![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 tunic in vein |
Tunic intima, tunic media, tunic externa |
|
|
What transports blood TO the heart |
Veins |
|
|
What transfers blood AWAY from the heart |
Arteries |
|
|
What is endothelium? |
Lining of tissues |
|
|
What is lumen |
Diameter of inside vessel. |
|
|
3 groups of arteries |
Elastic , muscular, arterioles |
|
|
Another name for elastic arteries |
Conducting |
|
|
Another name for muscular arteries |
Distributing |
|
|
Another name for arterioles |
Resistant vessels |
|
|
What does a cappilary do? |
Exchange 02, nutrients, waste |
|
|
What holds endothelial cells together |
Pericyte |
|
|
3 types of cappilaries |
Continuous(most common),finistrated, sinusoidal (leakiest) |
|
|
What allows wbc to leave circulation |
venules |
|
|
Percent of blood supply in veins? |
65 |
|
|
What do venous valves do |
Prevent backflow |
|
|
What is vascular anastomes |
Connecting of extra vessels |
|
|
Main artery to feed brain? |
Internal |
|
|
What is volume of blood through vessel |
Blood flow |
|
|
How much blood flow per minute? |
5L |
|
|
What contributes to blood flow resistance? |
Viscosity, blood vessel length, and blood vessel diameter |
|
|
What is atherosclerosis |
Plaquing of artery |
|
|
What is arteriosclerosis |
Hardening of artery |
|
|
What is pulse pressure |
Systolic-distolic |
|
|
Map formula |
Distolic+pulse pressure/3 |
|
|
What is blood pressure in cappilary |
35 |
|
|
What is BP I'm vena cava |
17 |
|
|
Hypertension without any underlying cause |
Primary |
|
|
Hypertension with identifying conditions |
Secondary |
|
|
What is tissue perfusion |
Blood flow through tissue |
|
|
What controls local vasodialtion |
Nitric Oxide |
|
|
What happens when MAP falls below 60 and goes above 160 |
Syncope / fainting |
|
|
What is hydrostatic pressure |
Forces fluids througj cappilary walls |
|
|
What is colloid osmotic pressure |
Pulls fluid into cappilary |
|
|
3 types of circulatory shock |
Hypovolemic, vascular, cardiogenic |
|
|
Most common type of circulatory shock |
Hypovolemic |
|
|
Artery that feeds lungs |
Bronchial |
|
|
2 arteries that feed brain |
Vertebral, and internal corotid |
|
|
How many brachiocephalic veins drain into SVC |
2 |
|
|
What is hepatic portal system |
Carries nutrient rich blood from digestive organ to liver |
|
|
Longest vein in body |
Great saphones vein |
|
|
Amount of interstitial fluid produced by lymph daily |
3l |
|
|
What is lymph |
Interstitial fluid that enters lymphatic system |
|
|
What is a lacteal |
Lymphatic cappilaries transport absorbed fat from sm intestine to bloodstream |
|
|
What is chyle |
Milky white lymph that drains througj lacteal |
|
|
Right thoracic duct drains what |
upper right limb and right side of head |
|
|
Thoracic duct drains what |
Drains rest of body |
|
|
What is lymphamgitis |
Enflamed lymphatic vessels, red lines, tender to touch |
|
|
What veins lymphatic ducts drain into |
Subclavian, internal jugular |
|
|
Major lymph cells |
T cells b cells and macrophage |
|
|
Define antigen |
Anything provoke immune response |
|
|
What is principal lymphoid organ in body |
Lymph node |
|
|
2 main functions of lymphoid organ |
Filteration, immune system acctivation |
|
|
Main structures of lymph node |
Cortex, medulla |
|
|
Circulatory pattern of lymph node |
Afferent lymphatic vessels-subscapular sinus- medullary sinus -hiliuk |
|
|
What is a buboes |
Swollen node, inflamed |
|
|
Function and characteristics of spleen |
Largest lymph organ, rbc graveyard |
|
|
Function of thymus |
Lacks b cells, |
|
|
White and red pulp functions of spleen |
White-immune functions. RED- where RBC are destroyed |
|
|
4 tonsils |
Palatine, linguial, pharyngeal, tubal |
|
|
What are peyers patches |
Clusters of lymphoid follicles, in small intestine |
|
|
How does thymus differ |
No follicles, doesn't fight antigens, has epithelial cells rather then reticular fibers |
|
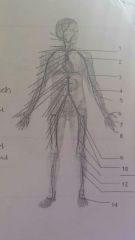
Arteries 1 2 3 |
1. Subclavian, 2. Axillary, 3. brachial |
|
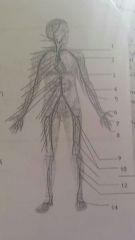
Arteries 4 5 6 7 |
4 radial 5 ulnar 6 deep Palmar arch 7 superficial Palmar arch |
|
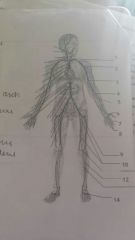
Arteries 8 9 10 11 |
8. Digital, 9. External illiac, 10. Femoral 11. Popliteal |
|
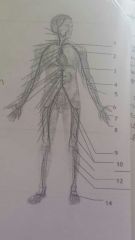
Artery 12 13 14 |
12. Anterior tibial 13. Posterior tibial 14. Arcucate |

