![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True or false: acetylcholine binding to nicotine cholinergic receptors always excites the postsynaptic cell. |
True. |
|
|
Dual intervention of organs by the ANS refers to the observation that __________ |
Both sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons innervate most organs. |
|
|
Erection of the penis or clitoris __________ |
Is primarily under parasympathetic control. |
|
|
Sympathetic division stimulation causes __________ |
Increased blood glucose, decreased GI peristalsis, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. |
|
|
Sympathetic division fibers leave the spinal cord in the __________ |
Thoracolumbar region, and the postganglionic fibers secrete norepinephrine. |
|
|
The "resting and digesting" division of the ANS is the __________ |
Parasympathetic division. |
|
|
The ANS innervates all the following effector organs and tissues except __________ |
Skeletal muscle. |
|
|
True or false: The ANS is also known as the involuntary nervous system. |
True. |
|
|
The division of the ANS that prepares the body for intense levels of activity and stress is the __________ |
Sympathetic division. |
|
|
The parasympathetic tone __________ |
Determines normal activity of the urinary tract. |
|
|
The somatic nervous system regulates the activity of __________ |
Skeletal muscle. |
|
|
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are subdivisions of the __________ |
Autonomic nervous system. |
|
|
Two divisions of the efferent side of the peripheral nervous system are __________ |
Somatic motor neurons and autonomic neurons. |
|
|
What is a uniquely sympathetic function? |
Regulation of body temperature. |
|
|
What is true for the parasympathetic nervous system but not the sympathetic nervous system? |
Postganglionic fibers release acetylcholine. |
|
|
What does not have nicotine cholinergic receptors? |
Effector organs for the parasympathetic nervous system. |
|
|
What is a characteristic of the parasympathetic nervous system? |
Decreased heart rate. |
|
|
Which neuron of the efferent branch of the peripheral nervous system does not release acetylcholine? |
Sympathetic postganglionic neurons. |
|
|
What physiological response is associated with an elevation in parasympathetic nervous system activity? |
Enhanced absorption of nutrients. |
|
|
What physiological response is associated with elevated sympathetic nervous system activity? |
Increased contractile force of the heart. |
|
|
After brain surgery, a patient receiving post-operative care in an intensive care unit began to pass large volumes of very dilute urine. The ICU nurse administered a medicine that mimics which hormone? |
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) |
|
|
Diabetes insipidus is caused by hyposecretion of which hormone? |
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) |
|
|
Excess secretion of growth hormone during early development will cause what? |
Gigantism |
|
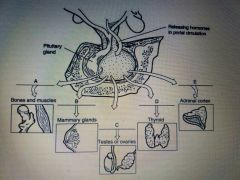
Using the figure above, match the following hypothalamic hormone with the pituitary hormone target: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) |
(C) Testes or Ovaries |
|
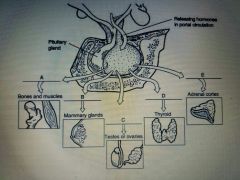
Using the figure above match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone target: Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) |
(E) Adrenal Cortex |
|
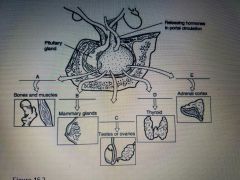
Using the figure above, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone target: Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) |
(D) Thyroid |
|

Using the figure above, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone target: Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) |
(D) Thyroid |
|
|
Hypersecretion of growth hormone after long bone growth has ended (as an adult) is called __________ |
Acromegaly |
|
|
Most endocrine organs are prodded into action by other hormones; this type of stimulus is called __________ |
Hormonal stimulus |
|
|
One of the Least Complicated of the endocrine Control Systems directly responds to changing blood levels of ions and nutrients. What kind of stimulation describes this mechanism? |
Humoral stimulation |
|
|
The hypothalamus acts as both a neural and a(n) __________ organ. |
Endocrine |
|
|
The hypothalamus controls secretion by the anterior pituitary by __________ |
Secreting releasing and inhibiting factors into a tiny portal system. |
|
|
The pituitary hormone that causes the kidney to reduce water loss is __________ |
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) |
|
|
The pituitary hormone that controls the release of glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex is __________ |
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
|
|
The pituitary hormone that stimulates cell growth and replication by accelerating protein synthesis is __________ |
Somatotropin |
|
|
The pituitary hormone that stimulates cell growth and replication by accelerating protein synthesis is __________ |
Somatotropin |
|
|
The pituitary hormone that stimulates milk production by the mammary glands is __________ |
Prolactin |
|
|
The primary function of ADH is to __________ |
Decrease the amount of water lost at the kidneys. |
|
|
Tropic hormones do what? |
Stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones. |
|
|
When hormones interact such that one does the opposite of the other they are said to be __________ |
Antagonistic |
|
|
What is not an anterior pituitary hormone? |
Antidiuretic hormone |
|
|
__________ are chemical messengers that are released in one tissue and transported in the bloodstream to alter the activities of specific cells in other tissues. |
Hormones |
|
|
A hormone that helps to regulate the sodium ion content of the body is __________ |
Aldosterone |
|
|
A hormone that promotes gluconeogenesis in the liver is __________ |
Cortisol |
|
|
A hormone that promotes gluconeogenesis in the liver is __________ |
Cortisol |
|
|
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) promotes __________ |
Vasodilation |
|
|
Cushing disease results from an excess of ___________ |
Glucocorticoids |
|
|
If a diabetic patient received too much insulin, the low blood sugar could be corrected by injecting what? |
Glucagon |
|
|
If a diabetic patient received too much insulin, the low blood sugar could be corrected by injecting what? |
Glucagon |
|
|
Increased levels of the hormone __________ will lead to increased levels of calcium ion in the blood. |
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) |
|
|
Mental and physical sluggishness and low body temperature may be signs __________ |
Hypothyroidism |
|
|
The beta cells of the pancreatic islets produce __________ |
Insulin |
|
|
The condition known as goiter can result from too little __________ in the diet. |
Iodine |
|
|
The enzyme renin is responsible for the activation of __________ |
Angiotensin |
|
|
True of false: The follicle cells of the thyroid gland produce thyroid hormones while the parafollicular cells produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). |
False |
|
|
The hormone that plays a pivotal role in setting the metallic rate and thus impacting body temperature is __________ |
Thyroxine |
|
|
The pancreatic hormone that causes blood sugar levels to fall is __________ |
Insulin |
|
|
The suprarenal medulla produces __________ |
Catecholamines |
|
|
The term used to describe excess production of urine is __________ |
Polyuria |
|
|
The zona fasciculata of the suprarenal cortex produces __________ |
Glucocorticoids |
|
|
Two little secretion of cortisol and aldosterone causes __________ |
Addison disease |
|
|
When blood glucose levels fall __________ |
Glucagon is released |
|
|
When blood glucose levels fall __________ |
Glucagon is released |
|
|
Which hormone increases production of red blood cells? |
Erythropoietin |
|
|
A boy who has not passed through puberty sustains an injury to his anterior pituitary such that FSH is no longer released, but LH is normal. After he grows to maturity one would expect that he would __________ |
Be unable to produce viable sperm. |
|
|
A low secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the normal male adult would cause__________ |
Decreased testosterone secretion |
|
|
A male bodybuilder starts taking injections of testosterone (an anabolic steroid) on a daily basis. After three weeks, what would you expect to observe? |
Decreased levels of GnRH, LH, and FSH, and an increased sex drive. |
|
|
Gametes are called haploid because __________ |
They contain one half the normal number of chromosomes. |
|
|
Gametes are called haploid because __________ |
They contain one half the normal number of chromosomes. |
|
|
Maturing sperm gain their ability to swim while in the __________ |
Epididymis |
|
|
Select the correct statement about testosterone control. 1. Inhibin an testosterone exert positive feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary. 2. The pineal gland is believed to be the gland that exerts the most influence in testosterone control. 3. GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH release from the anterior pituitary. 4. FSH stimulates testicular production of testosterone. |
GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH released from the anterior pituitary. |
|
|
Sperm production occurs in the __________ |
Seminiferous tubules |
|
|
Spermiogenesis involves the __________ |
Formation of a functional sperm by the stripping away of Superfluous cytoplasm movement of sperm in the female genital tract. |
|
|
The area of the sperm with densely packed chromosomes is the __________ |
Head |
|
|
The cells that produce testosterone in the testes are called __________ |
Interstitial endocrine cells |
|
|
The correct descending order of the male duct system from inside to outside is __________ |
Epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra |
|
|
The small paired glands at the base of the penis that producer lubricating secretion are the ___________ |
Bulbourethral glands |
|
|
The testicular cells that construct the blood-testis barrier are the __________ |
Sustenocytes (sustentacular cells) |
|
|
Thick, clear mucus that cleanses the urethra of acidic urine is produced by the __________ |
Bulbourethral glands |
|
|
Which male hormone inhibits the secretion of FSH? |
Inhibin |
|
|
Which of the choices below is not a part of the hypothalamic-pituitary gonadal-axis? 1. Thalamus 2. Hypothalamus 3. Interstitial cells 4. Anterior pituitary gland |
Thalamus |
|
|
Which of the choices below is not a part of the hypothalamic-pituitary gonadal-axis?
1. Thalamus
2. Hypothalamus
3. Interstitial cells
4. Anterior pituitary gland |
Thalamus |
|
|
Which of the following glands are responsible for 70% of the synthesis of semen?
1. The seminal vesicles
2. The pituitary
3. The prostate
4. The bulbourethral glands |
The seminal vesicles |
|
|
Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? 1. GnRH 2. FSH 3. LH 4. Testosterone |
GnRH |
|
|
Which of the following statements about spermatogenesis is not true? 1. The secondary spermatocytes each form two spermatids. 2. The primary spermatocyte forms two secondary spermatocytes. 3. The spermatogonium forms the primary spermatocyte. 4. Each spermatid forms two sperm. |
Each spermatid forms two sperm. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about spermatogenesis is not true? 1. The secondary spermatocytes each form two spermatids. 2. The primary spermatocyte forms two secondary spermatocytes. 3. The spermatogonium forms the primary spermatocyte. 4. Each spermatid forms two sperm. |
Each spermatid forms two sperm. |
|
|
Why is the blood-testis barrier important? |
Because spermatozoa and developing cells produce surface antigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system, because some blood contents are toxic to the spermatozoa. |
|
|
During oogenesis, an oogonium directly gives rise to __________ |
A primary oocyte. |
|
|
During the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle, progesterone is __________ estrogen. 1. Greater than 2. Less than |
Greater than. |
|
|
During the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle, progesterone is __________ estrogen. 1. Greater than 2. Less than |
Greater than. |
|
|
If the ovaries are removed from an otherwise healthy 20-year-old female, which of the following would you expect to see? 1. Increased blood levels of GnRH. 2. Increased blood levels of FSH. 3. Increased blood levels of LH. 4. Cessation of menstruation. 5. All of these observations. |
All of these observations. |
|
|
In the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the ovary is __________ |
Maturing a follicle. |
|
|
In the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the ovary is __________ |
Maturing a follicle. |
|
|
In the late follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, LH is __________ FSH. 1. Greater than 2. Less than |
Greater than |
|
|
In the late follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, LH is __________ FSH. 1. Greater than 2. Less than |
Greater than |
|
|
True or false: Ovulation occurs at the end of the ovarian cycle. |
False. |
|
|
True or false: Pain during ovulation is called dysmenorrhea. |
False. |
|
|
Sally is an avid jogger and she trains incessantly. She has slimmed down so that she is now underweight for her height and has very little fat tissue. You would expect Sally to be __________ |
Amenorrhetic. |
|
|
The basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis is that __________ |
In oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis, four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell. |
|
|
The cervix is __________ |
The neck of the uterus. |
|
|
The cervix is __________ |
The neck of the uterus. |
|
|
The corpus luteum is a special glandular structure of the ovaries that primarily produces __________ |
Progesterone. |
|
|
True or false: The corpus luteum secretes progesterone only. |
False. |
|
|
The first menstrual period, which usually occurs at approximately age 13, is called __________ |
Menarche. |
|
|
The inner mucosal layer of the uterus that is sloughed off approximately every 28 days is called the __________ |
Endometrium. |
|
|
The journey of the oocyte through the uterine tubes to the uterus following ovulation normally takes __________ |
1 week. |
|
|
The surge in LH that occurs during the middle of the ovarian cycle triggers __________ |
Ovulation. |
|
|
True or false: When a woman is not pregnant, the endometrial lining of the uterus is sloughed off about every 28 days. |
True. |
|
|
Which hormone is absolutely necessary for ovulation to occur? |
Luteinizing hormone (LH) |
|
|
Which hormone controls the release of the anterior pituitary gonadotropins? |
GnRH |
|
|
What occurs during days 15-28 of the menstrual cycle? |
The secretory phase. |

