![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Declaration of Independence
|
The document approved by representatives of the American colonies in 1776 that stated their grievances against the British monarch and declared their independence.
|
|
|
Articles of Confederation
|
The first constitution of the United STates, adopted by congress in 1777 and enacted in 1781. The ARticles established a national legislature, the Continental Congress, but most authority rested with the state legislatures.
|
|
|
U.S. Constitution
|
The document written in 1787 and ratified in 1788 that set forth the institutional structure of U.S. government and the tasks these institutions perform. It replaced the Articles of Confederation.
|
|
|
factions
|
Interest groups arising from the unequal distribution of property or wealth that James MAdison attacked in Federalist Paper #10. Today's parties or interest groups are what Madison had in mind when he warned of the instability in government caused by factions.
|
|
|
New Jersey Plan (Senate)
|
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for equal representation of each state in Congress regardless of the state's population.
|
|
|
Virginia Plan (House of Reps)
|
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for representation of each state in Congress in proportion to that state's share of the U.S. population.
|
|
|
Connecticut Compromise (Bicameral)
|
The compromise reached at the Constitutional Convention that established two houses of Congress: the House of Representatives, in which representation is based on a a state's share of the U.S. population, and the Senate, in which each state was two representatives.
|
|
|
Separation of Powers
|
A feature of the Constitution that requires each of the three branches of government - executive, legislative, and judicial - to be relatively independent of the others so that one cannot control the others. Power is shared among these three institutions.
|
|
|
Checks and Balances
|
Features of the Constitution that limit a government's power by requiring that power be balanced among the different governmental institutions. These institutions continually check one another's activities. This system reflects Madison's goal of settling power against power.
|
|
|
Republic
|
A form of government in which the people select representatives to govern them and make laws.
|
|
|
Federalists
|
Supporters of the U.S. Constitution at the time the states were contemplating its adoption.
|
|
|
Anti-Federalists
|
Opponents of the American Constitution at the time when the states were contemplating its adoption. What did they want?
|
|
|
Federalist Papers
|
A collection of 85 articles written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison under the name "Publius" to defend the Constitution in detail.
|
|
|
Bill of Rights
|
The first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution, drafted in response to some of the Anti-Federalist concerns. These amendments define such basic liberties as freedom of religion, speech, and press and guarantee defendants' rights.
|
|
|
Direct Democracy |
A democracy in which the power to govern lies directly in the hands of the people rather than being exercised through their representatives. |
|
|
Factions |
(Federalist #10) a small, organized, dissenting group within a larger one, especially in politics. |
|
|
3/5's Compromise |
Representatives and direct Taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective Numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three fifths of all other Persons. |
|
|
madisonian model |
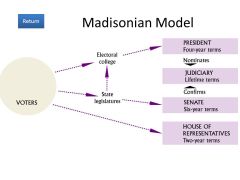
Federalist #10 |
|
|
unitary system |
The central government is supreme, and the administrative divisions exercise only powers that the central government has delegated to them. |
|
|
confederal system |
A political system in which states or regional governments retain ultimate authority except for those powers that they expressly delegate to a central government. |
|
|
federal system |
A system in which sovereignty is shared so that on some matters the national government is supreme and on others the state, regional, or provincial governments are supreme. |
|
|
Federalist #10 |
Theme? Purpose? |
|
|
Federalist #51 |
Theme? Purpose? |

