![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ovary
|
Ovary-
Where haploid oocytes are formed. |
|
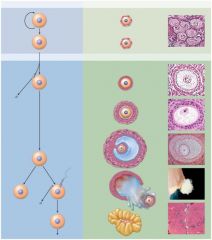
What are the stages and events involved in reproductive cycle involving ovary?(up to ovulation-Ovarian cycle)
|
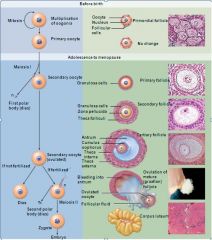
Stages and Events -Ovarian Cycle
(1) The oocytes start with a primordial follicle (2) → primary follicle (3) → secondary follicle (4) → mature (Graafian) follicle (5) → corpus hemorrhagicum (ruptured Graafian follicle (6) ovulation discharges a secondary oocyte (7) → corpus luteum (yellow body; produces progesterone, estrogens, relaxin, & inhibin) (8) → corpus albicians (white body; scar tissue) SUMMARY Starting with the primordial follicle the cell continues to get larger until it reaches its largest as a mature (Graafian) follicle. The mature follicle ruptures (ovulation) and the secondary oocyte has 12-24 hours to be fertilized and if it isn’t the cells degenerate. |
|
|
Corpus Luteum (Function in Pregnancy)
|
Corpus luteum-
FUNCTION: (1) in the beginning of pregnancy-produces the hormones progesterone and estrogens for the first 3 to 4 months of pregnancy. |
|
|
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
(Function in Pregnancy) |
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)-
(1) is secreted by chorion FUNCTION: (1) and stimulates the corpus luteum to continue the production of progesterone and estrogens (2) which is required to prevent menstruation (3) and for the continued attachment of the embryo and fetus to the lining of the uterus. |
|
|
Progesterone and estrogen (Function in Pregnancy)
|
Progesterone and estrogens-
FUNCTION: (1) to maintain endometrium of uterus during pregnancy (2) help prepare mammary glands for lactation (3) and prepares the mother’s body for the birth of a baby |
|
|
Placenta (Function in Pregnancy)
|
Placenta-
FUNCTION: (1) eventually takes on the role of hormonal secretion during pregnancy. (2) Relaxin (first produced by corpus luteum then by placenta) (3) Releases Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) and corticotrophin-releasing hormone |
|
|
Relaxin (Function in Pregnancy)
|
Relaxin-
FUNCTION: (1) increases flexibility of the pubic symphysis (2) and helps dilate the uterine cervix during labor. |
|
|
Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS)
(Function in Pregnancy) |
Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS)-
FUNCTION: (1) helps prepare mammary glands for lactation (2) enhances growth by increasing protein synthesis (3) and decreases glucose use and increases fatty acid use for ATP production. |
|
|
Corticotrophin-releasing hormone
(Function in Pregnancy) |
Corticotrophin-releasing hormone-
FUNCTION: (1) establishes the timing of birth and increases secretion of cortisol. |
|
|
Oxytocin (Function in Pregnancy)
|
Oxytocin
FUNCTION: (1) during labor- is released by the hypothalamus which causes contractions of the myometrium. |

