![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
condyle
|
rounded, convex projection
|
|
|
crest
|
narrow ridge of bone
|
|
|
epicondyle
|
raised area of a condyle
|
|
|
fissure
|
narrow depression or opening
|
|
|
foramen
|
opening through a bone
|
|
|
fossa
|
shallow depression
|
|
|
head
|
structure supported on neck
|
|
|
meatus
|
canal-like structure
|
|
|
process
|
projection or prominence
|
|
|
ramus
|
armlike projection
|
|
|
sinus
|
air-filled cavity
|
|
|
spine
|
sharp, slender process
|
|
|
trochanter
|
large, irregularly shaped projection
|
|
|
tubercle
|
small rounded projection
|
|
|
tuberosity
|
large rounded projection
|
|
|
Line |
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest |
|
|
Groove |
Furrow |
|
|
Notch |
Indentation at the edge of a structure |
|
|
Facet |
Smooth, nearly flat articular surface |
|
|
What are the 2 main divisions of the skeleton? |
Axial Appendicular |
|
|
Name the 3 major regions of the axial skeleton |
Skull Vertebral column Thoracic cage |
|
|
How many bones comprise the axial skeleton? |
80 |
|
|
How many bones comprise the skull? |
22 |
|
|
How are most skull bones connected? |
By sutures. Except the mandible. |
|
|
Name the 3 fossae in the skull |
Anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae |
|
|
How many cranial bones are there? Name them. |
The paired parietal and temporal bones, and the unpaired frontal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones. |
|
|
Point to your external occipital protuberance |
(touch it) |
|
|
Which bone is considered the "keystone" of the cranium? |
Sphenoid bone |
|
|
How many pairs of true ribs are there?
|
7
|
|
|
How are the cervical vertebrae distinguished?
|
Oval body, short, bifid process projects directly back, generally triangular foramen, each transverse process has a foramen.
|
|
|
How are the thoracic vertebrae distinguished?
|
The body is somewhat heart shaped, a small facet on each side, generally circular foramen, spinous process is long and points downward.
|
|
|
How are the lumbar vertebrae distinguished?
|
short, flat, hatchet shaped spinous process, triangular vertebral foramen.
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of the sternum?
|
Manubrium Body Xiphoid process |
|
|
How many pairs of false ribs are there?
|
5
|
|
|
What's the difference between true ribs and false ribs?
|
True ribs connect directly to the sternum. False ribs either connect indirectly, or not at all.
|
|
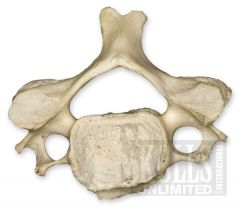
|
Cervical Vertebrae
|
|
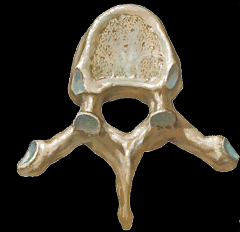
|
Thoracic Vertebrae
|
|
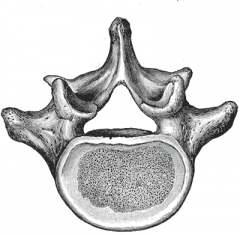
|
Lumbar Vertebrae
|
|
|
Which features connect to the styloid process? |
Several tongue and neck muscles and a ligament that secures the hyoid bone |
|
|
Which features attach to the mastoid process? |
Some neck muscles |
|
|
What structure is found in the hypophyseal fossa of the sella turcica (on the sphenoid bone) |
The pituitary gland |
|
|
What attaches to the crista galli? |
Dura mater of the brain (this helps secure the brain in the cranial cavity |
|
|
Which bones are considered the keystone of the facial bones? |
The maxilla(2) |
|
|
Bell's palsy can result from inflammation of which nerve as it passes through which structure? |
The facial nerve/stylomastoid foramen |
|
|
Which foramen covers with cartilage after birth? |
Foramen lacerum |
|
|
What passes through the incisive fossa? |
Sphenopalatine artery (supplies the mucous membrane), nasopalatine nerves |
|
|
What type of cartilage makes up the nose? |
Hyaline |
|
|
What feature(s) pass through the hypoglossal canal? |
The hypoglossal nerves |
|
|
What features connect with the hyoid bone? |
Neck muscles that aid in swallowing |
|
|
Which feature passes through the stylomastoid foramen? |
The facial nerve |
|
|
What 2 structures compose the intervertebral disc? |
Nucleus pulposus Anulus fibrosus |
|
|
What is the purpose of the appendicular skeleton? |
To carry out movement |
|
|
Which bones comprise the pectoral girdle? |
The scapula and clavicle |
|
|
What are the 2 ways joints are classified? |
Structurally Functionally |
|
|
Name the 3 structural classifications of joints |
Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
Name the 3 functional classifications of joints |
Synarthroses Amphiarthroses Diarthroses |
|
|
Describe the gliding movement of joints. |
When flat articular surfaces slip over one another, or "glide". (Intercarpal and intertarsal joints, flat articular processes in the vertebrae) |
|
|
Describe angular movement of joints. |
Increase or decrease the angle between 2 bones. (flexion, extension, hyperextension, abduction, adduction, circumduction) |
|
|
Describe rotation movement of joints. |
The turning of a bone around its own long axis. (turning the head side to side) |
|
|
Name the 6 categories of synovial joints. |
Plane Hinge Pivot Condylar Saddle Ball and Socket |

