![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four kinds of tissues?
|
epithelial, connective, nervous, muscle
|
|
|
Epithelial tissues are found where?
|
In coverings and linings
|
|
|
what two types of tissues are found within epithelial tissues?
|
simple cuboidal and stratified squamous
|
|
|
which is the most diverse group of tissues?
|
connective
|
|
|
which has collagen and elastin fibers?
|
connective
|
|
|
Within connective, which six types of tissue are there?
|
areolar, adipose, dense irregular, cartilage, bone, blood
|
|
|
skin is comprised of what?
|
the epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
|
|
|
which is the outer most layer of the skin?
|
the epidermis
|
|
|
which is the inner layer of the skin, under the epidermis?
|
dermis
|
|
|
which is the deepest layer of the skin?
|
hypodermis
|
|
|
What is the function of simple cuboidal tissue?
|
secretion and absorption
|
|
|
where is simple cuboidal tissue found?
|
kidneys tubules, ducts and glands
|
|
|
what is the function of stratified squamous tissue?
|
protection from damage, infection, UV light
|
|
|
Where is stratified squamous tissue found?
|
epidermis, vagina, mouth, tongue
|
|
|
which tissue has cells that are suspended in a gel like matrix?
|
connective tissue
|
|
|
fibroblasts make what?
|
collagen, elastin, reticular
|
|
|
Mast cells do what?
|
secrete histamine as part of the inflammatory response
|
|
|
what are macrophages?
|
eat bacteria, viruses through phagocytosis
|
|
|
what is the most abundant protein in the body?
|
collagen
|
|
|
what allows tissues to stretch?
|
elastin
|
|
|
what is the function of areolar tissues?
|
protection
|
|
|
where are areolar tissues found?
|
hypodermis
|
|
|
What is the function of adipose tissue?
|
cushioning/protection, heat retention, energy storage
|
|
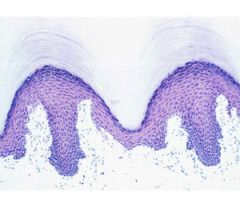
What is this a picture of?
|
stratified squamous epithelial tissue found in the epidermis of skin
|
|
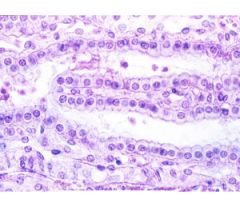
What is this a picture of?
|
simple cuboidal epithelial tissue found in glands
|
|
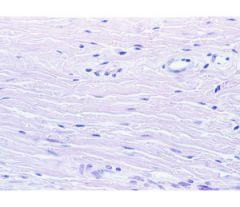
What is this a picture of?
|
dense irregular connective tissue found in the dermis of skin
|
|
What is this a picture of?
|
adipose connective tissue
|
|
what is this a picture of?
|
areolar connective tissue found under epidermis and around organs
|
|
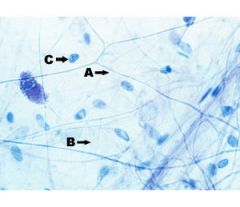
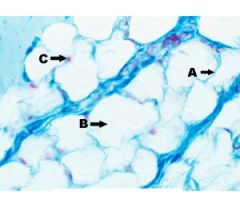
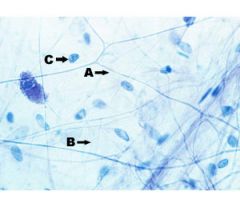
What are A, B and C in this picture?
|
collagen fibers, elastic fibers, fibroblast nuclei
|
|
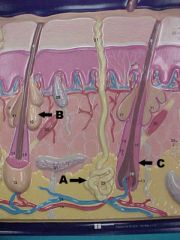
What is A,B and C in this picture?
|
free nerve ending, meissner's corpuscle, thermoreceptor
|
|
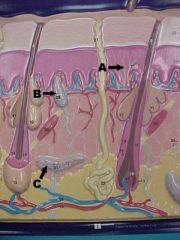
What are A, B and C in this picture?
|
Sweat gland, oil gland, hair follicle
|
|
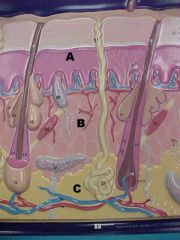
What are A, B and C in this picture?
|
skin layers, A) epidermis B) dermis C) hypodermis
|
|
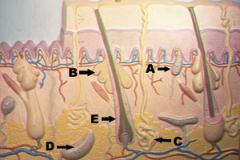
What are the arrows pointing to in this picture?
|
A) meissner's corpuscle B) oil gland C) sweat gland D) pacinian corpuscle E) hair
|
|
|
What is the function of dense irregular connective tissue?
|
protection from damage
|
|
|
what is the function of sweat glands?
|
cooling the body, protecting from infection
|
|
|
what is the function of oil glands?
|
protection from infection
|
|
|
what is the function of hair?
|
protection from UV, heat retention, touch receptions
|
|
|
what is the function of free nerve endings?
|
pain/temperature receptors
|
|
|
meissner's corpuscles are for...
|
touch reception
|
|
|
pacinian corpuscles are for...
|
pressure reception
|
|
|
identify the hormone produced by the skin
|
vitamin D
|
|
|
identify the active form of the hormone produced by the skin
|
calcitrol
|
|
|
list the steps in a thermoregulation feedback loop
|
stimulus - thermoreceptor - sensory nerve - control center - motor nerve - effector - response
|
|
|
In a TR feedback loop, what are the effectors?
|
muscles and glands
|
|
|
what happens to sweat glands when body temp increases?
|
they produce sweat to cool the body
|
|
|
what happens to blood vessels when body temp increases?
|
they dilate
|
|
|
what happens to blood vessels when body temp decreases?
|
they contract
|
|
|
what happens to skeletal muscles when body temp decreases?
|
they contract/shiver to create heat
|
|
|
where is the hormone vitamin D activated?
|
the kidneys
|
|
|
when is the hormone vitamin D activated
|
when calcium levels fall
|
|
|
what does the activated hormone, calcitriol, do?
|
it acts on the intestines to increase blood calcium absorption.
|

