![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy of Blood Vessels
|
*Arteries carry blood away from heart
*Veins carry blood back to heart *Capillaries connect smallest arteries to veins |
|
|
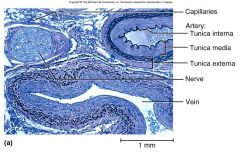
Vessel Wall
|
Tunica interna (intima)
*smooth inner layer that *repels blood cells and platelets *simple squamous endothelium overlying a basement membrane and layer of fibrous tissue Tunica media *middle layer *usually thickest; smooth muscle, collagen, some elastic smooth muscle for vasomotion Tunica externa (tunica adventitia) outermost layer loose connective tissue with vasa vasorum |
|
|
Tunica interna
|
(intima)of Vessel Wall
*smooth inner layer that *repels blood cells and platelets *simple squamous endothelium overlying a basement membrane and layer of fibrous tissue |
|
|
Tunica media
|
layer of vessel wall
*middle layer *usually thickest; smooth muscle, collagen, some elastic smooth muscle for vasomotion |
|
|
Tunica externa
|
Third layer of vessel wall(tunica adventitia)
outermost layer loose connective tissue with vasa vasorum |
|
|
Large Vessels
|
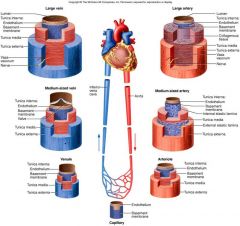
Large Vein
Medium sized vein venule Large Artery Medium sized argery Arteriole |
|
|
Control of Capillary Bed Perfusion
|
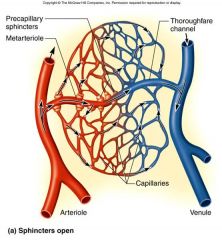
Sphincters Open and Close
|
|
|
Types of Capillaries
|
Continuous - occur in most tissues
*endothelial cells have tight junctions with intercellular clefts (allow passage of solutes) Fenestrated - kidneys, small intestine *organs that require rapid absorption or filtration *filtration pores – spanned by very thin glycoprotein layer - allows passage of only small molecules Sinusoids - liver, bone marrow, spleen *irregular blood-filled spaces; some have extra large fenestrations, allow proteins and blood cells to enter |
|
|
Continuous
|
Continuous - occur in most tissues
*endothelial cells have tight junctions with intercellular clefts (allow passage of solutes) |
|
|
Fenestrated
|
Fenestrated - kidneys, small intestine
*organs that require rapid absorption or filtration *filtration pores – spanned by very thin glycoprotein layer - allows passage of only small molecules |
|
|
Sinusoids
|
Sinusoids - liver, bone marrow, spleen
*irregular blood-filled spaces; some have extra large fenestrations, allow proteins and blood cells to enter |
|
|
Fenestrated Capillary
|
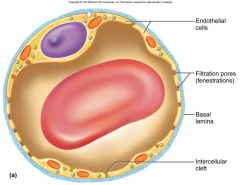
Fenestrated Capillary
|
|
|
Sinusoid in Liver
|
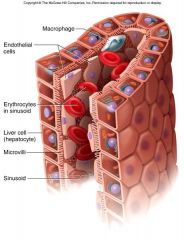
Sinusoid in Liver
|
|
|
Veins
|
lower blood pressure: 10mmHg with little fluctuation
thinner walls, less muscular and elastic tissue expand easily, have high capacitance valves aid skeletal muscles in upward blood flow |
|
|
Venules
|
postcapillary venules more porous than capillaries
muscular venules have tunica media |
|
|
Venous sinuses
|
veins with thin walls, large lumens, no smooth muscle
|
|
|
Blood Distribution
|
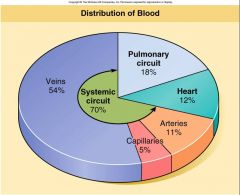
Resting Adult
|
|
|
Blood Pressure
|
Force that blood exerts against a vessel wall
Measured at brachial artery of arm Systolic pressure: BP during ventricular systole Diastolic pressure: BP during ventricular diastole Normal value, young adult: 120/75 mm Hg Pulse pressure: systolic - diastolic *important measure of stress exerted on small arteries |
|
|
Abnormalities of Blood Pressure
|
Hypertension
*chronic resting BP > 140/90 *consequences **can weaken small arteries and cause aneurysms Hypotension *chronic low resting BP *caused by blood loss, dehydration, anemia |
|
|
Peripheral Resistance
|
Blood viscosity - by RBC’s and albumin
*decrease in viscosity with anemia, hypoproteinemia *Increase in viscosity with dehydration Vessel length pressure and flow decrease with distance (friction) Vessel radius - very powerful influence over flow *most adjustable variable, controls resistance quickly *vasomotion: change in vessel radius **vasoconstriction, vasodilation |
|
|
vasomotion
|
change in vessel radius
**vasoconstriction, vasodilation |

