![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name one of the two functions of an articulation, or joint |
1. holds bones together
2. allows flexibility for movement |
|
|
The functional classification of joints is based on |
amount of movement allowed by the joint |
|
|
Structural classification of joints include fibrous, cartilaginous, and _____, which have a fluid-filled cavity between articulating bones |
synovial |
|
|
Sutures, which have their irregular edges of bone joined by short fibers of connective tissue, are an example of _____ joints |
fibrous |
|
|
True/False
All synovial joints are diarthroses, or freely moveable joints |
True |
|
|
Every muscle of the body is attached to a bone or other connective tissue structure at two points, The ____ is the more moveable attachment |
insertion |
|
|
The hip joint is an example of _____ synovial joint |
ball and joint |
|
|
Movement of a limb away from the midline or median plane of the body in the frontal plane is known as |
abduction |
|
|
This type of movement is common in ball and socket joints and can be described as the movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis. It is _____ |
rotation |
|
|
True/False
The knee joint is the most freely moveable joint in the body |
False (it is the shoulder) |
|
|
typically allows a slight degree of movement |
cartilaginous |
|
|
includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphosis |
cartilaginous |
|
|
essentially immovable joints |
fibrous |
|
|
sutures are the most remembered examples |
fibrous |
|
|
characterized by cartilage connecting the bony portions |
cartilaginous |
|
|
all characterized by a fibrous articular capsule lined with a synovial membrane surrounding a joint cavity |
synovial |
|
|
all are freely movable or diarthortic |
synovial |
|
|
bone regions united by fibrous connective tissue |
fibrous |
|
|
include the hip, knee, and elbow joints |
synovial |
|
|
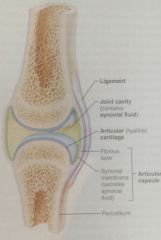
ligament |
dense connective tissue made out of fascia that connects one bone to another; helps stabalize joints during movement |
|
|
articular catilage |
connective tissue, cushions bones from rubbing on each other, allows gliding motion |
|
|
tendon |
connective tissue, connects muscles to bone |
|
|
synovial membrane |
soft connective tissue; secretes synovial fluid that lubricates the joint and reduces friction between bones in joints |
|
|
bursa |
fibrous connective tissue; prevents friction within the joints |
|
|
... |
|
|
joint between the axis and atlas |
pivot |
|
|
hip joint |
ball and socket |
|
|
intervertebral joints |
condylar |
|
|
joint between forearm bones and wrist |
condylar |
|
|
elbow |
hinge |
|
|
interphalangeal joints |
hinge |
|
|
intercarpal joints |
plane |
|
|
joint between talus and tibia/fibula |
hinge |
|
|
joint between skull and vertebral column |
condylar |
|
|
joint between jaw and skull |
hinge |
|
|
joints between proximal phalanges and metacarpal bones |
condylar |
|
|
a multiaxial joint |
ball and socket |
|
|
biaxial joints |
condylar and saddle |
|
|
uniaxial joints |
hinge and pivot |
|
|
Indicate the number of planes which each joint can move
uniaxial joints (a)____ biaxial joints (b)___ multiaxial joints (c)___
|
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 |
|
|
define condylar joint |
(biaxial) the oval condyle of one bone fits into an ellipsoidal depression in another bone to allow movement in two planes, usually flexion/extension and abduction/adduction
Ex: wrist and knuckles |
|
|
define plane joint |
(nonaxial) articulating surfaces are flat or slightly curved. These surfaces allow only grinding movements as the surfaces slide past one another.
Ex: intercarpal joints, joints between vertebral articular surface |
|
|
define hinge joint |
(uniaxial) the runded or cylindrical process of one bone fits into the concave surface of another bone, allowing movement in one plane, usually flexion/extension
Ex: elbow |
|
|
define pivot joint |
(uniaxial) the rounded surface of one bone articulates with a shallow depression or foramen in another bone, permitting rotational movement in one plane
Ex: proximal radioulnar joint |
|
|
define saddle joint |
(biaxial) articulating surfaces are saddle shaped; one surface is convex, and the other is concave. This type of joint permits movement in two planes, flexion/extension and abduction/adduction
Ex: carpometacarpal joints of the thumbs |
|
|
define ball and socket joints |
(multiaxial) the ball shaped head of one bone fits into a cuplike depression depression of another bone. These joints permit flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and rotation, which combines to allow movement in many planes
Ex: shoulder and hip |
|
|
What characteristic do all joints have in common |
movement |
|
|
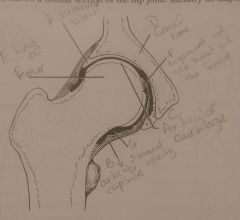
Which joint is more stable hip or or knee |
hip |
|
|
Name two important factors that contribute to the stability of the hip |
1. deep sockets 2. ligaments |
|
|
Name two important factors that contribute to the stability of the knee |
1. strength of the anterior/posterior cruciform ligaments 2. integrity of the cartilage on bones at the knees |
|
|
... |
|
|
The shoulder joint is built for mobility. List 4 factors that contribute to the large range of motion at the shoulder |
1. ball and socket joint 2. glenoid labrum deepens the cavity 3. few reinforcing ligaments 4. thin/loose articular cartilage encloses the joint |
|
|
In which direction does the shoulder usually dislocate |
downward displacement of the humerus |
|
|
During muscle contraction, the (a)_____ moves toward the (b)_____ |
(a) insertion (b) origin |
|
|
What structural joint changes are common to the elderly |
degeneration, adhesions may form at bone ligaments, extraneous bone tissue can grow along the joint edges |
|
|
define sprain |
ligaments are stretched or torn away from the bony attachment |
|
|
define dislocation |
bones are forced out of their normal position in the joint cavity |
|
|
What types of tissue damage might you expect to find in a dislocated joint |
torn or stressed ligaments |

