![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Benedict's solution
|
test that indicates the absence of starch (presence of simple sugars); blue changes to yellow/red/orange
|
|
|
Lugol's iodine
|
test that indicates presence of starch; dark purple
|
|
|
Litmus cream
|
dairy cream used as a pH indicator; pink = acidic and blue = alkaline
|
|
|
Exp. 3: Fat & Lipid Digestion
Which tube was most acidic, as indicated by its color? |
Tube #2
|
|
|
Exp. 3: Fat & Lipid Digestion
Which tube showed the most digestion? Why? |
Tube #2 because bile salts were added.
|
|
|
Exp. 3: Fat & Lipid Digestion
Where did the acid come from as the fat was digested? |
The breakdown of a triglyceride is a glycerol + fatty acid. <=== FATTY ACID!
|
|
|
Why are the tubes incubated at 37 degrees Centigrade?
|
They are incubated at this temperature to mimic the core body temperature of a normal. healthy adult.
|
|
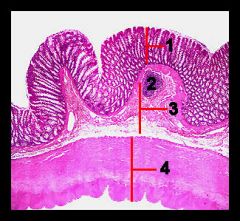
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Colon
|
|
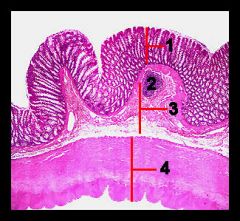
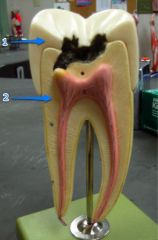
#1
|
Mucosa
|
|
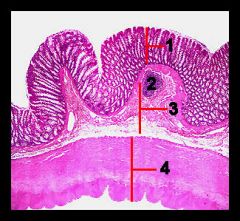
#2
|
Lymphoid nodule
|
|
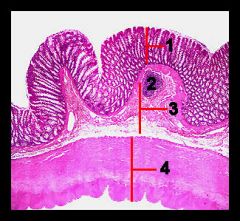
#3
|
Submucosa
|
|
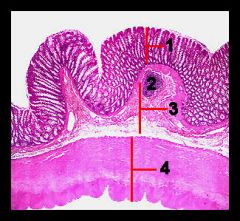
#4
|
Muscularis externa and serosa
|
|
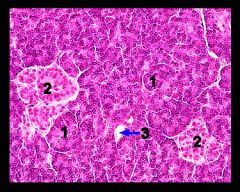
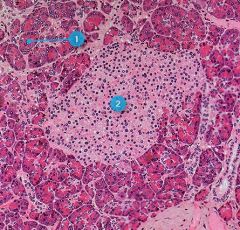
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Pancreas
Tip: Circles (acini) surrounding big circle (islet) |
|
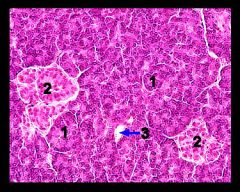
#1
|
Pancreatic acini
|
|
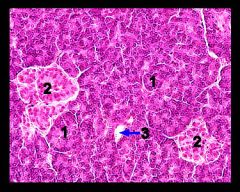
#2
|
Pancreatic islets
|
|
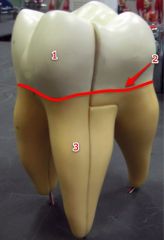
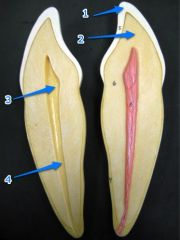
#1
|
Crown
|
|
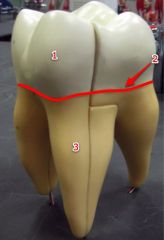
#2
|
Neck
|
|
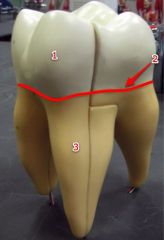
#3
|
Root
|
|
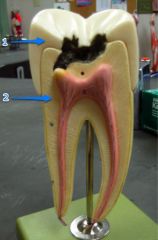
#1
|
Enamel
|
|
#2
|
Dentin
|
|
#3
|
Pulp cavity
|
|
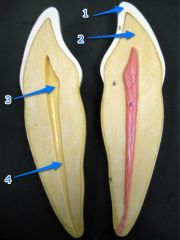
#4
|
Root canal
|
|
#1
|
Pancreatic acini
|
|
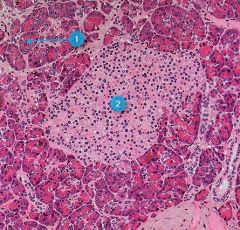
#2
|
Pancreatic islet
|
|
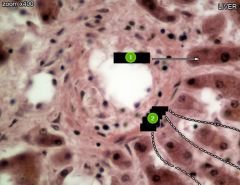
#1
|
Hepatocytes
|
|
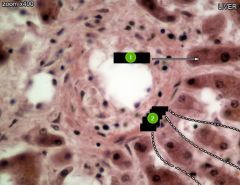
#2
|
Sinusoids
|
|
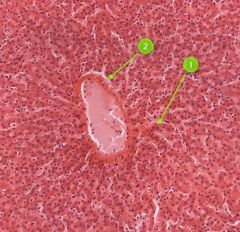
#1
|
Sinusoids
|
|
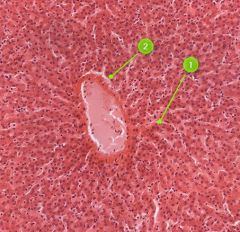
#2
|
Hepatocytes
|
|
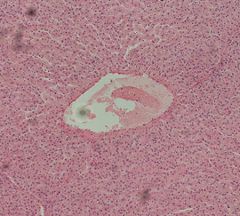
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Liver
Tip: Freckled (nuclei); Squiggles (sinusoids) coming out of white mass (central vein) |
|
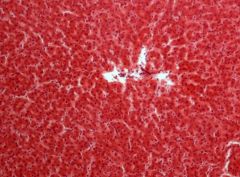
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Liver
|
|
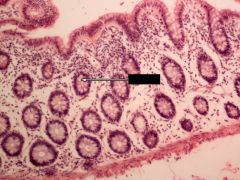
Identify this digestive structure.
Note: Empty goblet cells |
Large intestine (colon)
|
|
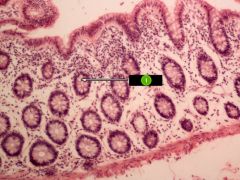
#1
|
Goblet cell
|
|
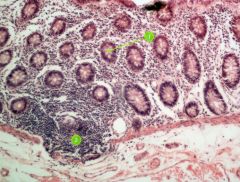
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Large intestine (colon)
|
|
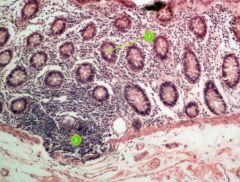
#1
|
Goblet cell
|
|
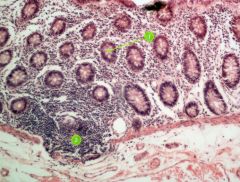
#2
|
Lymphoid nodule
|
|
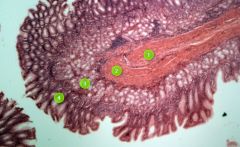
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Small intestine
Note: Presence of villi. |
|
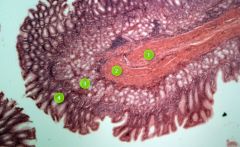
Identify layer #1.
|
Serosa
|
|
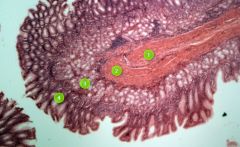
Identify layer #2.
|
Muscularis
|
|
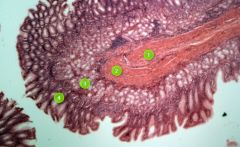
Identify layer #3.
|
Submucosa
|
|
Identify layer #4.
|
Mucosa
|
|
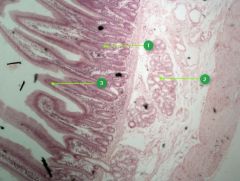
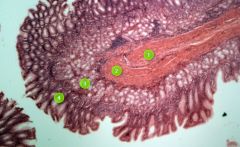
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Small intestine
Tip: Spikes (villi) |
|
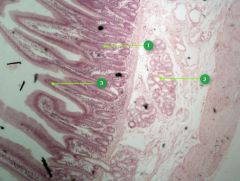
#1
|
Intestinal glands
Note: Beneath villi |
|
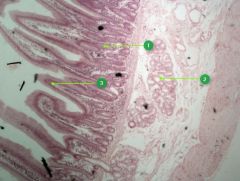
#2
|
Duodenal glands
Note: Cluster of empty-looking cells |
|
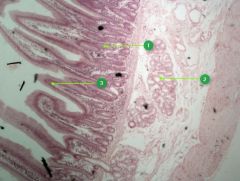
#3
|
Villi
Note: May look like fingers or circles |
|
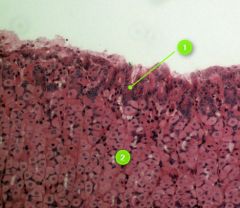
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Stomach
Tip: Stacked nuclei (rugae) |
|
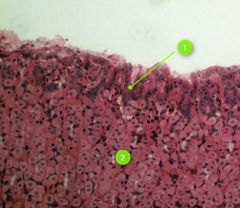
#1
|
Gastric pits
Note: Lie on top of rugae |
|
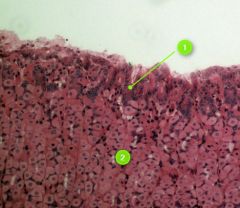
#2
|
Rugae
Tip: Stacked up nuclei |
|
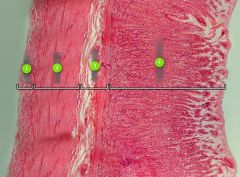
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Stomach
Note: Stacked rugae in layer #4 |
|
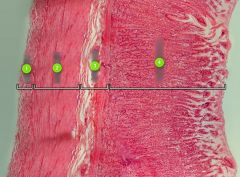
Identify layer #1.
|
Serosa
|
|
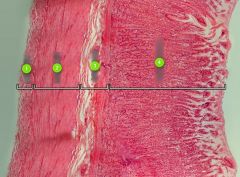
Identify layer #2.
|
Muscularis
Note: Striated muscle fibers |
|
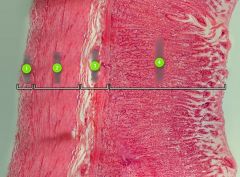
Identify layer #3.
|
Submucosa
|
|
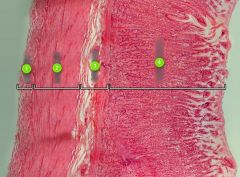
Identify layer #4.
|
Mucosa
|
|
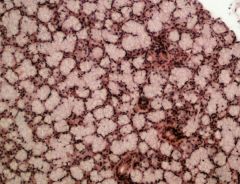
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Salivary glands
Tip: Spotted animal skin; usually mistaken for pancreas |
|
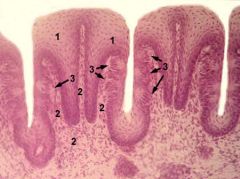
#3
Image © A Gunin, 2000-09 |
Taste buds
|
|
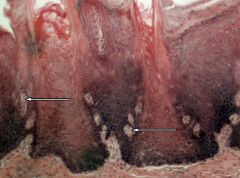
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Taste buds
Note: Oval-shaped; along sides of papillae |
|
|
pepsin
|
proteolytic enzyme secreted in the stomach as its inactive form pepsinogen
|
|
|
Exp. 1: Protein Digestion by Pepsin
Which tube digested the most protein and why? |
Tube #2 because HCl activates pepsin and it had the optimal pH for protein digestion.
|
|
|
Exp. 2: Digestion of Carbs
What is the resulting color after adding Lugol's iodine in a test tube of starch solution? What does this tell us? |
Dark purple
This tells us starch is present. |
|
|
salivary amylase
|
enzyme secreted by the salivary glands that begins the breakdown of complex sugars and starches in the oral cavity
|
|
|
Exp. 2: Digestion of Carbs
What is the resulting color after saliva/starch mix was added with Lugol's iodine? Why is this color different than before? |
Yellow
Salivary amylase (in the saliva) broke down the starch and now starch is no longer detected. |
|
|
Exp. 2: Digestion of Carbs
What is the final color... in the control? In the digested tube? Does this demonstrate the presence of sugar in digested tube? |
Control = Dark pink
Digested = Green Yes |
|
|
Exp. 2: Digestion of Carbs
What happened to starch during water bath, at 37 degrees Centigrade, in terms of enzymatic activity? |
Polysaccharides turned into monosaccharides via salivary amylase.
|
|
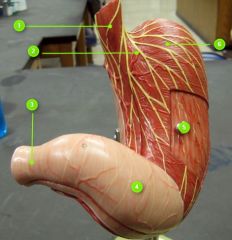
#1
|
Lower esophageal sphincter
|
|
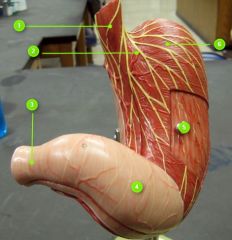
#2
|
Cardia
|
|
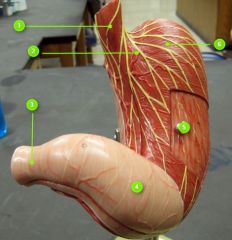
#3
|
Pyloric sphincter
|
|
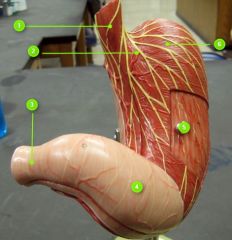
#4
|
Pyloric antrum
|
|
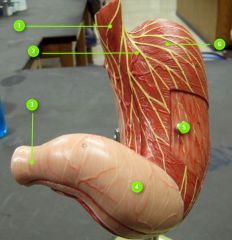
#5
|
Body
|
|
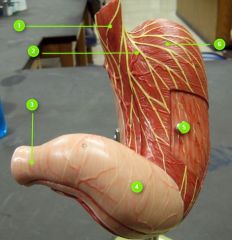
#6
|
Fundus
|
|
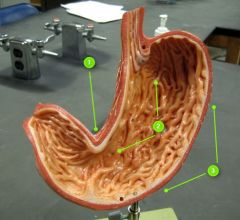
#1
|
Lesser curvature
|
|
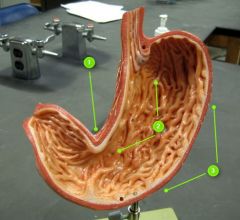
#2
|
Rugae
|
|
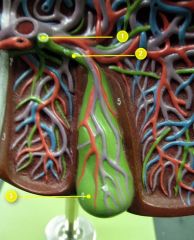
#1
|
Common bile duct
|
|
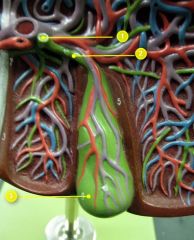
#2
|
Cystic duct
|
|
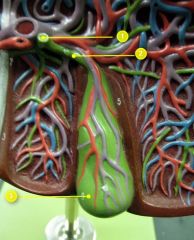
#3
|
Gallbladder
|
|
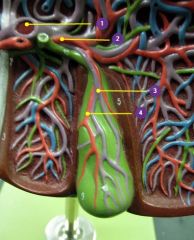
#1
|
Hepatic portal vein
|
|
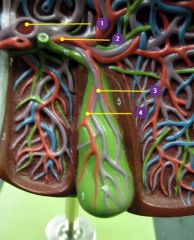
#2
|
Right hepatic a.
|
|
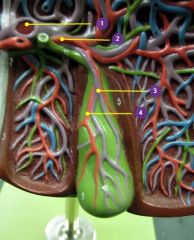
#3
|
Cystic v.
|
|
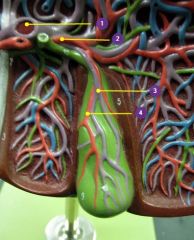
#4
|
Cystic a.
|
|

#1
|
Hepatic v.
|
|

#2
|
Left hepatic a.
|
|

#3
|
Left hepatic duct
|
|
|
Is your gallbladder on the left or right side of the body?
|
Right side of the body
|
|
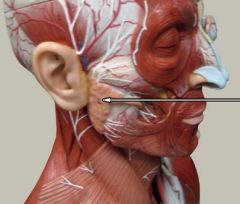
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Parotid gland
|
|
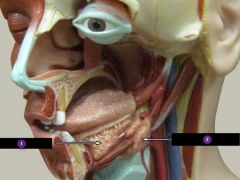
#1
|
Sublingual salivary gland
Note: Beneath the tongue |
|
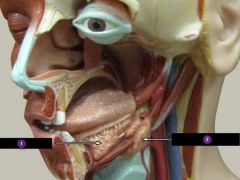
#2
|
Submandibular salivary gland
Note: Beneath the jaw |
|
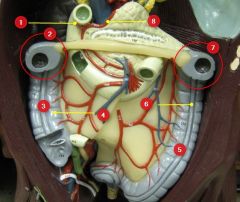
#1
|
Gastroepiploic a.
Note: Will follow along great curvature of stomach |
|
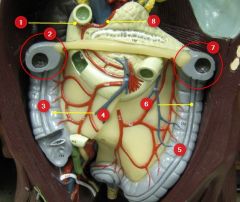
#2
|
Hepatic flexure
Note: Right side of the body |
|
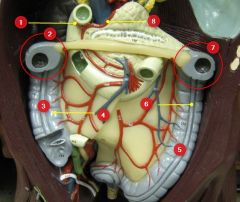
#3
|
Ascending colon
|
|
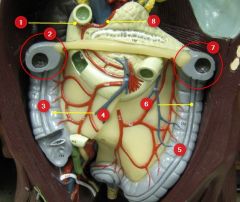
#3
|
Ascending colon
|
|
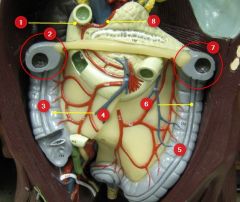
#4
|
Haustra
|
|
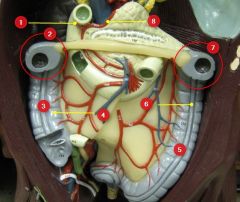
#5
|
Descending colon
|
|
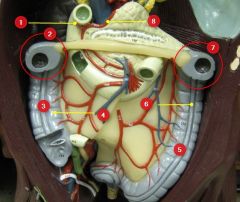
#6
|
Taenia coli
|
|
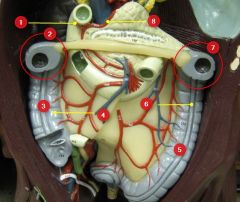
#7
|
Splenic flexure
Note: Left side, near spleen |
|
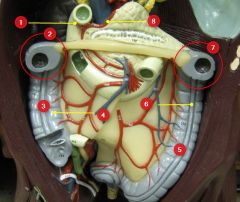
#8
|
Gastroduodenal a.
|
|
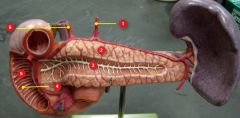
#1
|
Left gastric a.
|
|
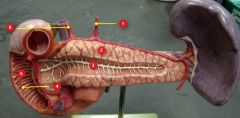
#2
|
Pancreas
|
|
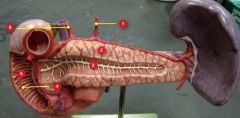
#3
|
Pancreatic duct
|
|
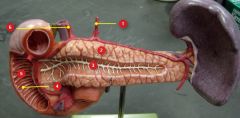
#4
|
Major duodenal papillae
|
|
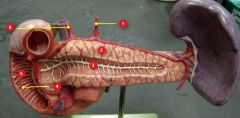
#5
|
Duodenum (of small intestine)
|
|
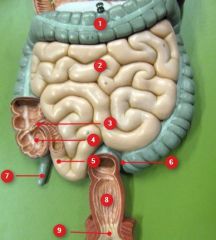
#1
|
Transverse colon
|
|
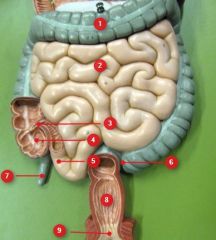
#2
|
Jejunum
|
|
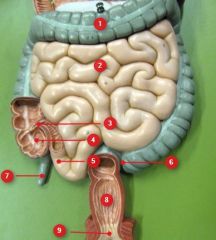
#3
|
Ileocecal valve
|
|
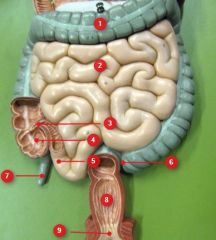
#4
|
Cecum
|
|
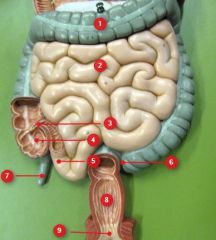
#5
|
Ileum
|
|
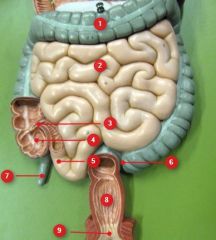
#6
|
Sigmoid colon
|
|
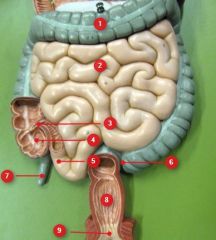
#7
|
Vermiform appendix
|
|
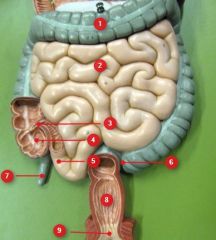
#8
|
Rectum
|
|
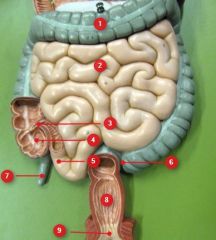
#9
|
Anal canal
|
|
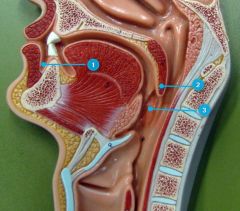
#1
|
Vestibule
|
|
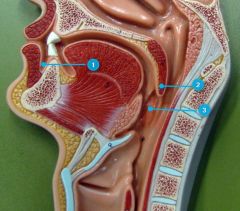
#2
|
Uvula
Note: Comes after soft palate |
|
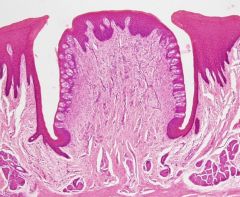
Identify this digestive structure.
|
Taste buds
|
|
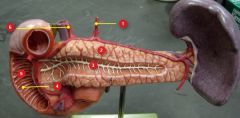
#6
|
Proper hepatic a.
|

