![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
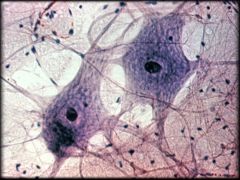
Nervous Tissue
|
Structure: Contains neurons (Cell Body, Axon, Dendrites). Also contains Glial Cells
Function: Neurons receive, send, and process nerve impulses while glial cells help support, protect, and nourish neurons Location: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves |
|
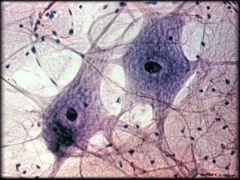
|
Nervous Tissue
Structure: Contains neurons (Cell Body, Axon, Dendrites). Also contains Glial Cells Function: Neurons receive, send, and process nerve impulses while glial cells help support, protect, and nourish neurons Location: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves |
|
|
Smooth Muscle Tissue
|
Structure & Characteristics: Nonstriated, Short, Tapered. Contain a centrally located nucleus. Under involuntary control
Function: Moves and propels materials through internal organs Location: Walls of hallow internal organs (Intestines, Stomach, Blood vessels) |
|
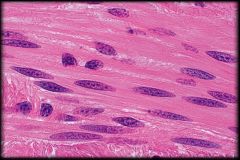
|
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Structure & Characteristics: Nonstriated, Short, Tapered. Contain a centrally located nucleus. Under involuntary control Function: Moves and propels materials through internal organs Location: Walls of hallow internal organs (Intestines, Stomach, Blood vessels) |
|
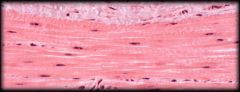
|
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Structure & Characteristics: Nonstriated, Short, Tapered. Contain a centrally located nucleus. Under involuntary control Function: Moves and propels materials through internal organs Location: Walls of hallow internal organs (Intestines, Stomach, Blood vessels) |
|
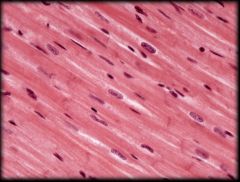
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
Structure & Characteristics: Short, Striated, and Branching. Contains one or two centrally located nuclei. Contain intercalated discs between cells. Under involuntary control
Function: Pumps blood through heart Location: Heart wall (myocardium) |
|
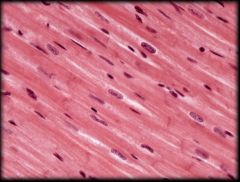
|
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Structure & Characteristics: Short, Striated, and Branching. Contains one or two centrally located nuclei. Contain intercalated discs between cells. Under involuntary control Function: Pumps blood through heart Location: Heart wall (myocardium) |
|
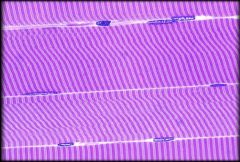
|
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Structure & Characteristics: Long, cylindrical, striated fibers (cells). Parallel and multinucleated. Under voluntary control Function: Responsible for moving skeleton and selected other components of the body Location: Attaches to bones or sometimes to skin (Facial muscles) |
|
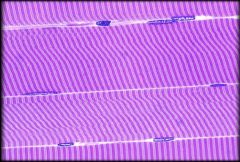
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
|
Structure & Characteristics: Long, cylindrical, striated fibers (cells). Parallel and multinucleated. Under voluntary control
Function: Responsible for moving skeleton and selected other components of the body Location: Attaches to bones or sometimes to skin (Facial muscles) |
|
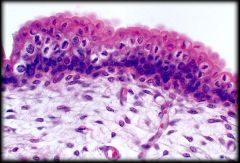
Transitional Epithelium
|
Structure: Can be stretched or relaxed. When relaxed it has rounded cells on apical surface and flattened cells when stretched. Some cells are binucleated
Function: Distension and relaxation to accommodate volume changes Location: Urinary bladder, Ureters, part of Urethra |
|
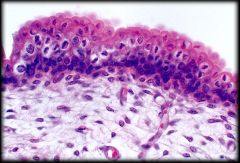
|
Transitional Epithelium
Structure: Can be stretched or relaxed. When relaxed it has rounded cells on apical surface and flattened cells when stretched. Some cells are binucleated Function: Distension and relaxation to accommodate volume changes Location: Urinary bladder, Ureters, part of Urethra |
|
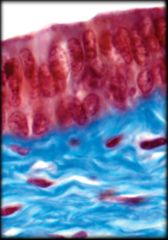
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
|
Structure: Two or more layers of cells; Cells at the apical surface are taller than they are wide
Function: Protection and Secretion Location: Large ducts of salivary glands and in membranous part of male urethra |
|
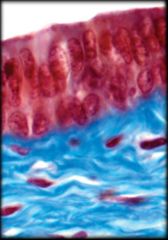
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Structure: Two or more layers of cells; Cells at the apical surface are taller than they are wide Function: Protection and Secretion Location: Large ducts of salivary glands and in membranous part of male urethra |
|
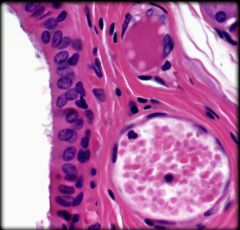
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
|
Structure: Two or more layers of cells; cells a the apical surface are about as tall as they are wide
Function: Protection and Secretion Location: Ducts of most exocrine glands and some regions of the male urethra |
|
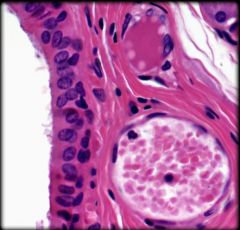
|
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Structure: Two or more layers of cells; cells a the apical surface are about as tall as they are wide Function: Protection and Secretion Location: Ducts of most exocrine glands and some regions of the male urethra |
|
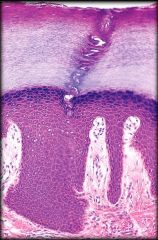
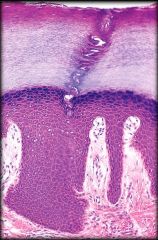
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
Structure: Multiple cell layers. Basal cells are cuboidal. Apical cells are dead and filled with protein keratin.
Function: Protection of underlying tissue Location: Epidermis of skin |
|
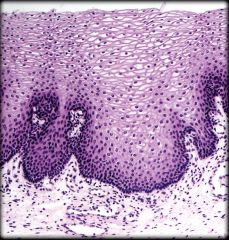
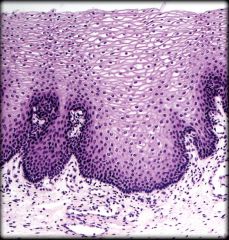
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
Structure: Multiple cell layers. Basal cells are cuboidal and apical cells are squamous
Function: Protection of underlying tissue Location: Lining of oral cavity, part of pharynx, esophagus, lining of vagina, and anus |
|
|
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Structure: Multiple cell layers. Basal cells are cuboidal. Apical cells are dead and filled with protein keratin. Function: Protection of underlying tissue Location: Epidermis of skin |
|
|
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Structure: Multiple cell layers. Basal cells are cuboidal and apical cells are squamous Function: Protection of underlying tissue Location: Lining of oral cavity, part of pharynx, esophagus, lining of vagina, and anus |
|
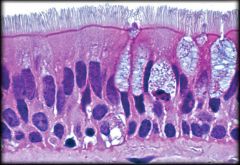
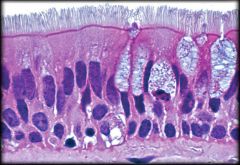
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
Structure: Single layer of cells with varying heights. All cells connect to the basement membrane but not all reach apical surface. Ciliated form has goblet cells and cilia. Nonciliated form lacks goblet cells and cilia
Function: Protection. Cilia moves mucus across surface Location: Ciliated respiratory tract, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. Nonciliated line part of male urethra and epididymis |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Structure: Single layer of cells with varying heights. All cells connect to the basement membrane but not all reach apical surface. Ciliated form has goblet cells and cilia. Nonciliated form lacks goblet cells and cilia Function: Protection. Cilia moves mucus across surface Location: Ciliated respiratory tract, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. Nonciliated line part of male urethra and epididymis |
|
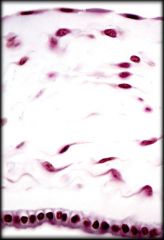
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
Structure: Single layer of flat cells. Centered nucleus
Function: Allows for rapid diffusion, filtration, and some secretion in mucous membranes Location: Aveoli (air sacs in lungs), Endotheliun, and Mesothelium |
|
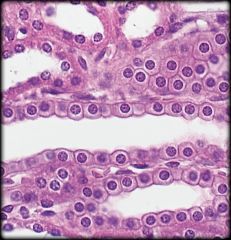
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
Structure: Single layer of cells about as tall as they are wide. Centrally located nucleus
Function: Absorption and secretion Location: Kidney tubules, Secretory regions & ducts of most glands |
|
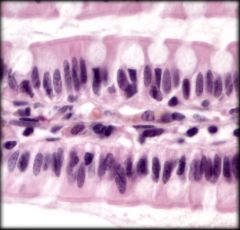
Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
Structure: Single layer of cells taller than wide. Oval shaped nucleus on basal region. Apical region may have microvilli. May contain goblet cells that secrete mucin
Function: Absorption and secretion; Secretion of mucin Location: Lining of most of digestive tract |
|
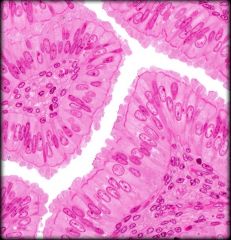
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
Structure: Single layer of ciliated cells taller than they are wide. Oval shaped nucleus in basal region. May contain goblet cells
Function: Secretion of mucin and movement of mucus. Oocyte movement through uterine tube Location: Large bronchioles of respiratory tract and lining of uterine tubes |
|
|
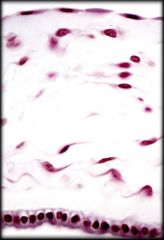
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Structure: Single layer of flat cells. Centered nucleus Function: Allows for rapid diffusion, filtration, and some secretion in mucous membranes Location: Aveoli (air sacs in lungs), Endotheliun, and Mesothelium |
|
|
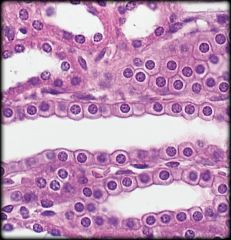
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Structure: Single layer of cells about as tall as they are wide. Centrally located nucleus Function: Absorption and secretion Location: Kidney tubules, Secretory regions & ducts of most glands |
|
|
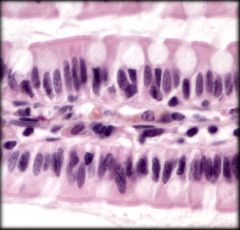
Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Structure: Single layer of cells taller than wide. Oval shaped nucleus on basal region. Apical region may have microvilli. May contain goblet cells that secrete mucin Function: Absorption and secretion; Secretion of mucin Location: Lining of most of digestive tract |
|
|
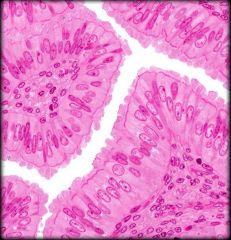
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Structure: Single layer of ciliated cells taller than they are wide. Oval shaped nucleus in basal region. May contain goblet cells Function: Secretion of mucin and movement of mucus. Oocyte movement through uterine tube Location: Large bronchioles of respiratory tract and lining of uterine tubes |

