![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy
|
structure, "cut up"
|
|
|
Physiology
|
function, "study of nature"
|
|
|
Why Anatomy and Physiology studied together?
|
function dependent on structure
|
|
|
Regulation of the body takes place on..
|
molecular, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism levels
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
process of assimilating materials and energy, used to grow
|
|
|
homeostasis
|
dynamic equilibrium, "stay the same", maintain conditions at a constant level
|
|
|
reproduction
|
cells can self copy, DNA (heredity)
|
|
|
response to stimulus
|
environmental factors: pathogens, climate, radiation, stress
|
|
|
growth and development and evolution
|
change in structure brings change in function
|
|
|
human organisms characteristics
|
regulation, use materials and energy, homeostasis, reproduction, response to stimuli, growth and development, ability to evolve
|
|
|
historical development
|
a&p began in greece
|
|
|
Hippocrates
|
Father of medicine, diseases from natural causes, not gods
|
|
|
History:20th century (anatomy)
|
A&p highly specialized ( gross or macroscopic, regional, systemic, surface, microscopic, developmental, pathological anatomy)
|
|
|
microscopic anatomy
|
cytology (internal cell structure)
histology (tissues composed of diff. cell types) |
|
|
History: 20th century (Physiology)
|
renal & excretory, cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine, muscle, gastrointestinal, reproductive, neurophysiology, cellular, pathophysiology
|
|
|
to understand function, learn structure
|
eg. proteins (enzymes)= digestion
DNA= genetic info blood cells (lymphocytes)= immune heart & cardiovascular= blood circulation |
|
|
anatomical position
|
Standing, feet together, arms to side, head forward, palms forward
|
|
|
body planes: sagittal
|
left and right
|
|
|
body planes: frontal
|
front and back
|
|
|
body planes: transverse
|
top and bottom
|
|
|
body cavities
|
protect organd, permit growth
|
|
|
ventral cavity (coelom)
|
divided by diaphragm: thoracic and adomniopelvic cavities
|
|
|
dorsal cavity
|
cranial (brain) and vertebral (spine) cavities
|
|
|
ventral body cavity
|
thoracic (heart and lungs): mediastinum and pleural
adomniopelvic: abdominal (digestive viscera) and pelvic (urinary, reproductive, rectum) |
|
|
adomniopelvic cavity
|
peritoneal cavity : parietal peritoneum (lines internal body wall)
visceral peritoneum (covers organs) |
|
|
directional terms: superior (cranial)
|
toward head
|
|
|
inferior (caudal)
|
toward feet
|
|
|
ventral (anterior)
|
front
|
|
|
dorsal (posterior)
|
Back
|
|
|
medial
|
midline
|
|
|
lateral
|
away from midline
|
|
|
intermediate
|
between medial and lateral
|
|
|
proximal
|
close to point of origin
|
|
|
distal
|
away from point of origin
|
|
|
superficial (external)
|
body surface
|
|
|
deep (internal)
|
away from body surface
|
|
|
4 quadrants
|
subjects point of view
|
|
|
regions
|
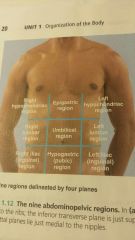
|

