![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
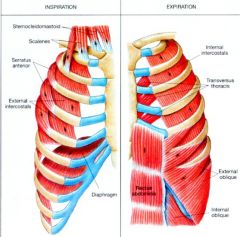
INTERNAL & EXTERNAL INTERCOSTALS
|
|
|
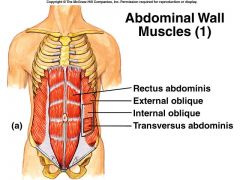
RECTUS ABDOMINUS
|
|
|
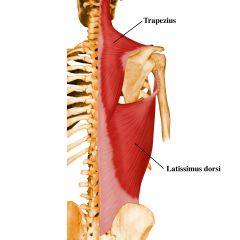
LATTISIMUS DORSI
|
|
|
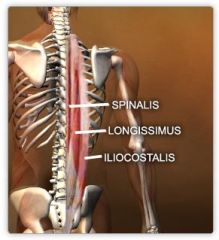
ERECTOR SPINAE
|
|
|
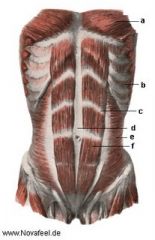
LINEA ALBA
|
|
|
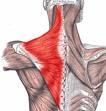
TRAPEZIUS
|
|
|
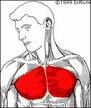
PECTORALIS MAJOR
|
|
|
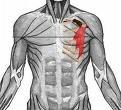
PECTORALIS MINOR
|
|
|
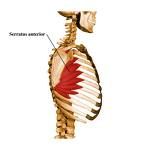
SERRATUS ANTERIOR
|
|
|
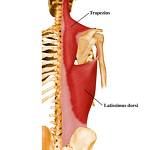
LATTISIMUS DORSI
|
|
|
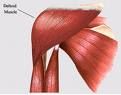
DELTOID
|
|
|
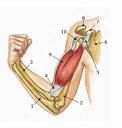
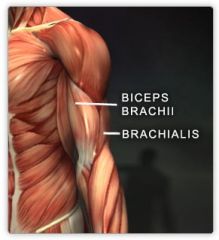
BICEPS BRACHII
|
|
|
BRACHIALIS
|
|
|
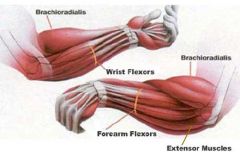
BRACHIORADIALIS
|
|
|
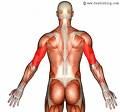
TRICEPS BRACHII
|
|
|
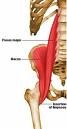
ILIOPSOAS
|
|
|
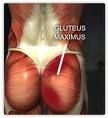
GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
|
|
|
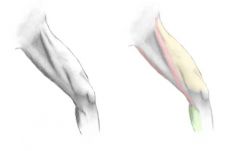
SARTORIUS
|
|
|
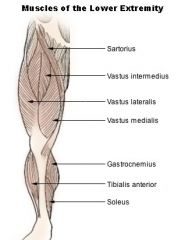
QUADRICEPS GROUP:
RECTUS FEMORIS, VASTUS LATERALIS, VASTUS MEDIALIS, VASTUS INTERMEDIUS |
|
|
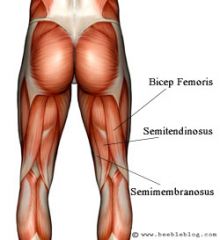
HAMSTRING GROUP:
BICEPS FEMORIS, SEMITENDINOSUS, SEMIMEMBRANOSUS |
|
|
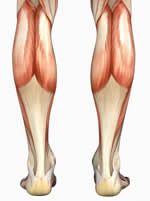
GASTROCNEMIUS
|
|
|
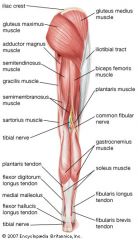
FLEXOR DIGITORUM LONGUS
|
|
|
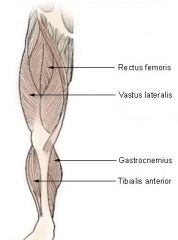
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR
|
|
|
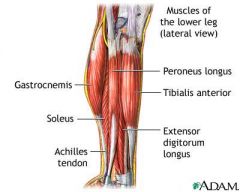
EXTENSOR DIGITORUM LONGUS
|
|
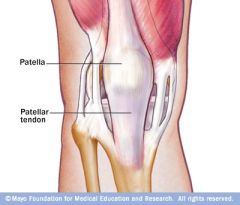
|
PATELLAR TENDON
|
|
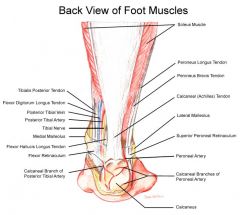
|
CALCANEAL TENDON
|
|
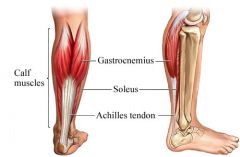
|
SOLEUS
|
|
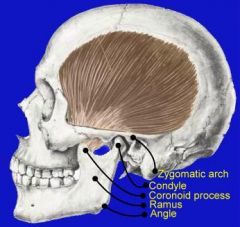
|
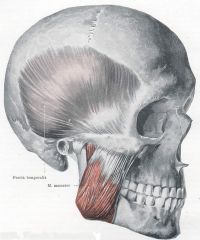
TEMPORALIS
|
|
|
MASSETER
|
|
|
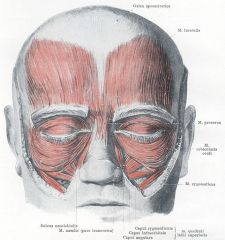
FRONTALIS
|
|
|
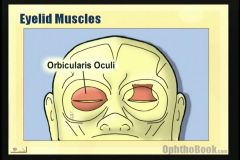
ORBICULARIS OCULI
|
|
|
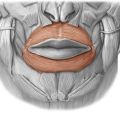
ORBICULARIS ORIS
|
|
|
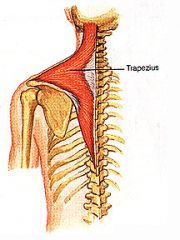
TRAPEZIUS
|
|
|
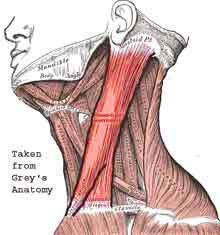
STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID
|
|
|
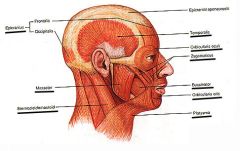
PLATYSMA
|
|
|
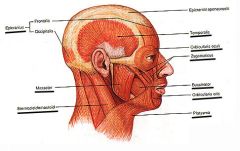
BUCCINATOR
|
|
|
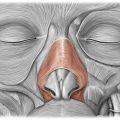
NASALIS
|
|
|
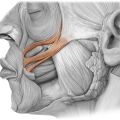
ZYGOMATICUS
|
|
|
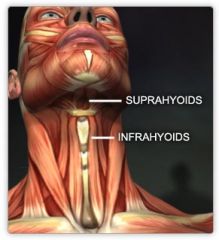
SUPRAHYOID/ INFRAHYOID
|
|
|
FLEXION
|
Bending movement that decreases the angle between two parts. Bending the elbow, or clenching a hand into a fist, are examples of flexion. When sitting down, the knees are flexed. Flexion of the hip or shoulder moves the limb forward (towards the anterior side of the body).
|
|
|
EXTENSION
|
The opposite of flexion; a straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts. In a conventional handshake, the fingers are fully extended. When standing up, the knees are extended. Extension of the hip or shoulder moves the limb backward (towards the posterior side of the body).
|
|
|
ABDUCTION
|
A motion that pulls a structure or part away from the midline of the body (or, in the case of fingers and toes, spreading the digits apart, away from the centerline of the hand or foot). Abduction of the wrist is called radial deviation. Raising the arms laterally, to the sides, is an example of abduction.
|
|
|
ADDUCTION
|
A motion that pulls a structure or part towards the midline of the body, or towards the midline of a limb. Dropping the arms to the sides, or bringing the knees together, are examples of adduction. In the case of the fingers or toes, adduction is closing the digits together. Adduction of the wrist is called ulnar deviation.
|
|
|
ROTATION
|
A motion that occurs when a part turns on its axis. The head rotates on the neck, as in shaking the head 'no'.
|
|
|
ELEVATION
|
Movement in a superior direction.
|
|
|
DEPRESSION
|
Movement in an inferior direction, the opposite of elevation.
|
|
|
CIRCUMDUCTION
|
The circular (or, more precisely, conical) movement of a body part, such as a ball-and-socket joint or the eye. It consists of a combination of flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction. "Windmilling" the arms or rotating the hand from the wrist are examples of circumductive movement.
|
|
|
RETRACTION
|
Posterior movement of the arms at the shoulders.
|

