![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
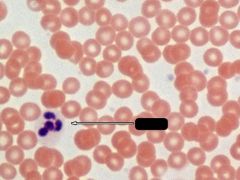
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Neutrophil
Note: Multilobed nucleus, slightly larger than RBC |
|
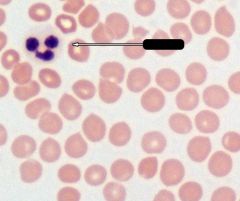
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Neutrophil
Note: Multilobed nucleus, slightly larger than RBC |
|
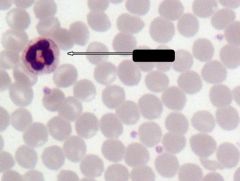
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Neutrophil
Note: Multilobed nucleus, slightly larger than RBC |
|
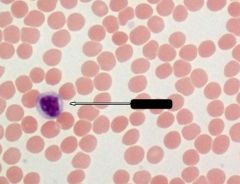
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Lymphocyte
Note: Round nucleus, very slightly visible cytoplasm |
|
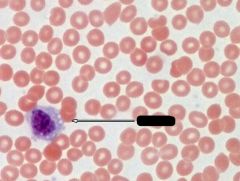
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Monocyte
Note: Large, 2x size of RBC |
|
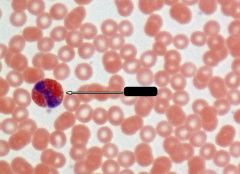
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Eosinophil
Note: Only WBC with red cytoplasm |
|
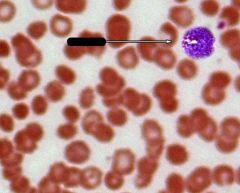
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Basophil
|
|
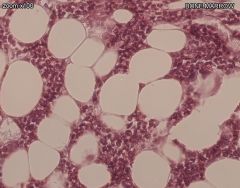
What is shown here?
|
Bone marrow
|
|
|
What are the 3 granulocytes?
|
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
|
|
|
What are the 2 agranulocytes?
|
Lymphocytes and monocytes
|
|
|
What is the microscope with specially ruled chamber used to measure RBC
|
Hemocytometer
|
|
|
When does your WBC count increase?
|
It increases when your body has been invaded by disease-producing microorganisms.
|
|
|
differential count
|
percentage of each type of leukocyte (blood smear test)
|
|
|
What kind of bone marrow produces the formed elements?
|
Red bone marrow
|
|
|
Which bone marrow is mostly fat?
|
Yellow bone marrow
|
|
|
What is the normal range of hematocrit in infants?
|
44-62%
|
|
|
What is the normal range of hematocrit in children?
|
35-47%
|
|
|
What is the normal range of hematocrit in adult males?
|
40-50%
|
|
|
What is the normal range of hematocrit in adult females?
|
36-45%
|
|
|
What are agglutinogens?
|
Genetically determined antigens
|
|
|
What are agglutinins?
|
Antibodies that react with antigens.
|
|
|
If there is an antigen-antibody reaction, what occurs?
|
Agglutination
|
|
|
What is agglutination?
|
The clumping together of RBCs after an antigen-antibody reaction.
|
|
|
What is the hematocrit average in the class for males?
|
47
|
|
|
What is the hematocrit average in the class for the females?
|
50
|
|
|
What is the class average for neutrophils?
|
58
|
|
|
What is the class average for basophils?
|
4
|
|
|
What is the class average for eosinophils?
|
5
|
|
|
What is the class average for lymphocytes?
|
25
|
|
|
What is the class average for monocytes?
|
6
|
|
|
Out of a sample, what is the normal % range of the following cell:
Neutrophils |
60-70 %
|
|
|
Out of a sample, what is the normal % range of the following cell:
Lymphocytes |
25-30 %
|
|
|
Out of a sample, what is the normal % range of the following cell:
Monocytes |
3-8 %
|
|
|
Out of a sample, what is the normal % range of the following cell:
Eosinophils |
2-4 %
|
|
|
Out of a sample, what is the normal % range of the following cell:
Basophils |
0.5-1 %
|
|
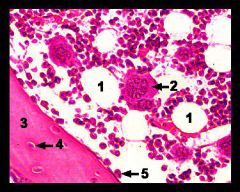
What slide is shown here?
|
Red bone marrow
Tip: Psychedelic |
|
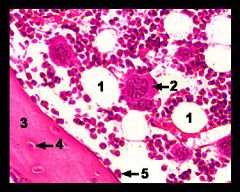
#1
|
Adipose cell
|
|
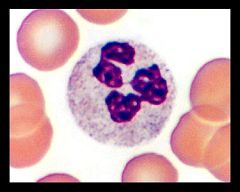
Name the WBC.
|
Neutrophil
|
|
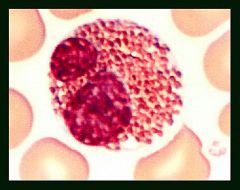
Name the WBC.
|
Eosinophil
|
|
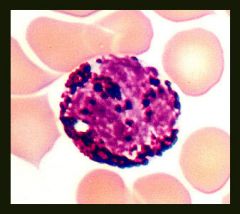
Name the WBC.
|
Basophil
|
|
|
Blood Typing |
|
|
|
Differential WBC Count |
|
|
|
Hematocrit |
|
|
|
The Hematocrit |
=(red cell column/total blood column) X 100 |
|
|
Eosinophils |
increase in severe allergic reaction |
|
|
Monocytes |
increase during long, chronic, infectious illnesses |
|
|
Nuetrophils |
increase during acute inflammation, infectious diseases, or tissue damage |
|
|
Heme |
A pigment combined with GLOBIN to for hemoglobin |
|
|
Globin |
a protein combined with heme to form hemoglobin |
|
|
Hemoglobin |
a substance that loosely combines with large amounts of O2 and smaller amounts of CO2 |
|
|
erythrocytes |
RBC responsible for transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. No nucleus |

