![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Muscles produce movement by exerting force on ____
which in turn pull on bones and other supporting structures like the skin. |
tendons
|
|
|
The attachment of a muscle's tendon to the stationary, usually proximal bone, is called the?
|
origin
|
|
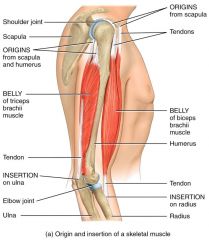
Origins and Insertions
|
Origins and Insertions
|
|
|
The origin of the Biceps is the ____ and the insertion is the ____?
|
Origin:Scapula
Insertion: Radius |
|
|
The action of the Biceps is to?
|
pronate and flex the arm
|
|
|
The origin of the Triceps is the ____ and the insertion is the ____?
|
Origin:Scapula near shoulder joint Upper lateral and posterior sites of humerus
Posterior surface of humerus Insertion: Back of olecranon process of ulna |
|
|
The action of the Triceps is to?
|
Action: Straighten (extend) the arm
|
|
|
Muscles, tendons, bones, and joints can form what three different types of levers in the body?
|
First-class levers, Second class levers, and Third class levers.
|
|
|
In a lever, the point of movement called the ____, is acted on by two different forces: Effort and load.
|
fulcrum
|
|
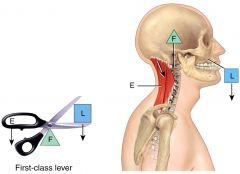
There are few first-class levers
in the body. This pic shows a example |
first-class levers
|
|
|
What levers always provide a distinct mechanical advantage in producing force?
Like a pry bar |
Second class levers
|
|
|
What levers are the most common and favor speed and range of motion over maximum force?
|
Third-class levers
|
|
|
Most skeletal muscles are arranged in opposing ____ pairs at joints.
|
antagonistic
|
|
|
Within opposing pairs, the prime mover or ____ is the muscle primarily responsible for causing the desired movement.
|
agonist (“the leader”)
|
|
|
The ____ stretches and yields to the effects of the prime mover.
|
antagonist
|
|
|
In flexing the forearm at
the elbow, the ____ is the prime mover or agonists, and the ____ ____ is the antagonist. |
brachialis, triceps
brachii |
|
|
What are muscles used to prevent unwanted movements at intermediate joints, or otherwise aid the movement of the prime mover?
|
Synergists
|
|
|
What muscles are a type of synergist muscle that are used to steady the proximal joints of a prime mover?
|
Fixator
|
|
|
Some of the more common muscles of the head and neck include:
|
Orbicularis oris
Extraocular muscles Sternocleidomastoid Rectus abdominus External oblique |
|
|
The muscles of facial expression move ____ rather than bones around a joint.
|
skin
|
|
|
Action: Closes and
protrudes lips for kissing Origin: Surrounding the opening of the mouth Insertion: The skin at the corner of the mouth. What Muscle is this? |
Orbicularis oris
|
|
|
Origin: Maxilla and zygomatic arch
Insertion: Mandible Action: Closes the mouth What muscle is this |
Masseter
|
|
|
3 pair give each eye very
precise movement Origin: Back of the orbit Insertion: Different parts of the eyeball Action: Precise and rapid movement of the eyes What muscle is this? |
The Extraocular muscles
|
|
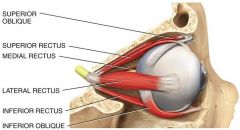
The Extraocular muscles
|
The Extraocular muscles
|
|
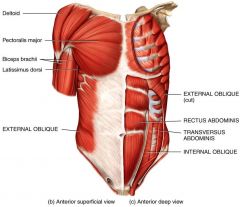
Some of the more common muscles that originate on the trunk include the ones shown
|
Some of the more common muscles that originate on the trunk
|
|
|
Origin: Clavicle and sternum
Insertion: Proximal humerus Action: Adducts and medially rotates thearm at the shoulder joint What muscle is this? |
Pectoralis major
|
|
|
Origin: Ribs 3–5
Insertion: Coracoid process of the scapula Action: Internally rotates the shoulder What muscle is this? |
Pectoralis minor
|
|
|
Origin: Lateral clavicle and upper scapula
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity on the shaft of the humerus Action: Abducts, flexes, and medially rotates the upper arm at the shoulder joint What muscle is this? |
Deltoid Muscle
|
|
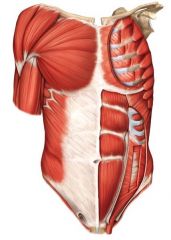
Deltoid
|
Deltoid
|
|
|
Origin: Occipital bone and
cervical spine Insertion: Clavicle, scapula and lower thoracic vertebrae Action: Supports the arm and moves the scapula up, down, in, and out What muscle is this? |
Trapezius
|
|
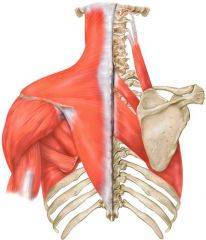
Trapezius
|
Trapezius
|
|
|
What is the Origin, Insertion and Action of the Sternocleidomastoid?
|
Origin: Clavicle and sternum
Insertion: Mastoid process of temporal bone Action: Flex and rotate the head |
|
|
Origin: Thoracic and lumbar
vertebrae and the iliac bone Insertion: Mid-humerus Action: Drives arm inferiorly and posteriorly (the swimmer’s muscle) |
Latissimus dorsi
|
|
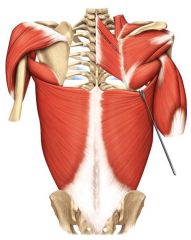
Latissimus dorsi
|
Latissimus dorsi
|
|
|
Anterior abdominal wall:
Origin: Pubic bone Insertion: Ribs and sternum |
Rectus abdominis
|
|
|
Anterior abdominal wall:
Origin: Ribs 5–12 Insertion: Iliac crest and linea alba Actions: Flexes vertebral column and compresses abdomen |
External oblique
|
|
|
The main muscle of inspiration is the?
Origin: Inferior 6 ribs (anteriorly) and lumbar vertebrae (posteriorly) Insertion: Centraltendon |
diaphragm
|
|
|
What is the Origin, insertion, and action of the Biceps brachii?
|
Origin: Scapula
Insertion: Radius Action: Flexes and supinates forearm at elbow joint and flexes arm at shoulder joint |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion and action of the Brachialis?
|
Origin: Distal anterior surface of humerus
Insertion: Ulna Action: Flexor of forearm at elbow |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and action of the Triceps brachii?
|
Origin: Scapula and posterior surface of humerus
Insertion: Olecranon process of ulna Action: Extends forearm at elbow joint and arm at shoulder joint |
|
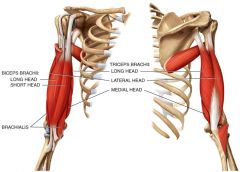
Triceps brachii
|
Triceps brachii
|
|
|
What is the origin, Insertion, and Action of the Brachioradialis?
|
Origin: Humerus
Insertion: Distal radius Action: Supinates the forearm at the radioulnar joint |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and action of the Gluteus maximus?
|
Origin: Iliac crest, sacrum, and coccyx
Insertion: Femur Action: Extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint |
|
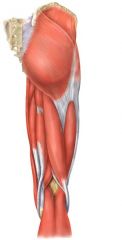
Gluteus maximus
|
Gluteus maximus
|
|
|
What is the origin, Insertion, and action of the Quadricep group (Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis)?
|
Origin: Iliac spine and proximal femur
Insertion: Patella and proximal tibia Action: Flexes thigh at high joint and extends leg at knee joint |
|
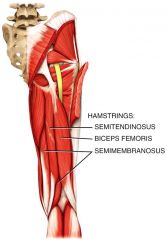
Muscles that move the femur, tibia, and fibula
Hamstring group |
Muscles that move the femur, tibia, and fibula
Hamstring group |
|
|
What is the origin, and insertion of the Hamstring group: (Biceps femoris,
Semitendinosus, and Semimembranosus)? |
Origin: Ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Proximal tibia and fibula |
|
|
What is the origin, insertion, and action of the Tibialis anterior?
|
Origin: Tibia
Insertion: First cuneiform and first metatarsal Action: Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot |
|
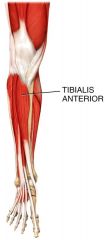
Tibialis anterior
|
Tibialis anterior
|
|
|
The Muscles that plantar flex the foot at the ankle joint are called?
|
Gastrocnemius and soleus muscles function as one – often called the gastrocsoleus muscle
|
|
|
What is the origin and insertion of the Gastrocnemius and soleus muscles?
|
Origin: Femur, capsule of
knee, and head of fibula Insertion: Calcaneus by way of calcaneal (Achilles) tendon |
|
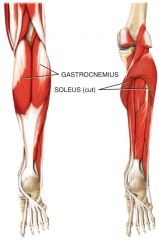
Gastrocnemius and soleus muscles
|
Gastrocnemius and soleus muscles
|
|
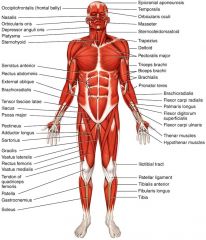
Major Skeletal Muscles Anterior View
|
Major Skeletal Muscles
|
|
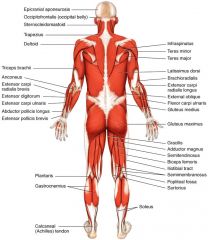
Major Skeletal Muscles
|
Major Skeletal Muscles
|

