![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The lymphatic trunks connect to which vessels?
|
The large veins in the thorax or lymphatic ducts which connect to large veins.
|
|
|
Which capillary is the most permeable?
|
Lymphatic capillary
|
|
|
Which duct is the largest lymphatic vessel?
|
The thoracic duct
|
|
|
The lymphatic nodule contains which type of cells?
|
Dense T cells and B cells
|
|
|
Which organs is considered the largest in the lyphatic system?
|
The spleen.
|
|
|
What is the function of the red pulp?
|
The ability to dispose off worn-out blood.
|
|
|
What is the fuction of the white pulp?
|
Serves the immune function.
|
|
|
What does the thymus secrete?
|
Thymosin and thymopoietin
|
|
|
What are the activating factors for the complement cascade?
|
Factors B, D and P (properdin); foreign substances; and antigen-antibody complex
|
|
|
Where do the B cells mature?
|
The red bone marrow.
|
|
|
Where do the pre T cells mature?
|
The thymus.
|
|
|
What is the secondary lymphatic organ?
|
The lymph nodule
|
|
|
Where is the antigen presenting cell expressed?
|
On the MCH-II
|
|
|
Which cells can express the antigen presenting cell?
|
Microphages, dendritic cells, and B cells.
|
|
|
Why is the antigen-binding site different from the rest of the other components?
|
The site is variable and changes.
|
|
|
Which responce is greatly larger?
|
The secondary responce; it consits mostly of IgG antibodies.
|
|
|
What form of immunity is given to a patient injected with serum from a horse?
|
Passive artificial immunity
|
|
|
What must occur to prevent food from going into the trachea and force it down the esophagus?
|
The epiglottis must fold over
|
|
|
What controls the movement of the vocal folds?
|
The arytenoid cartilage
|
|
|
What does the aveolar cell secrete?
|
It secretes surfactants
|
|
|
The tertiary bronchus feeds to which segments?
|
The broncho-pulmonary segments.
|
|
|
How many lobes are in the right and left lung?
|
Right lung has three lobes and the left lung has two lobes.
|
|
|
What are the muscles of inspiration?
|
Sternocleidomastoid, scalenes, and external intercostals.
|
|
|
Which muscle is the most important for inspiration?
|
The diaphragm, it is responsible for 75% of the air.
|
|
|
What form of respiration occurs when gas exchanges between the pulmonary capillaries and the alveoli?
|
External respiration
|
|
|
What happens when the partial pressure of oxygen drops below 20mmHg?
|
The hemoglobin releases over 70% of its oxygen.
|
|
|
What happens when hemoglobin starts to release oxygen?
|
Its quaternary structure changes, which encourages the release of more oxygen.
|
|
|
What cells are bags of hemoglobin?
|
The red blood cells.
|
|
|
What happens when increased oxygen is release to tissues?
|
The curve shifts to right as pH drops, CO2 rises, and temperature rises.
|
|
|
What is peristalsis?
|
Is the wave of relaxation and contraction.
|
|
|
Which tooth is responsible to ripping food?
|
The canine or cuspid.
|
|
|
What are the functions of the small intestine?
|
Secretes mucous, chemical digestion, and water reabsorption.
|
|
|
Where do the exocrine secretions enter?
|
At the hepatopancreatic ampulla.
|
|
|
Where is bicarbonate ion produced?
|
In the intercalated duct cell or parital cell.
|
|
|
What does the intercalated duct cells produce?
|
An aqueous component of pancreatic juice.
|
|
|
What cell produces enzymatic component of pancreatic juice?
|
The acinar cell
|
|
|
What is function for the appendix?
|
It has no digestive function.
|
|
|
Where do the carbohydrates (monosachrides) and the protiens (amino acids) enter the circulation?
|
They enter through the villus or villi.
|
|
|
Where do lipids (micelle) enter the circulatory system?
|
It enters as chylomicron through lacteal vessel (from the lymphatic system).
|
|
|
What are vitamins?
|
They are small organic molecules that function as part of enzymes (coenzymes).
|
|
|
What are the functions of minerals?
|
They establish resting membrane potentials, generate action potentials, add strength to bone and teeth, buffers, involved in osmotic balance.
|
|
|
What occurs during strenous excersice?
|
It shunts the glucose oxidation pathway, known as anarobic respiration.
|
|
|
Where does the cytric acid cycle and aerobic respiration occur?
|
In the mitochondrial matrix.
|
|
|
What does liver convert the fatty acids into?
|
To ketone bodies for the brain, when glucose is limited or low.
|
|
|
What are the steps for amino acids to be oxdized as fuel?
|
The amine group must be removed; alpa ketoglutaric acid must be regenerated; ammonia must be converted to urea.
|
|
|
What form of heat exchange occurs when placing a patient with heat exhaustion into a tub of cool water?
|
Conduction
|
|
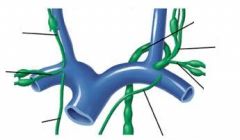
Where does the lymph enter the blood circulation?
|
Right subclavian trunk; left subclavian trunk
|
|
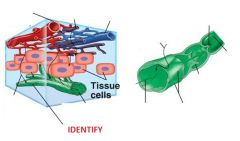
Identify the green structure.
|
Lymphatic vessel.
|
|
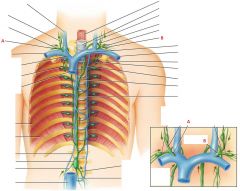
Identify A and B
|
A. the right lymphatic duct
B. the thoracic duct |
|
Identify A and B
|
A. Right lymphatic duct
B. Thoracic (left lymphatic) duct |
|
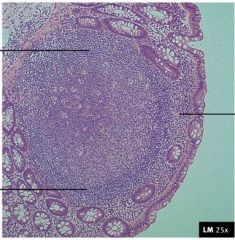
Identify slide
|
Lymphatic nodule
|
|
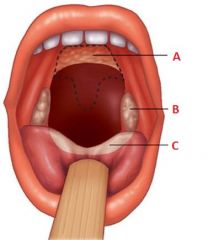
Identify A, B, and C
|
A. Pharyngeal tonsil
B. Palatine tonsil C. Lingual tonsil |
|
Identify figure
|
Lymphatic nodule
|
|
Identify figure
|
Left side: white pulp
Right side: red pulp |
|
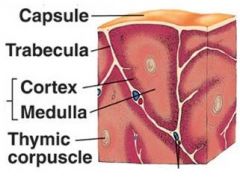
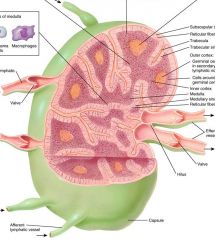
Identify figure
|
Thymus
|
|
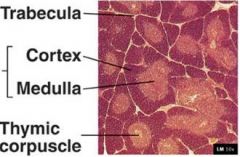
Identify figure
|
Thymus
|
|
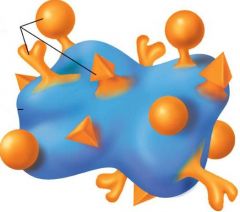
Identify figure
|
Antigen Determinants
|
|
|
Which number express the APC?
|
five; the MHC-II
|
|
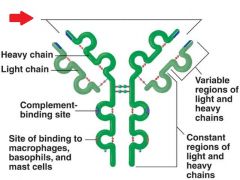
Identify the arrow
|
Antigen binding site
|
|
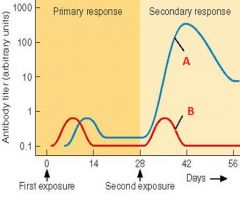
Identify A and B
|
A. IgG (secondary responce)
B. IgM (primary responce) |
|
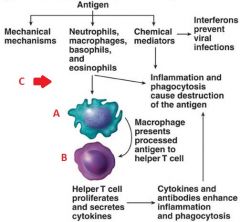
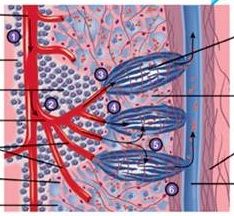
Identify A, B, and C
|
A. Microphage
B. Helper T cell C. Innate immunity |
|
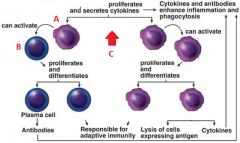
Identify A, B, and C
|
A. Helper T cell
B. B cell C. Adaptive Immunity |
|
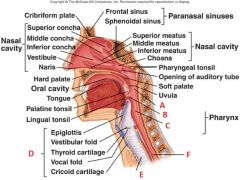
Identify the nasopharynx and the trachea.
|
A. Nasopharynx
E. Trachea |
|
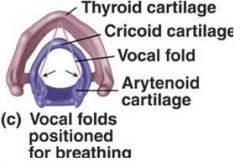
Identify figure
|
Arytenoid Cartilage
|
|
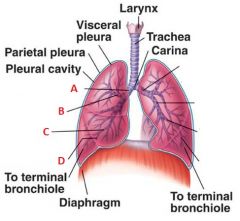
Identify A, B, C, and D
|
A. Primary bronchus
B. Secondary Bronchus C. Tertiary Bronchus D. Bronchiole |
|
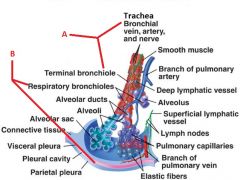
Identify A and B
|
A. Conducting Zone
B. Respiratory Zone |
|
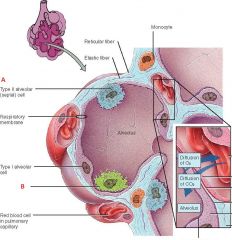
Identify A and B
|
A. Alveolar cell
B. Alveolar macrophage |
|
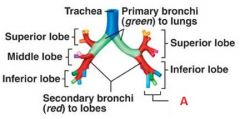
Identify A
|
Tertiary bronchi to bronchopulmonary segments
|
|
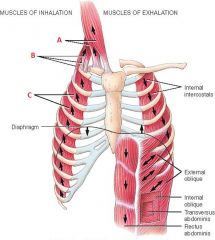
Identify A, B, and C
|
A. Sternocleidomastoid
B. Scalenes C. External intercostals |
|
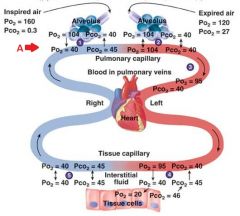
Identify figure
|
External respiration
|
|
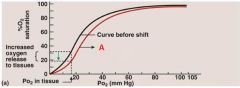
Identify A
|
Curve shift to right, pH drops, CO2 rises, and temperature rises
|
|
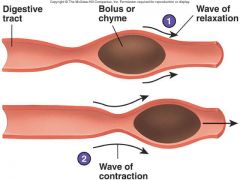
Identify figure
|
Peristalsis
|
|
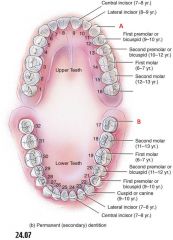
Identify A and B
|
A. Canine
B. Third Molar |
|
Identify figure
|
Stomach
|
|
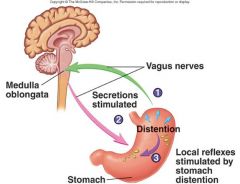
Idenify figure
|
Gastric phase
|
|
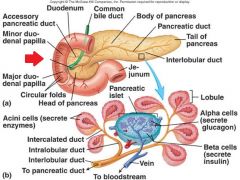
Identify arrow
|
Hepatopancreatic papilla
|
|
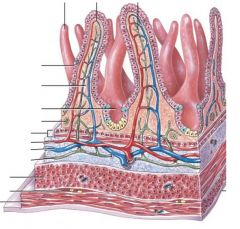
Identify figure
|
Small intestine
|
|
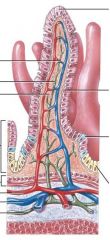
Identify figure
|
Small intestine
|
|
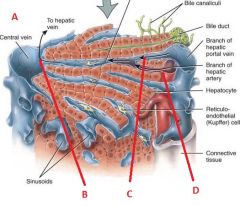
Identify A, B, C, and D
|
A. Liver cross section
B. Blood to vena cava C. Blood from digestive tract D. Blood from heart |
|
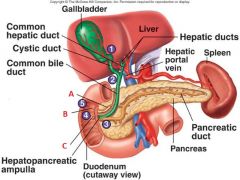
Identify A, B, and C
|
A. Accessory pancreatic duct
B. Minor duodenal papilla C. Major duodenal papilla |
|
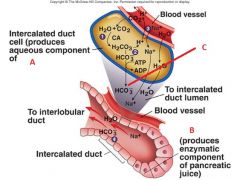
Identify A, B, and C
|
A. pancreatic juices
B. Acinar cell C. Biocarbonate ion |
|
|
Identify A, B, C, and D
|
A. Cecum
B. Colon C. Rectum D. Anal canal |
|
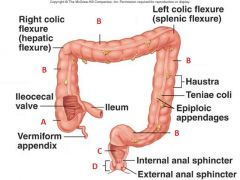
Identify A, B, C, and D
|
A. Cecum
B. Colon C. Rectum D. Anal canal |
|
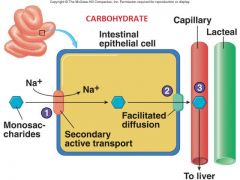
Identify figure
|
Carbohydrate entering through villus
|
|
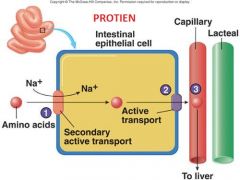
Identify figure
|
Protein entering through villus
|
|
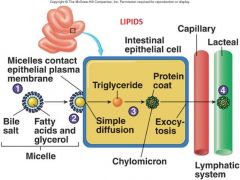
Identify figure
|
Lipid entering as chylomicron
|
|
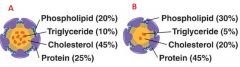
Identify A and B
|
A. LDL cholesterol
B. HDL cholesterol |
|
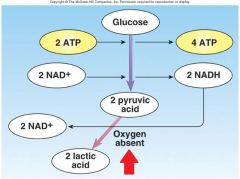
Identify arrow
|
Anarobic respiration
|
|
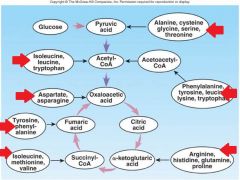
Identify arrows
|
Amino acid metabolism
|
|
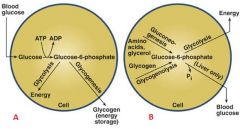
Identify A and B
|
A. High blood glucose
B. Low blood glucose |
|
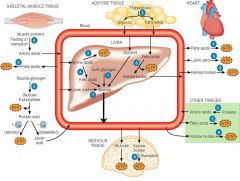
Identify figure
|
Post absorptive state
|

