibre and Vitamins/Minerals
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|

Release Energy
|
|
|
Fats
|

Release energy as well as keeping the body warm
|
|
|
Protein
|

For growth, cell repair and cell replacement
|
|
|
Fibre
|

Smooth's the flow of food through the digestive system
|
|
|
Vitamins and Minerals
|

Maintains healthy bones, skin and blood
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
The rate at which chemical reactions happen within cells
|
|
|
People with High Metabolic Rates
|
People who have a larger proportion of muscle to fat (a body builder for example - this is why men on average have a higher rate
|
|
|
How do you increase your Metabolic Rate?
|
To increase your metabolic rate you simply exercise more
|
|
|
The higher your metabolic rate...
|
... the more energy you should consume
|
|
|
Un-Balanced diets cause either...
|

... malnourishment, a change in weight or health problems
|
|
|
Bacteria
|
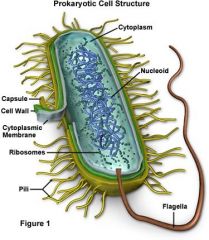
Small cells that divide and reproduce rapidly in the body causing illness by damaging the cells and producing toxins (poison)
|
|
|
Virus
|
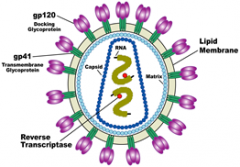
NOT A CELL - replicate in the body by inhabiting cells and reproducing until the cell bursts, the cell damage is what causes the feeling of illness
|
|
|
First Line of Defence
|
Skin, hair and mucus
|
|
|
Secondary Line of Defence
|
Platelets in the blood clot when and opening (cut/wound appears) forming a scab. The more platelets in your blood the better
|
|
|
Final Line of Defence
|
The immune system - Majorly, White blood cells
|
|
|
White Blood Cells
|
1) Engulf foreign cells and digest them 2) Produces antibodies to interlock with the antigens (foreign cells) to lock and kill the antigens foreign 3) Produce antitoxins to counteract the toxins that the foreign cell creates |
|
|
Vaccination
|
An injection of a weaker form or inactive version of the antigens so that the body produces antigens that prevent them. The body memorizes the antigen meaning if it ever re occurs then the antibodies can be redistributed to kill it.
|
|
|
Vaccination (Advantages)
|
- Control infectious diseases e.g.: polio and smallpox - Epidemics can be prevented |
|
|
Vaccination (Disadvantages)
|
- Not 100% successful in prevention - Some people can react badly to vaccines |
|
|
Drug Relief
|
Pain killers and antibiotics work great against bacteria only and vaccines cannot be prevented. Unfortunately, using drugs to often drastically lower your immune systems strength and therefore you are more likely to become ill more often.
|
|
|
Resistant Bacteria
|
Some bacteria can mutate and become resistant to the antibiotics meaning it is pointless using them
|
|
|
Dangers of Resistant Bacteria becoming more Common
|
Every bacteria in the world could become more resistant meaning an epidemic of an un-treatable virus or bacteria will spread and kill before we find a cure (as long as the bacteria isn't 100% resistant)
|
|
|
The Nervous System
|
All the nerves in your body are a chain - Peripheral nervous system, Central Nervous System, Brain etc..
|
|
|
The 5 Senses
|
Sight, smell, sound, taste and touch
|
|
|
The 5 Sense Organs
|
Eyes, nose, ears, tongue and skin
|
|
|
Central Nervous System (CNS)
|
The "motorway" in which all impulses travel down as the fastest route to the brain
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
|
The "A-Roads" in which impulses travel down to reach receptors or neurones
|
|
|
Sensory Neurones
|
The nerve cells that carry electrical signals from the receptors to the CNS
|
|
|
Relay Neurones
|
The nerve cell that carries signals from sensory neurones to the motor neurones
|
|
|
Motor Neurones
|
The nerve cells that carry the signals from the CNS to the effectors
|
|
|
Effector
|
Muscle or glands the respond in different ways to specific neurological impulses
|
|
|
Synapses
|
The connection between two neurones, uses diffusion to diffuse chemicals across the synapse. The time taken to diffuse across the synapse is effected by depressants and anti depressants such as drugs, alcohol, coffee etc...
|
|
|
Reflex Arc
|
The quick way of reacting to danger via a circuit. stimuli > receptor > sensory neurone > relay neurone > motor neurone > effector > response |
|
|
Advantages of Reflexes
|
Allow quick responses to avoid injury or to maintain posture
|
|
|
Automatic Reactions
|
Like reflexes but they go unnoticed such as blinking and breathing
|
|
|
Hormones
|
Chemicals that are released into the blood plasma via glands
|
|
|
Effects of Hormones
|
Long-lasting effect of development and can also alter the mood of the person secreting the hormone
|
|
|
Menstrual Hormones
|
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) = pituitary gland Luteinizing hormone (LH) = pituitary gland Oestrogen = Ovaries |
|
|
The Menstrual Cycle
|
The four stage process of which a female produces and removes an egg in a 28 day cycle
|
|
|
Stages of the Menstrual Cyclestage
|
stage 1 - bleeding begins and lasts through days 1 - 4 stage 2 - uterus walls rebuild through days 4 - 14 stage 3 - a new egg is released on day 14 stage 4 - the wall is maintained through days 14 - 28 the process the repeats itself every 28 days |
|
|
FSH
|
Made in the Pituitary Gland and causes an egg to mature in the ovaries as well as stimulating the ovaries to release oestrogen
|
|
|
Oestrogen
|
Made in the ovaries and causes the Pituitary Gland to produce LH which stops the further release of FSH
|
|
|
LH
|
Made in the Pituitary Gland and stimulates the release of an egg
|
|
|
Uses of Hormones
|
They can be used to stimulate the body which puts the reproductive system in a contraceptive mode - usually activated by 'the pill'
|
|
|
Pros of the Pill
|
- It's over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy - It reduces the risks of some specific cancers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
|
Collecting eggs from the ovary and sperm which are then fertilised in a lab until thy reach the stage of an embryo (undeveloped ball of cells). the embryo is then transferred back into the mother's uterus.
|
|
|
Pros of IVF
|
- can give an infertile couple a baby - increases the chances of a 'pregnancy' |
|
|
Cons of IVF
|
- Some women can have very bad reactions to the hormones - increased risk of cancer via the hormones - the cells can divide into multiple babies - higher chance of a miss carriage if multiple babies are made |
|
|
Auxin
|
A plant hormone near the roots and shoots that controls growth in response to light, gravity and moisture
|
|
|
Phototropism
|
When a root or shoot grows towards light
|
|
|
Gravitropism
|
When a root grows in the direction of gravity and shoots grow opposite the direction of gravity
|
|
|
Geotropism
|
When a root or shoot grows towards moisture
|
|
|
Use of Plant Hormones in Agriculture
|
They can disrupt the growth of weeds/bad plants and can induce the growth of the useful plant the farmer needs such as corn or wheat
|
|
|
Homeostasis
|
How the body keeps conditions inside it the same.
|
|
|
Kidney
|
Ions and urea are filtered in the kidneys and are regulated to healthy levels so the human survives
|
|
|
Water Loss via Homeostasis
|
water is lost from; - the skin as sweat - the lungs as moisture - the kidneys as urine |
|
|
Water Loss is higher on...
|
... a hot day than a cold day as you drink more fluids to counteract the water loss
|
|
|
Maintenance of the Core Body Temperature
|
The brain maintains a constant body heat of around 37 degrees Celsius as this is the optimum temperature for enzymes to function at
|
|
|
Blood Sugar Levels
|
Insulin helps to maintain the right concentration of blood sugar but it also keeps some excess in case of a sudden demand for energy (e.g. if you start vigorous exercise)
|
|
|
Drugs
|
A chemical that changes your body chemistry
|
|
|
Pro Drugs
|
People take the choice to take the drug however harmful it may be - people use different ways of gaining advantages such as athletes drinking protein shakes
|
|
|
Anti Drugs
|
- it's unfair and selfish for people to take drugs to gain an advantage - there are serious health risks labelled with most drugs - almost all drugs are addicting |
|
|
Statins
|
Prescription drugs that help lower heart and circulatory diseases, they also lower blood cholesterol
|
|
|
Illegal Drugs
|
Drugs that are prohibited by law as the government see them to be dangerous
|
|
|
Drug Testing
|
The three main stages to drug testing are: - testing on human cells and tissues (no direct effect) - test drugs on live animals (causes ethical issues) - tests on human volunteers to calculate the safest and most effective doses for the drug for when it is mass manufactured |
|
|
Past Problems - Thalidomide
|
Thalidomide was an intended sleeping pill but it wasn't tested on the pregnant woman. It was found to be a relief for morning sickness so pregnant woman took the drug and when the baby was born, it was deformed and only half the infected babies survived. an estimate predicts that there were around 10'000 babies effected by this drug
|
|
|
Recreational Drugs
|
Drugs divided into classes of legal and illegal and soft and hard. hard being drugs that are harmful and/or highly addictive. the use of recreational drugs is mostly for socializing or relaxing.
|
|
|
Problems with Smoking
|
-causes disease and internal failure - can cause cancer - it is addictive |
|
|
Problems with Alcohol
|
- affects the nervous system - causes poor coordination or even unconsciousness - leads to liver disease and brain damage - also addictive like smoking |

