![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Get it? |
Got it? |
|
|
Stores water waste and other substances inside a cell |
Vacuole |
|
|
Infection fighting blood cell |
White blood cells |
|
|
Large molecules that carry genetic information |
Dna |
|
|
A random change in cells genetic information |
Mutation |
|
|
Blood cell that aids in clotting |
platelets |
|
|
Supports the cells and allows some substances to move in and out of the cell |
organelle |
|
|
The adjustment knob that is not used with medium or high power Objective lens |
Coarse adjustment knob |
|
|
An environmental factor that causes cancer |
Carcinogens |
|
|
Division of cells cytoplasm and organelles |
Cytokinesis |
|
|
Transports oxygen and nutrients and waste hormones and other substances to and from all cells in the body |
Circulatory system |
|
|
Tissue composed of living cells and nonliving materials that support protect and connect the bodies organs |
Connective tissue |
|
|
The part of the cell cycle when the chromosomes are pulled towards the opposite side of the cell |
Anaphase |
|
|
Division of the nucleus |
Mitosis |
|
|
The name of the new cell once a cell divides |
Daughter cells |
|
|
The part of the cell cycle that includes growth of the cell and preparation for division |
Interphase |
|
|
Carries blood cells away from the heart under pressure |
veins |
|
|
Tissue made of cells that shorten or contract to allow movement |
Muscle tissue tissue |
|
|
Protects internal structure and supports the body and allows body to move |
Musculoskeletal system |
|
|
Allows the exchange of gases nutrients and waste between the body and the body tissue |
Capillaries |
|
|
Takes an oxygen from the air and remove carbon dioxide from the body |
Respiratory system |
|
|
Carries blood towards the heart under low-pressure |
Arteries |
|
|
Tissue that covers surfaces and lines internal organs |
Epithelial tissue |
|
|
When a greater than usual number of people in the area become ill |
Pandemic |
|
|
What happens during telophase |
The chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell |
|
|
Which blood component is responsible for blood clotting |
Platelets |
|
|
Which organelle contains the cells DNA |
Nucleus |
|
|
Which type of cell can divide many times without specializing |
Stem |
|
|
Which organ system works together to remove carbon dioxide from the body |
Respiratory system and circulatory system |
|
|
The final stage of cell division when the cytoplasm divides is known as... |
cytokinesis |
|
|
Which organ are cardiac muscles found |
Heart |
|
|
What does epithelial tissue do |
To support protect and connect the bodies organs |
|
|
Name three respiratory diseases |
Emphysema Influenza Tuberculosis |
|
|
Describe the function of a red blood cell and nerve cell |
Red blood cell: transports oxygen and will 1o2 Nerves: Feels! |
|
|
Briefly describe the faces of mitosis |
1 cell to two cells |
|
|
Where is the cells genetic information found |
DNA in the nucleus |
|
|
How many chromosomes do we have in the DNA |
22 |
|
|
What happens if the DNA does not copy before dividing |
Cells become confused since they dont have any instructions |
|
|
List three reasons why cells divide |
1. To pass down information 2. Replace old ones 3. Heal wounds/fight diseases |
|
|
Difference between asexual for reproduction and sexual reproduction |
Asexual equal one Sexual equal two |
|
|
List three stages of cell cycle (four if you can) |
Prophase metaphase anaphase telophase |
|
|
Example of a cell that lives for a day and an example of a cell that would last year |
Day: skin cells, replace them self when new ones are needed an example would be a cut A year: White blood cell, inside only needed one sick |
|
|
Why are carcinogens harmful to cells. Provide an example of a carcinogen |
They increase risk of cancer ( damaged dna in cell) Example: gamma rays |
|
|
One known cause of cancer is radiation. Describe the effect of radiation on chromosomes and how this can result in a tumor |
Changes letter in DNA - in rare case, area gets really messed up = tumor |
|
|
Name three organ systems and their functions |
Respiratory system = breathing cardiovascular system = heart digestive system =food |
|
|
What are two types of medical technology for each describe how they form an image and what scenario they be useful in. |
Cat scan: like an x-ray but for organs and tissues. Rays bounce of the organs not the bones M.R.I: uses magnetic radio frequencies (knocks protons out of alignment) |
|
|
Describe how the respiratory ,digestive and circulatory system works together together to provide ourselves with essential materials. |
Respiratory gets oxygen Digestive gets nutrients Circulatory moves the two and gets rid of the bad stuff (an example carbon dioxide and the ****) |
|
|
Two organ features that fish have that we don't |
Gills: instead of lungs Two chambers for hearts (one circuit): instead of four Chambers (two circuits) |
|
|
For the respiratory system provide two diseases or health concerns and list the causes symptoms and ways of prevention (if not genetic) |
Asthma: shortness of breath, trachea not completely clear, it's genetic so can't be avoided Lung cancer: shortness of breath, smoking, avoid smoke |
|
|
For the cardiovascular system provide two diseases or health concerns and list the causes symptoms and ways of prevention (if not genetic) |
Heart tremor: heart tremors, Difficulty breathing when lying flat or when, genetics and not avoided so unavoidable Heart cancer: chest pain, cause unknow |
|
|
For the digestive provide two diseases or health concerns and list the causes symptoms and ways of prevention (if not genetic) |
Hepatitis B: cause unprotected sex , symptom fever Liver cancer: symptom loss of appetite, cause high cholesterol |
|
|
What muscle causes the heart to beat |
Cardiac |
|
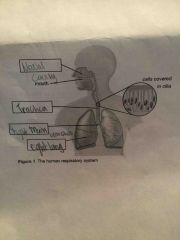
Front (Term) |
Memorized? |
|
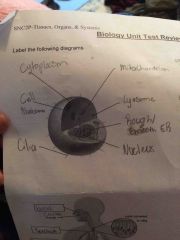
Front (Term) |
Memorized? |
|
|
List the biological levels of organization in order and provide an example for each |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Four types of tissue |
Nervous tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue |
|
|
Four types of tissue |
Nervous tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue |
|
|
Where is nervous tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: tells brain when lungs are full Circulatory system: tells brain when cut Digestive system: tells brain when stomach upset |
|
|
Four types of tissue |
Nervous tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue |
|
|
Where is nervous tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: tells brain when lungs are full Circulatory system: tells brain when cut Digestive system: tells brain when stomach upset |
|
|
Where is muscle tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: to extract lungs Circulatory system: contracts the heart and moves blood Digestive system: moves food along |
|
|
Four types of tissue |
Nervous tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue |
|
|
Where is nervous tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: tells brain when lungs are full Circulatory system: tells brain when cut Digestive system: tells brain when stomach upset |
|
|
Where is muscle tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: to extract lungs Circulatory system: contracts the heart and moves blood Digestive system: moves food along |
|
|
Where is connective tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system protects lungs with rib cage Circulatory system protects circuits i.e. veins digestive system protects intestines |
|
|
Four types of tissue |
Nervous tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue |
|
|
Where is nervous tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: tells brain when lungs are full Circulatory system: tells brain when cut Digestive system: tells brain when stomach upset |
|
|
Where is muscle tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system: to extract lungs Circulatory system: contracts the heart and moves blood Digestive system: moves food along |
|
|
Where is connective tissue found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system protects lungs with rib cage Circulatory system protects circuits i.e. veins digestive system protects intestines |
|
|
Where is Epithelial system found in the respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system |
Respiratory system prevents infections in lungs circulatory system prevents infections in cuts digestive system prevent stomach infection |

