![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
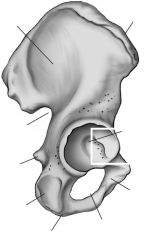
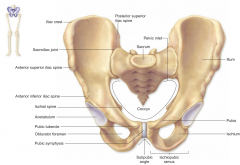
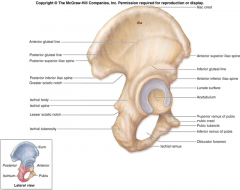
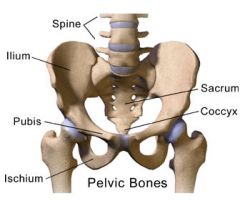
Iliac crest
|
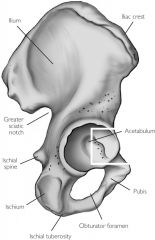
Top ridge
|
|
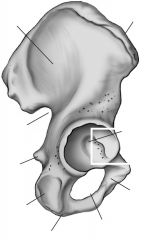
Acetabulum
|
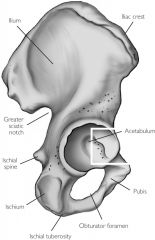
Socket for head of femur
|
|
|
Iliac fossa
|
Inner or medial surface of bone
|
|
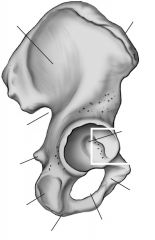
Greater sciatic notch
|
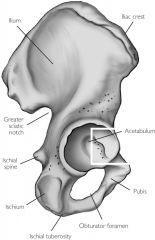
Large posterior notch; allows sciatic nerve to exit hip area
|
|
|
Auricular surface
|
Surface for articulation with auricular surface of sacrum
|
|
Obturator foramen
|
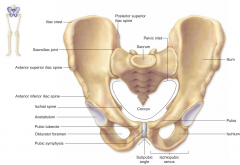
Inferior to the acetabulum; allows for passage of nerve and vessels down the medial side of the thigh
|
|
|
Symphysis pubis
|
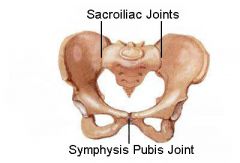
Anterior surface where two pubic bone articulate
|
|
Pubic tubercle
|
One of the attachment points for the inguinal ligament
|
|
Ischial tuberosity
|
On inferior & posterior end
|
|
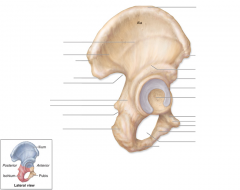
Ischial spine
|
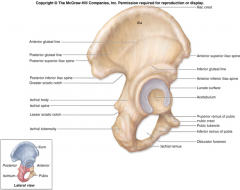
Notch below greater sciatic notch
|
|
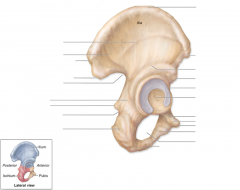
Ischium
|
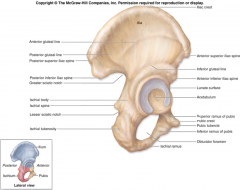
|
|
Pubis
|
|
|
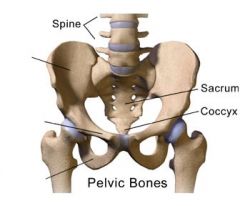
Ilium
|
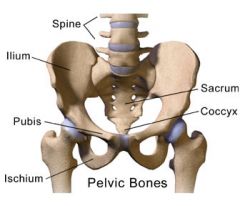
|
|

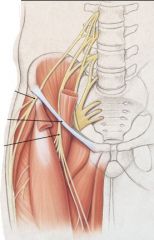
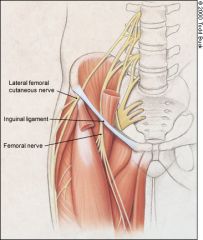
Inguinal ligament
|

The inguinal ligament is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine.
|
|
|
Sacroiliac joint
|

Strong fibrous and synovial articulation between the sacrum and ilium
|
|

Greater trochanter
|

Proximal end on lateral side
|
|

Lesser trochanter
|

Proximal end on posterior/medial side
|
|

Intertrochanteric line
|
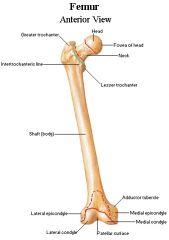
Ridge on anterior surface joining greater to lesser surfaces
|
|
|
Intertrochanteric crest
|
Joins greater to lesser trochanter on posterior side
|
|
|
Gluteal tuberosity
|
Roughening on lateral side just below greater trochanter; attachment of gluteus maximus
|
|
|
Medial and lateral condyles rest on:
|
The shallow fossae of the tibia (covered with articular cartilage)
|
|
|
Patellar surface
|
Anterior articular surface at distal end, for articulation of patella
|
|
|
Intercondylar notch
|
Notch/fossa between medial and lateral condyles
|
|
|
Adductor tubercle
|

On medial epicondyle; for attachment of the adductor magnus muscle
|
|
|
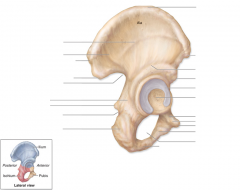
Iliofemoral ligament
|
Joins femur to iliac part of acetabulum, visible from anterior view.
Superior to the pubofemoral ligament. Tightens with hip extension. |
|
|
Pubofemoral ligament
|
Joins the femur to the pubic aspect of the acetabulum. Visible with anterior view.
Inferior to the iliofemoral ligament. Tightens with hip abduction. |
|
|
Ischiofemoral ligament
|
Posterior ligament.
Attaches femur to ischial aspect of acetabulum. Curls around to attach to the intertrochanteric line. Tightens with medial hip rotation. |
|
|
All three pelvis-femur ligaments take a ________ direction to ________
|
All three pelvis-femur ligaments take a twisting/spiral direction to strengthen the articulation
|
|
|
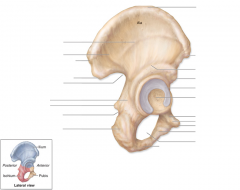
Acetabular labrum
|
This cartilage ring deepens acetebulum socket for the head of the femur.
|
|
|
Movements of the hip joint
|
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction medial/lateral rotation circumduction (combination of flexion/extension/adduction/abduction) |
|
|
Tibia medial and lateral condyles are located at the _____ end and covered in _______
|
Tibia medial and lateral condyles are located at the proximal end and covered in articular cartilage
|
|
|
Intercondylar eminence (tibia)
|
Protrusion between two condyles of tibia.
Attachment for the cruciate ligaments. |
|
|
Medial malleous
|
Medial protrustion on distal end
|
|
|
Fibular notch
|
Notch at lateral side at distal end for articulation with the fibula.
|
|
|
Patella base
|
Superior flat edge
|
|
|
Patella apex
|
Inferior pointed edge
|
|
|
Fibular articular surface
|
Fibula attaches to this socket located on the proximal end of the tibia.
|
|
|
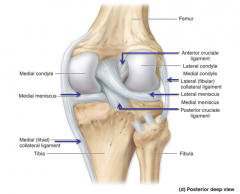
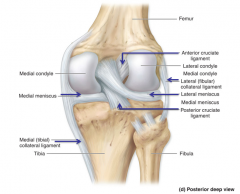
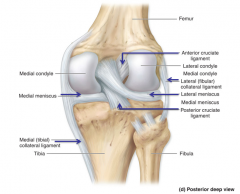
Medial (tibial) collateral ligament (MCL)
|
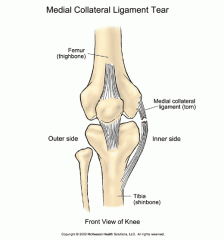
Thickening of the fibrous capsule on the medial side of the knee.
Provides medial support to the knee. |
|
|
Lateral (fibular) collateral (LCL)
What is it? What does it prevent? |
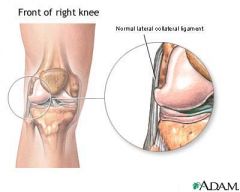
Thickening of fibrous capsule on the lateral side.
Prevents hyperadduction of the leg at the knee. |
|
|
Anterior cruciate (ACL)
Where's it located? Where does it attach? What does it prevent? Tightens when... |
Located within the knee joint.
Runs from tibia upward, backward and lateral to attach to the medial side of the lateral condyle of the femur. Prevents hyperextension - prevents the tibia from moving too far anteriorly on the femur Tightens when we lock our knees. |
|
|
Anterior cruciate (ACL) injury
|
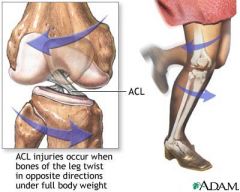
|
|
|
Posterior cruciate (PCL)
Where's it located? Where does it attach? |
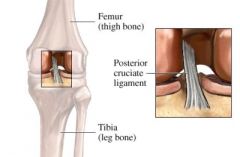
Located within the knee joint.
Runs from tibia upward, forward and medial to attach to the lateral side of the medial condyle of the femur. Prevents posterior displacement of the tibia on the femur. Prevents hyperflexion of the knee joint. |
|
|
Posterior cruciate (PCL) injury
|
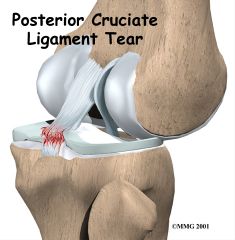
|
|
|
Medial and lateral menisci
What are they for? Where are they? |
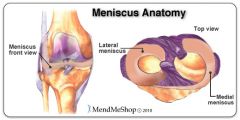
"C" shaped fibrocartilage between femur and tibia, helps deepen the joint and provide cushioning
|
|
Medial meniscus
|
|
|
Lateral meniscus
|
|
|
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
|
|
|
Lateral (fibular) collateral ligament
|
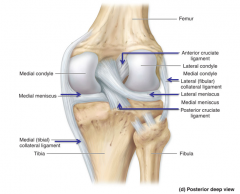
|
|
Posterior cruciate ligament
|
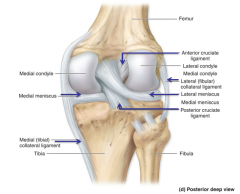
|
|
Medial (tibial) collateral ligament
|
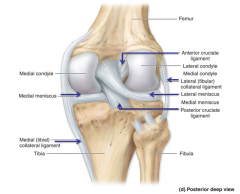
|
|
|
Explain "screw-home mechanism"
|
The femur rotates MEDIALLY on the tibia during full extension. This helps the femur line up with the tibia without much muscular support.
The POSTERIOR cruciate ligament (PCL) becomes taut and provides most of the integrity in this position. |
|
|
The lateral malleolus on the fibula is located at the _____ end.
|
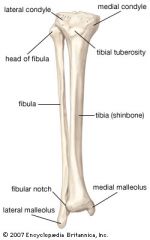
The lateral malleolus on the fibula is located at the distal end.
|
|
|
Popliteus
Is located... Which does... (helps with flexion or extension? Lateral or medial rotation?) |
The popliteus is located at the back of the knee. It initiates knee flexion by LATERALLY rotating the femur on the tibia. This aligns the condyles so flexion can proceed.
|
|
|
Talus [on tarsals]
|
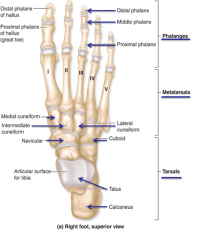
Articular surface for tibia
|
|
|
Calcaneous
|
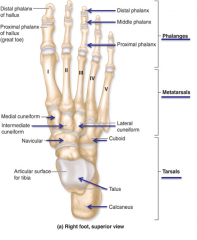
aka heel
|
|
|
Navicular
|
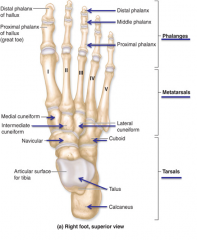
Right before cuneiforms
|
|
|
Cuneiforms
|
1. Medial cuneiform
2. Intermediate cuneiform 3. Lateral cuneiform |
|
|
Deltoid ligament (of ankle joint)
|
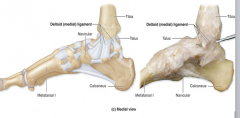
Binds distal end of the tibia to the medial side of the foot.
Gives medial support to ankle, helps prevent overeversion of foot. |
|
|
Calcaneofibular lateral ligament
|
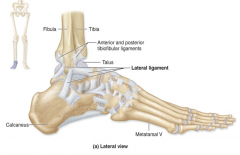
From the lateral malleolus downward to the back of the calcaneous (heel)
Helps prevent overinversion of the foot (1/3) |
|
|
Anterior talofibular lateral ligament
|
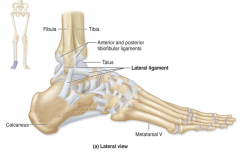
Thickening of the fibrous joint capsule from talus to the lateral malleolus
Helps prevent overinversion of the foot (2/3) |
|
|
Posterior talofibular lateral ligament
|
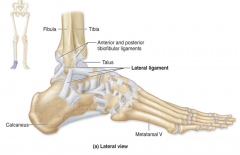
Posterior horizontal ligament joining the lateral malleolus to the talus
Helps prevent overinversion of the foot (3/3) |
|
|
Plantarflexion and dorsiflexion takes place at...
|
Plantarflexion and dorsiflexion takes place at talocrural joint (joint formed b/w the medial & lateral malleoli and the talus)
Talus = point of articulation from tibia to foot |
|
|
Inversion and eversion (plantar surface in and outwards) takes place at...
|
Inversion and eversion (plantar surface in and outwards) takes place at...
A combination of: **Subtalar joint** between talus and calcenous + **Transverse tarsal joint** formed by the talus articulating with the navicular & the calcaneous articulating with the cuboid |
|
|
1st digit in the foot (distal phalanx of hallux) articulates with...
|
The navicular bone
(In the hand, the thumb articulates with the trapezium [saddle shaped joint] allowing the thumb to roll & move. Big toe cannot do this.) |
|
|
2nd and 3rd metatarsals articulate with...
|
2nd and 3rd metatarsals articulate with...
"pocket" formed by the cuneiforms, little movement. (Similar to hand with little movement @ the carpal-metacarpal joint) |
|
|
4th and 5th metacarpals articulate with...
|
4th and 5th metacarpals articulate with...
Cuboid bone, very little movement |
|
|
Movements of phalanges:
|
Movements of phalanges:
@ the metatarsal-phalangeal joint (akin to foot knuckles) for all digits: Flexion/extension & abduction/adduction @ the interphalangeal joint for all digits: flexion/extension |

