![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Which of the following is the blood vessel that distributes blood to organs?
|
a) arteries
|
|
|
2. This is a blood vessel that conveys blood from the tissues back to the heart.
|
d) vein
|
|
|
3. Which artery wall is responsible for vasoconstriction?
|
b) tunica media
|
|
|
4. This layer of the artery is composed mainly of elastic and collagen fibers.
|
c) tunica externa
|
|
|
5. When an artery or arteriole is damaged, its smooth muscle contracts producing
|
c) a vascular spasm
|
|
|
6. Elastic arteries function as a
|
d) pressure reservoir
|
|
|
7. These vessels make up the largest blood reservoir.
|
d) Veins and venules
|
|
|
8. This vessel plays a key role in regulating blood flow into capillaries.
|
b) arterioles
|
|
|
9. Which of the below is NOT found in arteries but is found in veins?
|
valves
|
|
|
10. Capillaries are also known as
|
a) exchange vessels
|
|
|
11. Which of the below is the most important capillary exchange method?
|
a) Diffusion
|
|
|
12. These control the flow of blood through a capillary bed.
|
b) precapillary sphincter
|
|
|
13. Continuous capillaries can be found in the following tissues.
|
e) All of the above
|
|
|
14. The alternate route of blood flow to a body part through an anastomosis is called
|
d) collateral circulation
|
|
|
15. The largest factor that promotes reabsorption of fluids, into blood, from the interstitial fluids is
|
c) Blood osmotic pressure
|
|
|
16. The pressure driven movement of fluids and solutes from blood into interstitial fluid is called
|
b) filtration
|
|
|
17. This is the volume of blood that flows through any tissue in a given time period.
|
c) blood flow
|
|
|
18. Blood flow depends on which of following criteria.
|
d) Blood pressure and systemic vascular resistance
|
|
|
19. Which of the below would NOT increase blood pressure.
|
e) Decreased cardiac output
|
|
|
20. Which of the below factors do NOT increase systemic vascular resistance?
|
c) decreased vessel length
|
|
|
21. This depends mostly on the ratio of RBC to plasma volume.
|
b) blood viscosity
|
|
|
22. Circulation time
|
c) in a resting person is normally 1 minute
|
|
|
23. The cardiovascular center is located
|
d) in the medulla oblongata
|
|
|
24. Which of the below factors is most important in forcing blood flow through veins?
|
c) muscular activity
|
|
|
25. Which of the below would be the response of the body as a result of decreased frequency of action potentials arising from the baroreceptors?
|
a) Increased blood pressure
|
|
|
26. Which of the following hormones would NOT cause an increase in blood pressure?
|
a) Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
|
|
|
27. Chemoreceptors in blood vessels measuring high levels of blood carbon dioxide would NOT cause which of the following
|
d) Decreased respiratory rate
|
|
|
28. The myogenic response make smooth muscle
|
a) Contract more forcefully when stretched
|
|
|
29. What do these chemicals have in common: potassium, hydrogen ions, lactic acid, nitric oxide and adenosine?
|
b) They are all potent vasocdilators
|
|
|
30. Where can pulse not be felt?
|
d) Capillaries
|
|
|
31. This pressure provides information about the condition of the cardiovascular system such as atherosclerosis and patent ductus arteriosus.
|
c) Pulse pressure
|
|
|
32. This type of shock is due to decreased blood volume.
|
a) Hypovolemic
|
|
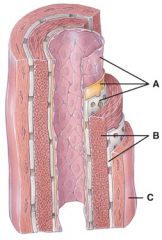
33. This layer consists mainly of elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers that extend circularly around the lumen.
|
b) B
|
|
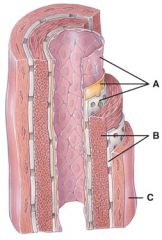
34. This layer contains a lining of simple squamous epithelium, a basement membrane and a layer of elastic tissue.
|
a) A
|
|
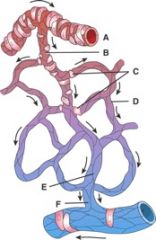
35. Where is the metarteriole?
|
b) B
|
|
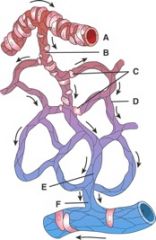
36. Where is the capillary?
|
d) D
|
|
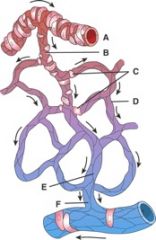
37. Where is the postcapillary sphincter?
|
e) None of the above
|
|
38. This type of capillary wall has an incomplete or absent basement membrane.
|
c) C
|
|
39. This type of capillary wall is commonly found in the kidneys, villi of the small intestine, choroids plexuses and some endocrine glands.
|
b) B
|
|
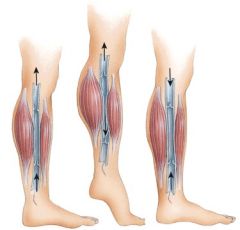
40. What does this figure represent?
|
b) Skeletal muscle pump
|
|
|
41. What do the following have in common: superficial temporal artery, brachial artery and dorsal artery of the foot?
|
c) They are all pulse points
|
|
|
42. Which of the following is not a response to hypovolemic shock?
|
d) Release of vasoconstrictors
|
|
|
43. All the veins of the systemic circulation drain into the
|
e) Superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus
|
|
|
44. The pulmonary trunk divides into
|
d) Right and left pulmonary arteries
|
|
|
45. In fetal circulation what is the opening between the right and left atria called?
|
d) Foramen ovale
|
|
|
46. Which of the below vessels is a pulse point at the wrist?
|
Radial artery
|
|
|
47. Which of the below vessels supplies blood to the intestines?
|
Mesenteric artery
|
|
|
48. Which of the below vessels supplies blood to the kidney?
|
b) Renal artery
|
|
|
49. Which of the below vessels drains blood from the lower leg?
|
) Coronary vein
|
|
|
50. Which of the below vessels drains blood from the head and neck?
|
) Jugular vein
|
|
|
51. Which of the below vessels drains blood from the lower body to the right atrium?
|
a) Inferior vena cava
|
|
|
52. After birth when the umbilical cord is cut what do the umbilical arteries fill with?
|
c) Connective tissue
|
|
|
1. Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic and immune system?
|
b) Maintaining water homeostasis in the body
|
|
|
2. What is the major difference between lymph and interstitial fluid?
|
c) Location
|
|
|
3. Lack of resistance is also known as:
|
d) Susceptibility
|
|
|
5. What causes lymph from the small intestines to appear white?
|
d) Lipids
|
|
|
6. Which of the following is not considered an organ of the immune system?
|
e) Pancreas
|
|
|
7. The left subclavian vein receives lymph from
|
d) Thoracic duct
|
|
|
8. The lymph from the right foot empties into the
|
d) Thoracic duct
|
|
|
9. The skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps are used in
|
e) Lymphatic, Immune and Cardiovascular systems
|
|
|
11. Which of the below produces the hormone that promotes maturation of T cells?
|
d) Thymus
|
|
|
12. In the thymus, where is it speculated that T cells die.
|
d) Hasall’s corpuscles
|
|
|
13. This portion of the lymph node does not contain any lymphatic nodules.
|
a) Inner cortex
|
|
|
14. Which of the following is a function of the spleen?
|
a) Removes worn out blood cells
|
|
|
15. Which of these does NOT provide a physical or chemical barrier?
|
a) Macrophages
|
|
|
17. Which of these provides a non-specific cellular disease resistance mechanism?
|
a) Macrophages
|
|
|
18. These anti-microbial substances will diffuse to uninfected cells and reduce production of viral proteins.
|
e) Interferons
|
|
|
19. These anti-microbial substances promote cytolysis, phagocytosis and inflammation.
|
c) Complement proteins
|
|
|
20. These are mainly used to kill infectious microbes and tumor cells.
|
a) Natural killer cells
|
|
|
21. Which of the following is NOT a sign of inflammation?
|
d) Mucus production
|
|
|
22. Which of the following intensifies the effect of interferons and promotes the rate of repair?
|
c) Fever
|
|
|
23. Which of the below do NOT induce vasodilation and permeability (increased fluid flow) to an infection site.
|
c) Perforin
|
|
|
24. When B and T cells are fully developed and mature, they are known to be
|
a) Immunocompetent
|
|
|
25. This induces production of a specific antibody.
|
b) Antigen
|
|
|
26. This can only stimulate an immune response if attached to a large carrier molecule.
|
c) Hapten
|
|
|
27. Which of the following is responsible for diversity in the immune system?
|
d) MHC and antigen receptors
|
|
|
28. This class of cells includes macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells.
|
a) Antigen presenting cells
|
|
|
29. This can only become activated when bound to a foreign antigen and simultaneously receiving a costimulate.
|
b) T Cell
|
|
|
30. These display CD 4 in their membrane and are associated with MHC class II molecules.
|
b) Helper T Cells
|
|
|
31. T Cells secrete this toxin that is used to fragment DNA.
|
d) Lymphotoxin
|
|
|
31. T Cells secrete this toxin that is used to fragment DNA.
|
d) Lymphotoxin
|
|
|
33. This class of antibodies is mainly found in sweat, tears, breast milk and GI secretions.
|
b) IgA
|
|
|
34. This will lead to inflammation, enhancement of phagocytosis and bursting of microbes.
|
d) Classical and Alternative complement systems
|
|
|
35. This action makes microbes more susceptible to phagocytosis.
|
a) Opsonization
|
|
|
36. This is a self-responsive cell that is inactive.
|
d) Anergy cell
|
|
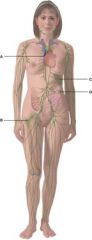
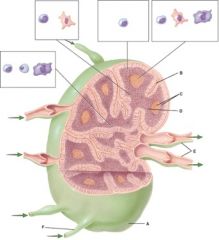
37. In the diagram, where do pluripotent stem cells come from?
|
b) B
|
|
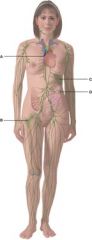
38. In the diagram, where do T cells mature?
|
a) A
|
|
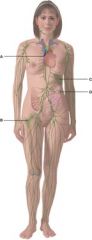
39. In the diagram, what is comprised of white and red pulp?
|
c) C
|
|
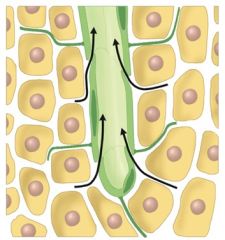
40. What does this diagram represent?
|
Ans: The one-way flow of lymph through a lymph vessel.
|
|
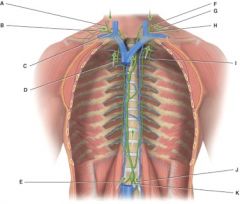
41. In the diagram this vessel drains lymph from the upper right side of the body into venous blood using a subclavian vein.
|
b) C
|
|
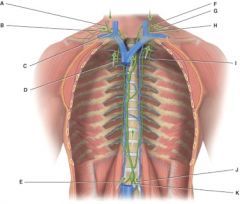
42. In the diagram these are the bronchomediastinal trunks.
|
d) D and I
|
|
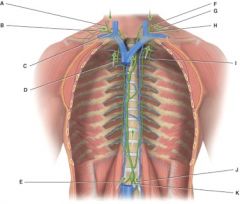
43. In the diagram, what are the principle trunks?
|
d) A,B,D,E,F,G,I,J,K
|
|
44. In the diagram, this consists of a medulla, medullary sinus and reticular fibers.
|
c) D
|
|
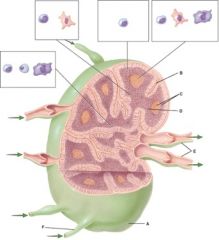
45. In the diagram, cells found in this region include B cells, follicular dendritic cells and macrophages.
|
b) C
|
|
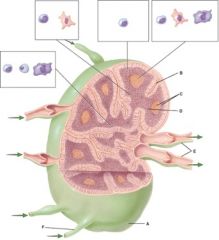
46. In the diagram, cells found in this region include B cells, plasma cells and macrophages.
|
e) None of the above
|
|
|
49. This is characterized by the inability of the immune system to protect the body from a pathogen.
|
a) immunodeficiency diseases
|
|
|
50. An acute allergic response can lead to:
|
c) anaphylactic shock
|
|
|
51. A natural exposure to an infectious agent leads to:
|
b) B. Active immunity
|
|
|
52. This class of antibodies is produced after an initial exposure to antigens.
|
c) IgM
|
|
|
53. Of the following which is involved in the body’s second line of defense?
|
d) Natural killer cells
|
|
|
54. Lymphocytes can recognize
|
b) Foreign cells
|
|
|
55. In B cell receptors, the light/heavy variable regions are located
|
b) Tips of the molecules
|
|
|
56. What is the most polymorphic molecule in the immune system?
|
c) MHC
|
|
|
57. The primary response will peak how many days after an exposure?
|
c) 10-17
|
|
|
58. Which type of immunity defends against any type of invader?
|
a) Nonspecific
|
|
|
59. This is the ability of an antigen to react specifically with the antibodies or cells it has provoked.
|
c) Reactivity
|
|
|
60. This is a small hormone that can stimulate or inhibit many normal cell functions.
|
c) Cytokine
|

