![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
List the 12 cranial nerves. |
I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducens VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear IX. Glossopharyngeal X. Vagus XI. Accessory XII. Hypoglossal |
|
|
|
Name Cranial nerve I. |
Olfactory |
Smell sensory |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve II. |
Optic |
Sight sensory |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve III. |
Oculomotor |
Motor to eye (4 of 6) PS ciliary muscle and iris |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve IV. |
Trochlear |
Motor to superior oblique eye muscle (down and lateral) |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve V. |
Trigeminal |
Major sensory to face Motor for mastication |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve VI. |
Abducens |
Motor to lateral rectus eye muscle (abducts/moves laterally) |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve VII. |
Facial |
Major motor to face Taste of anterior 2/3 tongue PS salivary and lacrimal |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve VIII. |
Vestibulocochlear |
95% sensory Inner ear, vestibular apparatus, coclea |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve IX. |
Glossopharyngeal |
Motor to pharynx Taste of posterior 1/3 tongue PS salivary |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve X. |
Vagus |
Motor to pharynx and larynx PS ventral body cavity |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve XI. |
Accessory |
Primary motor to neck muscles "Accessory to vagus" |
|
|
Name Cranial nerve XII. |
Hypoglossal |
Motor to tongue |
|
|
Which nerves are purely sensory? |
Cranial nerve I. Olfactory Cranial nerve II. Optic
(95%) Cranial nerve VIII. Vestibulocochlear |
|
|
|
Which nerves are mainly motor? |
Cranial nerve III. Oculomotor Cranial nerve IV. Trochlear Cranial nerve VI. Abducens Cranial nerve XII. Hypoglossal |
Do carry some sensory axons from muscle proprioceptors. |
|
|
Which nerves carry both somatic motor and parasympathetic motor? |
Cranial nerve III. Oculomotor Cranial nerve VII. Facial Cranial nerve IX. Glossopharangeal Cranial nerve X. Vagus |
|
|
|
How many spinal nerves are there and how do they break down by region? |
31 spinal nerves 8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral 1 coccygeal |
|
|
|
Cervical plexus |
C1-C5 Phrenic nerve |
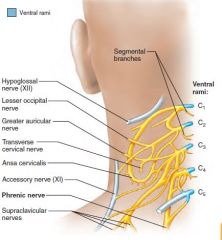
c3,c4,c5 keeps the diaphragm alive |
|
|
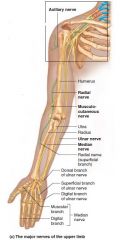
Brachial plexus |
C5-T1 Axillary nerve Median nerve Musculocutaneous nerve Radial nerve Ulnar nerve |
|
|
|
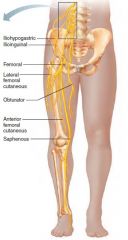
Lumbar plexus |
L1-L4 Femoral nerve |
|
|
|
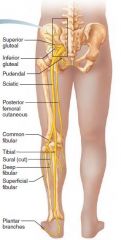
Sacral plexus |
L4-S4 Sciatic nerve |
Longest and thickest nerve |
|
|
Intercostal nerves |
Ventral rami T2-T12 (no plexus) Ribs and skin |
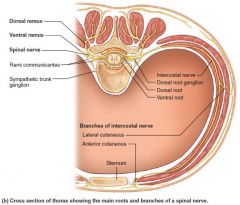
|
|
|
Phrenic nerve |
Cervical plexus Motor and sensory of diaphram Runs below sternocleidomastoid muscle. |
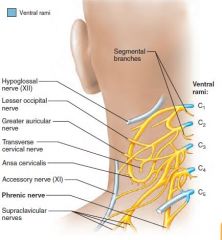
Irritation causes hiccups |
|
|
Axillary nerve |
Brachial plexus Shoulder joint and deltoid |
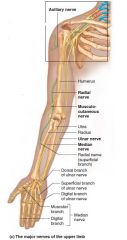
Arm abduction |
|
|
Musculocutaneous nerve |
Brachial plexus L. Lateral forearm Biceps, sensory lateral forearm |
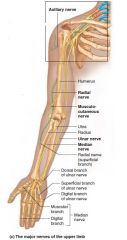
|
|
|
Median nerve |
Brachial plexus L. Middle of forearm Flex wrist and fingers Oppose thumb. Digits 1-4 |
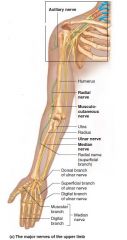
Affected in carpal tunnel syndrome |
|
|
Ulnar nerve |
Brachial plexus L. Medial forearm and hand. Most hand muscles superficial digits 4-5 |
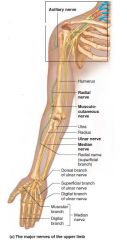
Funny bone Claw hand |
|
|
Radial nerve |
Brachial plexus L. Posterior arm to hand Extensors (wrist drop) |
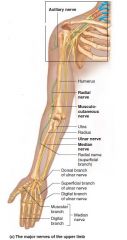
Crutch compresses |
|
|
Femoral nerve |
Lumbar plexus Anterior thigh muscles Hip flex, knee extend |
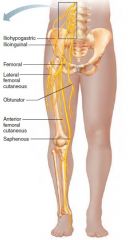
Herniated disk = gait problems |
|
|
Sciatic nerve |
Sacral plexus Posterior thigh, buttocks, lower limb and foot Thigh extend, knee flex, plantar flex |
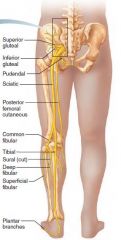
|
|
|
Dermatone |
Mapping of skin area or sensory field |
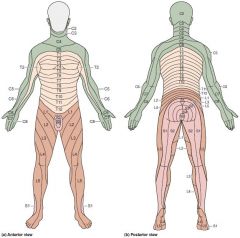
|
|
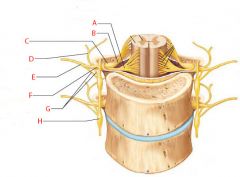
A |
Ventral root |
|
|
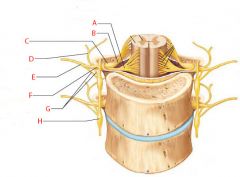
B |
Dorsal root |
|
|
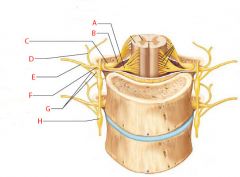
C |
Dorsal root ganglion |
|
|
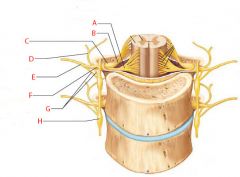
D |
Dorsal ramus of spinal nerve |
|
|
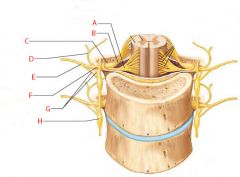
E |
Ventral ramus of spinal nerve |
|
|
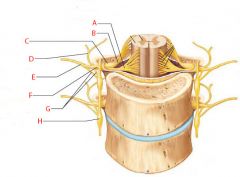
F |
Spinal nerve |
|
|
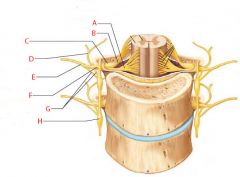
G |
Rami communicantes |
|
|
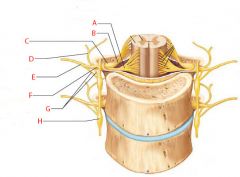
H |
Sympathetic trunk ganglion |
|
|
|
What are the steps to nerve regeneration? |
1. Axon becomes fragmented at the injury site. 2. Macrophages clean out dead axon distal to the injury. 3. Axon sprouts, or filaments, grow through regeneration tube formed by Schwann cells. 4. Axon regenerates and a new myelin sheath forms. |
|
|
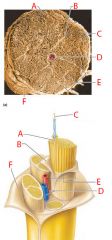
A |
Endoneurium |
|
|
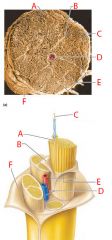
B |
Perineurium |
|
|
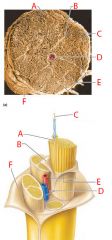
C |
Nerve fibers |
|
|
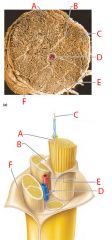
D |
Blood vessel |
|
|
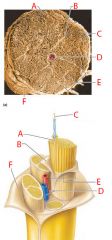
E |
Fascicle |
|
|
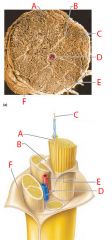
F |
Epineurium |
|
|
|
What are the components of a reflex arc? |
1. Receptor 2. Sensory neuron 3. Integration center 4. Motor neuron 5. Effector |
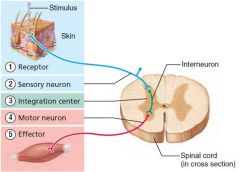
|
|
|
Somatic vs Visceral reflex arc? |
Somatic reflexes activate skeletal muscle.
Autonomic (visceral) reflexes activate visceral effectors (smooth or cardiac muscle or |
|

