![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Interphase- period of general cell growth and DNA replication |
|

|
Prophase- nuclear membrane disappears, nucleolus disappears, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, spindle apparatus forms |
|
|
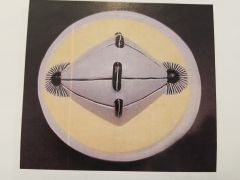
Metaphase- chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate |
|
|
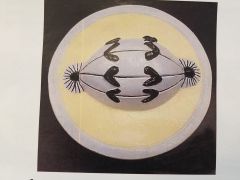
Anaphase- centromere splits to end metaphase and begin anaphase. Sister chromatids pulled to opposite poles by spindle apparatus |
|

|
Telophase/Cytokinesis- chromosomes reach opposite poles and clump, events of prophase are reversed. Cytokinesis (division of the cell) is completed |
|
|
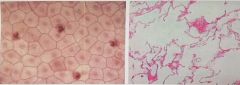
Simple Squamous Epithelium- Single layer of flattened cells with disk shaped central nuclei. . Allows passage of material by diffusion .Found in air sacs of the lungs |
|

|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium- Single layer of cube like cells with spherical central nuclei. . Secretion and absorption . Kidney tubules |
|

|
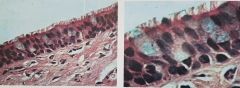
Simple Columnar Epithelium- Single layer of tall sells with oval nuclei. . Absorption . Digestive tract |
|
|
Pseudostratified Ciliated Coloumnar Epithelium- Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface, nuclei seen at different levels. . Secretion of the mucous by ciliary action . Lining the trachea |
|
|
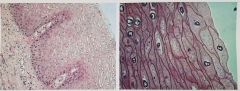
Stratified Squamous Epithelium- Thick membrane composed of several cell layers. . Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion .Found in the moist lining of the mouth |
|
|
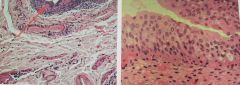
Transitional Epithelium- Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cubodial, basal cells cubodial or columnar, surface cells like squamous depending on the degree of organ stretch. . Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ . Found in lining of the bladder |
|

|
Areolar Connective Tissue- Gel like matrix with 3 fiber types . Wraps and cushions organs, plays an important role in inflammation and holds and conveys tissue fluid . Found widely distributed under the epithelia of body. |
|

|
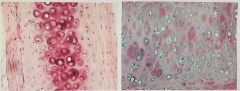
Apidose Tissue- closely packed fat cells . Provides reserve fuel, insulates against heat loss, supports and protects organs . Found under skin within abdomen and breasts |
|
|
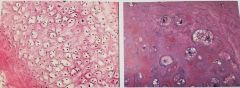
Hyaline Cartilage- Firm matrix. Mature chondrocytes lie in lacunae . Supports, reinforces, and resist compressive stress . Covers ends of long bones |
|
|
Elastic Cartilage- dense regular connective tissue containing a high proportion of elastic fibers . Maintains the shape and structure while allowing great flexibility . Supports the external ear |
|

|
Fibrocartilage- Less firm than hyaline cartilage . High tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock .Found in intervertebral discs |

