![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
categorical
|
A categorical variable places an individual into one of several groups or categories.
|
|
|
quantitative
|
A quantitative variable takes numerical values for which arithmetic operations such as adding and averaging make sense.
|
|
|
distribution
|
The distribution of a variable tells us what values the variable takes and how often it takes these values.
|
|
|
When describing the overall pattern of a distribution, you MUST address the following 4 things.
|
1. The CENTER of the data
2.The SHAPE of the data 3. The SPREAD of the Data 4. Any OUTLIERS in the data |
|
|
Percentile |
= (number of scores x)/(total number of scores) * 100
|
|
|
Q1 |
First Quartle |
|
|
Q3 |
Third Quartile |
|
|
Symmetry:
|
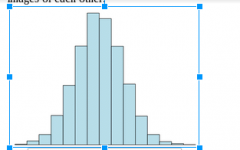
A distribution is symmetric if the right and left sides of the histogram are approximately mirror images of each other.
|
|
|
Skewed Right |
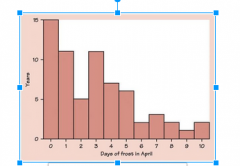
A distribution is skewed to the right if the right side of the histogram extends far to the righ
|
|
|
Skewed Left |
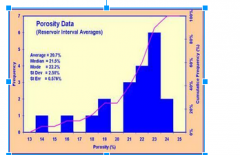
A distribution is skewed to the left if the left side of the histogram extends far to the left.
|

