![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fiscal Policy |
The changing of government expenditures or taxes to reach a desired economic goal. |
|
|
What can the federal government do to institute expansionary fiscal policy? |
increase government spending or lower taxes |
|
|
What happens to the interest rates during expansionary fiscal policy? |
They increase |
|
|
What are automatic stabilizers? |
Corporate and personal taxes |
|
|
Crowding Out |
Where increased interest rates lead to a reduction in private investment spending which dampens the initial increase of total investment spending. |
|
|
Entitlement Spending |
Guaranteed benefits under a government program such as Social Security, Medicare, or Medicaid. |
|
|
What happens to the exchangeable value of the US dollar during expansionary fiscal policy? |
increases |
|
|
What happens to net exports during contractionary fiscal policy? |
decreases |
|
|
What does the Laffer curve measure? |
Between tax revenues and tax rate |
|
|
What is Fiat currency? |
Non-convertible money created by the government |
|
|
What is the difference between M1 and M2? |
M1: Currency, coins, check accounts, traveler's accounts M2: M1 + saving deposits, money markets, "near money" |
|
|
What does the Federal Open Market Committee do? |
the policy-making body of the federal reserve (fed). Composed of 12 members. |
|
|
Monetary Policy |
the actions of a central bank to determine the size and rate of growth of the money supply. |
|
|
What tools of monetary policy does the Federal Reserve have available? |
open market operations, discount rate, and reserve requirements |
|
|
What happens to the money supply when the federal reserve buys securities? |
It increases |
|
|
What happens to the price of bonds when the Fed sells securities? |
They decrease |
|
|
What impacts does expansionary monetary policy have on the exchangeable value of the US dollar? |
it decreases |
|
|
What is the difference between assets and liabilities? |
Assets: What they own Liabilities: What they owe |
|
|
What happens to the potential money multiplier when the reserve requirement increases? |
It also increases |
|
|
Difference between calculating the change in the money supply and change in loanable fund? |
Loanable: 0=b-(1/100)(1100) |
|
|
What is the velocity of money? |
How many times it is spent/ being put into circulation. |
|
|
What is monetarism? |
the theory/practice of controlling the supply of money as its chief method of stabilizing the economy. |
|
|
Keynesian Economics |
- Creates deficit to fix recessions - Creates surplus to fix inflation |
|
|
Expansionary Policy |
- Expand GDP - Promote job growth |
|
|
John Maynard Keynes' Ideologies |
- Believed deficits are caused by recessions - Believed they cause Aggregate Demand (AD) to increase |
|
|
Time Lags |
when an actual economic shock happens and when it is recognized by economists, central bankers, and the government. |
|
|
Supply Side Economics |
- Reduces the government (more right-wing) - Increases tax breaks |
|
|
Laffer Curve |
- Against Higher Taxes - Gov. cuts marginal tax rates = no loss in revenue - Lower tax rates = more tax revenue |
|
|
What is the Laffer Curve based on? |
Tax Revenue and Tax Rate |
|
|
Direct Expenditure Offsets |
Increase in consumption (C) causes government spending (G) to go down |
|
|
Who gets crowded out? |
Private Investors |
|
|
Money is... |
- A medium exchange - Unit of accounting - Store of value - A liquid asset that can be used in various transactions |
|
|
Commodity |
The money itself holds it own value |
|
|
Representative |
Paper and coin money backed up by a commodity. (US before 1971) |
|
|
Fiduciary Monetary Standard |
Trust that the government will protect the value of money |
|
|
What is M3? |
M3: M2 plus CD's over 100,000 and money held by banks abroad, pension funds |
|
|
What does M1, M2, and M3 all represent? |
It represents the money aggregate and monetary aggregate. |
|
|
Are credit cards considered money? |
No |
|
|
What is the discount rate? |
.75% |
|
|
What is the Prime rate? |
3.25% |
|
|
Federal Funds Rate |
.25 |
|
|
What is fractional reserve banking? |
Concept that all banks hold onto a fraction of the deposit and they keep the rest. |
|
|
Legal Reserves |
Includes the money in the bank puts in the Fed or the cash in its vaults. |
|
|
Required Reserves |
Ratio established by the Fed (10%) |
|
|
Excess Reserves |
All the money that meets the legal reserve requirements, which is above the required reserves |
|
|
Can Excess Reserves be loaned by banks? |
Yes |
|
|
Net Worth |
Difference between assets and liabilities |
|
|
What can the Fed do to alter the money supply? |
By buying and selling government bonds in the private market. |
|
|
Potential Money Multiplier Equation |
.1/Required Reserve Ratio |
|
|
M1 multipier: |
1.5 - 2.0 |
|
|
Monetary policy |
- Loose money |
|
|
Ways Fed can raise Money Supply |
- Buying bonds on the open market - Lowering the discount rate - Lowering the reserve rate |
|
|
Lowering the reserve rate would cause the money supply to... |
Increase |
|
|
Lowering the discount rate would cause the money supply to... |
Increase |
|
|
The Fed buying bonds on the open market would cause... |
and Increase in money supply |
|
|
Deposit continuation process |
Money multiplies |
|
|
What's MD?
|
Demand for money |
|
|
What's MS? |
Supply of Money |
|
|
When can the Fed cause MS to shift? |
If they increase or decrease the money supply. |
|
|
Stagflation is... |
- High Unemployment - High interest rate |
|
|
The Phillips curve measures between... |
Inflation and unemployment rate. |
|
|
What is Contractionary fiscal policy? |
a decrease in government expenditures and/or a decrease in taxes that cause the government's budget deficit to decrease. |
|
|
Draw an expansionary fiscal policy |
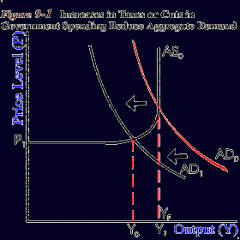
|
|
|
Draw a contractionary fiscal policy |
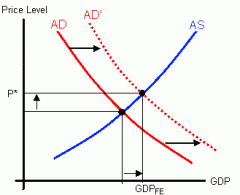
|
|
|
What is deficit? |
An excess of expenditure or liabilities over income and assets in a given period. |
|
|
What is debt? |
Money that is owed, accompanied by interest rates. |
|
|
What is deficit spending? |
government spending in excess of revenue of funds raised by borrowing rather than from taxation. |
|
|
What is financial intermediation? |
An institutional unit incurs liabilities on its own account for the purpose of gaining financial assets by engaging in financial transactions on the market. |
|
|
What is adverse selection? |
When undesired results occur when buyers and sellers have access to different information, which causes an imbalance of power. |
|
|
Define moral hazard. |
a lack of incentive to guard against the risk where one is protected from its consequences. |
|
|
Describe the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) |
a committee within the fed which oversees the nation's open market operations. |
|
|
What are the roles of the Fed? |
- Finance economy w/ money it has from trusts - Provides payment clearing systems - Holds depository institution reserves - Acts as gov.'s fiscal agents - Supervises depository institutions - Acts as the lender of the last resort - Intervenes in foreign currency markets |
|
|
What would be described as an Open Market Operation? |
an activity by a central bank to give or take liquidity into currency to or from a bank or a group of banks. |
|
|
How do you calculate the expansion of the money supply? |
Change in MS= Change in reserves x Money multiplier |
|
|
What aspects can impact the price of bonds? |
- interest rates - inflation |
|
|
If the Fed has a lower reserve requirement, what will happen to their money supply? |
They'll have more money to loan out, since they will have excess reserves. |
|
|
What happens to net exports when the demand for the US dollar decreases? |
Net exports increase. |
|
|
What kind of interest rate do foreign investors prefer? |
Higher interest rates. |
|
|
What is real GDP times the Price Level? |
Nominal GDP |
|
|
Draw an inflationary gap. |
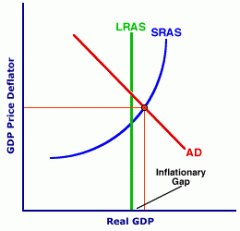
|
|
|
Draw a recessionary gap. |
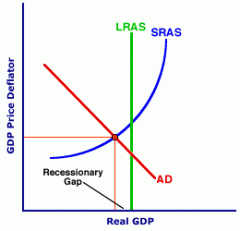
|
|
|
Equation of Exchange |
MV = Py M: Money supply V: Velocity P: Price Level y: Real GDP |

