![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
177 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the components of the compact bone
|
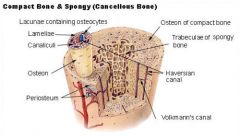
list all
|
|
|
A calcium phosphate complex that is the primary mineral component of bone.
|
hydroxyapatite
|
|
|
The compact noncancellous portion of bone that consists largely of concentric lamellar osteons and interstitial lamellae.
|
compact bone
|
|
|
Various passages in compact bone through which blood vessels, nerve fibers, and lymphatics pass.
|
haversian canal
|
|
|
A thin layer of connective tissue that lines the walls of the bone marrow cavities and haversian canals
|
endosteum
|
|
|
The cell associated with the growth and development of bone
|
osteoblasts
|
|
|
An osteoblast that has become embedded within the bone matrix, occupying a bone lacuna
|
osteocyte
|
|
|
Connects the osteocytes with eachother and with the Haversian canal.
|
canaliculi
|
|
|
Run at right angles to the Haverisian canal,transmit blood vessels from the periosteum into the bone
|
Volkmanns's canals
|
|
|
Bone in which the spicules surround blood-filled spaces called cancelli. Spaces between blood and bone cells are small,
|
cancellous or spongy bone
|
|
|
Functions of Compact bone.
|
Support against gravity, protection from direct trauma,trasmission of muscular force, make blood cells, Ca++ Storage
|
|
|
The production of red blood cells
|
hemotopoiesis
|
|
|
Portion of a long bone between the ends or extremities, which are cylinder, with outer wall composed of compact bone
|
diaphysis
|
|
|
The wider part at the end of the shaft of a long bone, joins the shank of the bone to its heads
|
metaphysis
|
|
|
The end of a long bone;composed of layers of compact bone lined with cacellous bone
|
epiphysis
|
|
|
seed shaped bones
|
patella
|
|
|
Actively involved in blood cell generation
|
red marrow
|
|
|
Dormant and is dominated by the presence of fat cells that give it its color
|
yellow marrow
|
|
|
The marrow cavity in the shaft of a long bone;hollow contains no bone tissue
|
medullary cavity
|
|
|
An opening in the compact bone tat allows for the passage of nutrient artery and nutrient vein
|
nutrient foreman
|
|
|
An artery of variable origin that supplies the medullary cavity of a long bone
|
nutrient artery
|
|
|
formation of bone in the emryonic development is called?
|
osteogenesis
|
|
|
Flat bones if the skull, the clavicle and mandible are formed by a method called?
|
intramembranous osteogenesis
|
|
|
If the connective tissue precursor is in the form of cartilage , the formation of bone is called?
|
endochondral osteogenesis
|
|
|
Collagen fibers of the matrix are arranged irregularly in the form of interlacing networks
|
woven bone
|
|
|
The thin plate of cartilage between the epiphysis and the metaphysis of a growing long bone.
|
epiphyseal plate
|
|
|
Composed of collegen and anchor the periosteum to the underlying bone.
|
Sharpey's fibers
|
|
|
By the time of maturity, the epiphyseal plate has become fully calcified to form the metaphysis. At this point no further ______________ of the bone is possible.
|
lengthening
|
|
|
In adults, bone mass is maintained by a balance between _______________ and ________________ .
|
deposition;dissolution
|
|
|
Giant migrating cells that crawl across periosteal and endosteal surfaces, releasing enzymes and acid that dissolve bone; cause cell breakdown
|
osteoclasts
|
|
|
A polypeptide hormone secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland that promotes growth of the body, especially by stimulating release of somatomedin, and that influences the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids
|
growth hormone (hGH)
|
|
|
Necessary for calcium uptake from the diet, thus an adequate amount is necessary for bone growth and maintenance of of bone mass after maturity
|
1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol (Vit D)
|
|
|
A hormone that is made by the parathyroid gland and that is critical to calcium balance, also stimulates retention of Calcium by the kidneys
|
parathormone (PTH)
|
|
|
Thyroid secretion that acts to protect against increase in plasma Calcium by stimulating bone formation
|
calcitonin
|
|
|
Stimulate bone growth, contributing to the growth spurt of puberty;also responsible for changes between male and female bone structure after puberty
|
sex hormones (estrogen;testosterone)
|
|
|
Articular surfaces can be easily defines as ?
|
joints
|
|
|
A shallow depression;the term fovea is also used for such features
|
fossa
|
|
|
Small articular surface or site of attachment of a tendon or ligament
|
facet
|
|
|
rounded articular surface that forms part of a sliding joint
|
condyle
|
|
|
raised area of a condyle, typically the site of attachment of ligaments for that joint
|
epicondyle
|
|
|
Grooved articular surface that has the appearance of a pulley
|
trochlea
|
|
|
proximal end of a long bone in which the metaphysis and epiphysis are expanded to increase the size of the articular surface
|
Head
|
|
|
Literally means "little hammer" the distal end of the tibia and fibula such projections that articulate with the talus of the foot to form the ankle bone
|
malleolus
|
|
|
A distinct projection from the bone surface.
|
process
|
|
|
Pointed process
|
spine
|
|
|
elongated line or ridge
|
crest
|
|
|
small/large rounded process, typically a site of attachment for a tendon or ligament;greater and lesser trochanters
|
tubercle/tuberosity
|
|
|
hook shaped process
|
hamulus
|
|
|
horn shaped process
|
cornu
|
|
|
Wing shaped process
|
ala
|
|
|
Round or oval opening allowing passage of nerves and blood
vessels. |
foreman
|
|
|
Narrow slit like opening
|
fissure
|
|
|
Groove or trench in which nerves, blood vessels or tendons lie
|
sulcus
|
|
|
Tubular passage containing soft tissue
|
meatus
|
|
|
Refers to cavity filled with air, and lined with mucus membrane(found only in the skull)
|
sinus
|
|
|
Tough flexible connective tissue;lacks blood and lymphatic vessels
|
cartilage
|
|
|
Lays down cartilage.
|
chondroblasts
|
|
|
Chondroblasts entrapped in cavities (lacunae) in the tissue they
have created in a manner reminiscent of the entrapment of osteoblasts in growing bone. |
chondrocytes
|
|
|
A membranous capsule that surrounds most cartilaginous
structures. |
perichondrium
|
|
|
Wing shaped process
|
ala
|
|
|
Round or oval opening allowing passage of nerves and blood
vessels. |
foreman
|
|
|
Narrow slit like opening
|
fissure
|
|
|
Groove or trench in which nerves, blood vessels or tendons lie
|
sulcus
|
|
|
Tubular passage containing soft tissue
|
meatus
|
|
|
Refers to cavity filled with air, and lined with mucus membrane(found only in the skull)
|
sinus
|
|
|
Tough flexible connective tissue;lacks blood and lymphatic vessels
|
cartilage
|
|
|
Lays down cartilage.
|
chondroblasts
|
|
|
Chondroblasts entrapped in cavities (lacunae) in the tissue they
have created in a manner reminiscent of the entrapment of osteoblasts in growing bone. |
chondrocytes
|
|
|
A membranous capsule that surrounds most cartilaginous
structures. |
perichondrium
|
|
|
Name 3 types of cartilage.
|
hyaline;fibrous;elastic
|
|
|
A glassy, translucent material that forms the bearing surfaces of
joints between long bones and makes up the costal cartilages of the ribs. It supports the flexible portion of the nose and forms the cartilaginous rings of the trachea. |
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Makes up the intervertebral discs that separate vertebrae of the
spinal column and forms a shock-absorbing pad that protects the knee joint.(meniscus) |
fibrous cartilage
|
|
|
Contains elastin fibers as well as collagen fibers, making it
stretchier than other types of cartilage. This is the material that gives the skin and lung wall their elasticity. |
elastic cartilage
|
|
|
Junctions between bones in the skeleton
|
joints
|
|
|
A joint that is immobile.
|
synarthrotic joint
|
|
|
Joints that are slightly flexible.
|
amphiarthrotic joint
|
|
|
Joints that are freely flexible.
|
diarthrotic joint
|
|
|
Structurally joints can be categorized as?
|
fibrous;cartilaginous or synovial
|
|
|
The bones are bound tightly together;these joints are generally
synarthrotic. |
fibrous joints
|
|
|
A link of cartilage connects the bones.
|
cartilaginous joints
|
|
|
A cartilaginous joint cavity formed at the ends of the jointed
bones. |
synovial joints
|
|
|
Formed by the extension of the periosteum of the two jointed
bones, surrounding a cartilaginous joint cavity. Within the capsule is a synovial membrane, containing a small amount of synovial fluid;amphiarthrotic joints |
articular capsule
|
|
|
Within the capsule is a ____________, containing a small amount of synovial fluid;bursa;diarthrotic joints
|
synovial membrane
|
|
|
Types of Synovial Joints
|
Plane;Hinge;Pivot;Condyloid;Saddle;ball and Socket
|
|
|
The articular surfaces are flat planes. Only short gliding
movements are possible, and neither bone can rotate around its axis. |
Plane Joint
|
|
|
A round end of one bone fits into a ring formed by an encircling
ligament on the end of the other bone, allowing the first bone to rotate around its long axis. |
pivot joint
|
|
|
The jointed articular surfaces fit together like a rider and saddle,
allowing the same range of motion as condyloid joints but with more protection against lateral forces. |
saddle joints
|
|
|
The characteristic feature is an articular surface shaped like a
trough into which a mating cylindrical surface fits. This allows movement like that of a swinging door. Examples: elbow, ankle, knee. |
hinge joint
|
|
|
An egg-shaped articular surface on one bone fits into an oval
concavity in the mating bone, allowing both side-to-side and back-and-forth movement planes but not rotation. Examples: the knuckles, wrist. |
condyloid joint
|
|
|
A spherical head fits into a corresponding socket, giving
universal movement, including axial rotation. Examples: the shoulder and hip. |
ball-and-socket
joint |
|
|
List Cranial bones
|
Frontal;Parietal;Temporal;Occipital:Sphenoid:Ethmoid
|
|
|
An immovable joint.
|
suture
|
|
|
Suture that joins frontal to parietal
|
coronal suture
|
|
|
Suture that joins parietal to parietal
|
Sagittal suture
|
|
|
Suture that joins temporals to parietals
|
Squamosal suture
|
|
|
Suture that joins occipital to parietals
|
Lambdoidal suture
|
|
|
Suture that joins occipital to temporals
|
Occiptomastoid suture
|
|
|
The point at which the coronal suture unites with the sagittal
suture. |
bregma
|
|
|
The point at which the coronal suture unites with the sagittal suture is the region of the anterior fontanel, one of two “soft spots” in infants.
|
anterior fontanel
|
|
|
Exists at the juncture of lambdoidal and sagittal sutures; within
two years after birth this fontanel closes to form the lambda. |
posterior fontanel
|
|
|
At the juncture of lambdoidal and sagittal sutures, formed when
this fontanel closes within two years after birth. |
lambda
|
|
|
The facial skeleton consist of __________ bones.
|
fifteen (15)
|
|
|
Forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place.
|
mandible
|
|
|
Articulates with all the facial bones-from upper jaw and central part of face
|
maxilla
|
|
|
Forms posterior part of hard palate and nasal cavity
|
palatine
|
|
|
Lacrimal groove carries lacrimal duct to drain tears from orbit to nasal cavity.
|
lacrimal
|
|
|
forms bridge of nose and attachment points for nasal cartilages
|
Nasal
|
|
|
Articulate with zygomatic processes of temporal bones to form zygomatic arch
|
Zygomatic
|
|
|
Contribute to complex surface of nasal cavity
|
Inferior nasal concha (conchae)
|
|
|
Forms inferior part of nasal septum.
|
Vomer
|
|
|
Supports the tongue-no articulations to other facial bones
|
Hyoid
|
|
|
the adult vertebral column consist of ____________ vertebrae.
|
twenty-six (26)
|
|
|
Cushions consisting of a rather tough outer annulus fibrosus surrounding a softer nucleus pulposus that separates the twenty-six vertebrae in the adult vertebral column.
|
intervertebral disc
|
|
|
In the adult vertebral column, the outer tough part of the intervertebral discs.
|
annulus fibrosus
|
|
|
Within the intervertebral discs, the soft interior surrounded by a tough outer annulus fibrosus.
|
nucleus pulposus
|
|
|
A feature common to all vertebrae, a depression in which the intervertebral disc rests.
|
centrum
|
|
|
Project posteriorley from the centrum and support the two superior and two inferior articular processes, points of contact between adjacent vertebrae.
|
bilateral pedicles
|
|
|
Points of contact between adjacent vertebrae.
|
articular processes
|
|
|
Extends toward the midline from each articular process, forming a roof over the vertebral foramen, the opening through which the spinal cord passes.
|
lamina
|
|
|
Bilateral branches of the spinal cord that pass in the spaces between the pedicles of adjacent vertebrae.
|
spinal nerves
|
|
|
The vertebral column is divided into 5 regions, which are?
|
Cevical;Thoracic;Lumbar;Sacral;Coccygeal
|
|
|
Articulates with the occipital condyles and permits head movement in the saggital plane.
|
C1 (cervical 1)
|
|
|
Allows side to side rotation of the head
|
C2 (cervical 2) Axis
|
|
|
Serve as the joint surfaces for the heads of ribs.
|
superior facets
|
|
|
A cartilaginous synarthrotic joint, the breastbone.
|
sternum
|
|
|
Located on the rib in the inferior inner surface that carries a costal
nerve and blood vessels. |
costal groove
|
|
|
Three pairs of false ribs that articulate to the next superior rib through costal cartilages.
|
vertebrochondral ribs
|
|
|
The sternum consist of 3 sections called?
|
Manubrium;Body;Xiphoid Process
|
|
|
Located in the center of the superior edge of the manubrium section of the sternum.
|
jugular notch
|
|
|
Joins the medial end of the clavicle.
|
clavicular notch
|
|
|
A ridge that marks the hinge joint between the manubrium and the body
|
sternal angle
|
|
|
Part of the sternum, located between the body and xiphoid
process. |
xiphisternal joint
|
|
|
One of distinguishing features is the side-to-side dimension of body is larger than anterior-posterior dimension; transverse foramina are present in the transverse processes.
|
cervical vertebrae
|
|
|
Vertebrae that are jointed to the ribs.
|
thoracic vertebrae
|
|
|
The five sturdy and massive vertebrae in the vertebral column that receive the most stress. The large muscles of the back attach to them.
|
lumbar vertebrae T
|
|
|
Allow the passage of sacral spinal nerves.
|
sacral foramina
|
|
|
Formed by fused vertebral spines.
|
sacral crest
|
|
|
The lamina of the fifth sacral vertebra ordinarily do not fuse so that the sacral canal ends in an opening, on the inferoanterior surface of the sacrum.
|
sacral hiatus
|
|
|
Small triangular bone composed of three to five fused vertebrae
|
coccyx
|
|
|
Consists of the limb bones and their girdles.
|
appendicular skeleton
|
|
|
A complete girdle that consists of the sacrum and a pair of coxal bones.
|
pelvic girdle
|
|
|
An incomplete circle of bones that consists of the clavicles or
collarbones and scapulae or shoulder blades. |
pectoral girdle
|
|
|
Armpit.
|
axilla
|
|
|
The joint with the humerus of the arm.
|
glenoid cavity
|
|
|
The posterior surface of the scapula bears a prominent spine that widens at its lateral end to form an articulation with the clavicle.
|
acromion
|
|
|
Projects anteriorly from the superior scapular border. This is the
attachment of the biceps muscle and for ligaments that bind the clavicle to the scapula. |
coracoid process
|
|
|
An attachment site for the deltoid muscle of the shoulder.
|
deltoid tuberosity
|
|
|
One of two condyles at the distal end of the humerus that articulates with the radius.
|
capitulum
|
|
|
Serves as attachment site for ligaments and muscles
|
medial/lateral epicondyle
|
|
|
A flat ligament that binds the radius and the ulna.
|
interosseous membrane
|
|
|
The radius and ulna are bound together by a flat ligament, the
interosseous membrane, which forms a freely movable ____________. |
syndesmosis
|
|
|
Bones of the wrist
|
carpal bones
|
|
|
Bones of the palm
|
metacarpal
|
|
|
Bones of the fingers
|
phalanges (phalanx)
|
|
|
A complete girdle that consists of the sacrum and a pair of coxal
bones. |
pelvic girdle
|
|
|
Within the pelvic girdle, consists of an inferior body and a superior ala.
|
ilium
|
|
|
Consists of a heavy body and a lighter ramus that, anteriorly, joins the pubis.
|
ischium
|
|
|
At the point of the fusion of three the ilium, ischium, and pubis in which a deep socket articulates with the head of the femur.
|
acetabulum
|
|
|
An amphiarthrotic cartilaginous joint.
|
pubic symphysis
|
|
|
The ilium consist of an inferior body and a ______________.
|
superior ala
|
|
|
Within the pelvic girdle, the superior margin of the ala.
|
iliac crest
|
|
|
In the ilium, a deep notch through which the sciatic nerve passes from the sacral spinal cord to the thigh.
|
greater sciatic notch
|
|
|
Consists of a heavy body and a lighter ramus that, anteriorly,
joins the pubis. |
ischium
|
|
|
The ischium consists of a heavy body and a lighter ramus that,
anteriorly, joins the pubis. |
ramus
|
|
|
Bears the weight of the sitting body.
|
ischial tuberosity
|
|
|
A landmark of the ischium.
|
lesser sciatic notch
|
|
|
An attachment site for a ligament that runs from ischium to
sacrum. |
ischial spine
|
|
|
The anterior border of the pubis.
|
pubic crest
|
|
|
A ridge of bone that runs from the pubic crest across the medial
face of the ilium to the sacrum. |
pelvic brim
|
|
|
A large opening in the space between the pubis and the ischium, closed by a fibrous membrane.
|
obturator foramen
|
|
|
Connect the medial meniscus with the medial epicondyle.
|
cruciate ligaments
|
|
|
Found on the anterior surface of the tibia just inferior to the condyles, the point of attachment of the patellar tendon.
|
tibial tuberosity
|
|
|
Forms the medial bulge of the ankle.
|
medial malleolus
|
|
|
Forms the lateral bulge of the ankle.
|
lateral malleolus
|
|
|
The bones of the foot are:
|
tarsals, metatarsals;phalanges
|
|
|
A tarsal bone that articulates with the tibia and fibula.
|
talus
|
|
|
Tarsal bone that forms the heel.
|
calcaneus
|

