![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The ____ skeleton is made up of 126 bones of the limbs and girdles |
appendicular |
|
|
The ____ girdle attaches the upper limb to the axial |
pectoral |
|
|
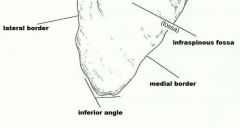
The ____, on the posterior thorax, are roughly triangular in shape. They have no direct attachment to the axial skeleton but are held in place by trunk muscles |
scapula |
|
|
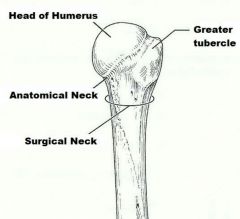
The arm consists of one long bone which is the |
humerus |
|
|
The hand consists of three groups of bones. The carpals make up the wrist. The ______ make up the palm, and the phalanges make up the fingers |
metacarpals |
|
|
You are studying a pelvis that is wide and shallow. The acetabula are small and far apart. The pubic arch/angle is rounded and greater than 90*. It appears to be tilted forward, with a wide, short sacrum. Is this a male or female pelvis |
female |
|
|
The strongest, heaviest bone of the body is the |
femur |
|
|
The ______, or the "knee cap," is a sesamoid bone that is found within the quadricips tendon |
patella |
|
|
True/False
The fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot-- with the exception of the great toe and the thumb-- each of three phalanges |
True |
|
|
Each foot has a total _____ bones |
26 |
|
|
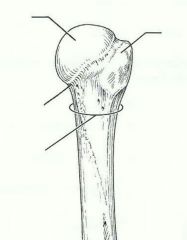
raised area on lateral surface of humerus to which deltoid muscle attaches |
deltoid tuberosity |
|
|
arm bone |
humerus |
|
|
bones of the shoulder girdle |
clavicle and scapula |
|
|
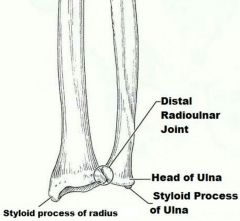
forearm bones |
radius and ulna |
|
|
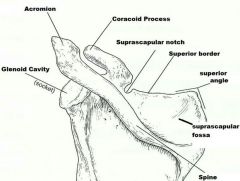
scapular region to which the clavicle connects |
acromion |
|
|
shoulder girdle bone that does not attach to the axial skeleton |
scapula |
|
|
shoulder girdle bone that articulates with and transmits forces to the bony thorax |
clavicle |
|
|
depression in the scapula that articulates with the humerus |
glenoid cavity |
|
|
process above teh glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment |
coracoid process |
|
|
the "collarbone" |
clavicle |
|
|
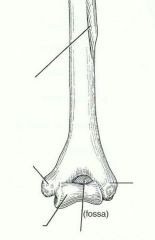
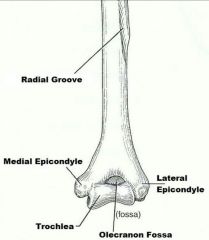
distal condyle of the humerus that articulates with the ulna |
trochlea |
|
|
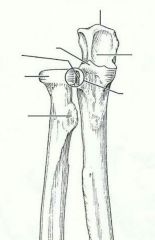
medial bone of forearm in anatomical position |
ulna |
|
|
rounded knob on the humerus; adjoins the radius |
capitulum |
|
|
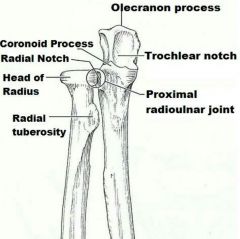
anterior depression, superior to the trochlea, that receives part of the ulna when the forearm is flexed |
coronoid fossa |
|
|
forearm bone involved in formation of the elbow joint |
ulna |
|
|
wrist bones |
carpals |
|
|
finger bones |
phalanges |
|
|
heads of these bones form the knuckles |
metacarpals |
|
|
bones that articulate with the clavicle |
scapula and sternum |
|
|
How is the arm held clear of the widest dimension of the thoracic cage |
The clavicle acts as a strut to hold the glenoid cavity of the scapula (therefore the arm) laterally from the narrowest area of the ribs/rib cage |
|
|
What is the total number of phalanges in the hand |
14 |
|
|
What is the total number of carpals in the wrist |
8 |
|
|
Name the carpals (medial to lateral) in the proximal row |
pisiform, triquetral, lunate, scaphoid |
|
|
Name the carpals (medial to lateral) in the distal row |
hamate, capitate, trapezoid, trapezium |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
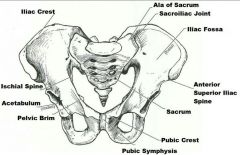
What organs are protected, at least in part, by the pelvic girdle |
uterus, urinary bladder, small intestine, rectum |
|
|
Distinguish between the true pelvis and the false pelvis |
The true pelvis is the region inferior to the pelvic brim, which is encircled by bone.
The false pelvis is the area medial to the flaring iliac bones and lies superior to the pelvic brim |
|
|
Deduce why the pelvic bones of a four legged animal such as the cat or pig are much less massive than those of the human |
The pelvic girdle does not have to carry the entire weight of the trunk in the quadraped animal |
|
|
A person instinctively curls over his abdominal area in times of danger. Why... |
The abdominal area organs are the most vulnerable because it is not protected by the skeleton |
|
|
What structural changes result in "fallen arches" |
flat feet/flat footed |
|
|
fuse to form the coxal bone |
ilium, ischium, pubis |
|
|
"sit down" bone of the coxal bone |
ischium |
|
|
point where the coxal bones joins anteriorly |
pubis symphosis |
|
|
superiormost margin of the coxal bone |
iliac crest |
|
|
deep socket in the coxal bone that receives the head of the thigh bone |
acetabulum |
|
|
joint between axial skeleton and pelvic girdle |
sacroiliac joint |
|
|
longest, strongest bone in the body |
femur |
|
|
thin lateral bone |
fibula |
|
|
heavy medial leg bone |
tibia |
|
|
bones forming the knee joint |
femur and tibia |
|
|
point where the patellar ligament attaches |
tibial tuberosity |
|
|
kneecap |
patella |
|
|
shinbone |
tibia |
|
|
medial ankle projection |
medial mallolus |
|
|
lateral ankle projection |
lateral malleolus |
|
|
largest tarsal bone |
calcaneus |
|
|
ankle bones |
tarsals |
|
|
bones forming the instep of the foot |
metatarsals |
|
|
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami |
obturator |
|
|
sites of muscle attachment on the proximal femur |
gluteal foramen and greater and less trochanters |
|
|
tarsal bone that "sits" on the calcaneus |
talus |
|
|
weight-bearing bone of the leg |
tibia |
|
|
tarsal bone that articulates with the tibia |
talus |

