![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
Studies the form and structure of the body, examines the relationship among parts of the body as well as the structure of organs. |
Greek root that means "to cut apart" |
|
|
Physiology |
Examines how the body FUNCTIONS, the study of chemistry and physics of the body and the ways in which they work together to support the functions of life. |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
The tendency of the body to seek and maintain a condition of balance or equilibrium within it's internal environment |
One in the body |
|
|
Microscopic Anatomy |
Examines structures that cannot be observed by the unaided eye |
|
|
|
What are the 2 main divisions of specimens examined under microscope? |
Cytology and Histology |
|
|
|
Cytology |
The study of body cells and their internal STRUCTURE |
|
|
|
Histology |
The study of tissues |
|
|
|
Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy |
Investigates structures visible to the unaided eye. |
|
|
|
What 5 ways can specimens be examined in Macroscopic Anatomy? |
Regional, Embryology Comparative, Systemic and Surface |
RECSS |
|
|
Systemic Anatomy |
Study of structures that make up a discrete body system; a group of structures that work together to perform a unique body function. |
|
|
|
Regional Anatomy |
Examines all the structures in a particular region of the body; the study of interrelationships of all structures in a specific body region. E.g. the abdomen |
|
|
|
Surface Anatomy |
Focuses on superficial anatomic markings and related internal body structures. |
|
|
|
Comparative Anatomy |
Examines similarities and differences in anatomy of DIFFERENT SPECIES |
|
|
|
Embryology |
Studies developmental changes from conception to birth. |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of specialized branches of Anatomy? |
Pathological and Radiographic |
|
|
|
Pathologic Anatomy |
Examines anatomic changes RESULTING FROM DISEASE |
|
|
|
Radiographic Anatomy |
Investigates internal structures by scanning procedures |
|
|
|
What are the 5 subdiciplines of physiology that focus on a particular body system? |
Cardiovascular, Nuerophysiology, Respiratory, Reproductive, and Pathophisiology |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular physiology |
The functioning of the heart, blood vessels and blood. |
|
|
|
Neurophysiology |
The functioning of nerves and nervous system organs |
|
|
|
Resipriratory Physiology |
The functioning of respiratory organs |
|
|
|
Reproductive physiology |
The functioning of the reproductive hormones and the reproductive cycle. |
|
|
|
Pathophysiology |
The relationship between the function of an organ system and disease or injury to the system. |
|
|
|
Levels of Structural Organization of the Human Body |
Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, Organismal Level |
|
|
|
Integumentary System |
Encloses internal body structures-site of many sensory receptors(i.e. skin) |
Hair, Skin and Nails |
|
|
Skeletal system |
Supports the body- enables movement(with muscular system) |
Cartilage, Bones and Joints |
|
|
Muscular System |
Enables movement(with skeletal system) helps maintain body temperature |
Skeletal Mucles and Tendons |
|
|
Nervous System |
Detects and processes sensory information, activates bodily responses. |
Brain, Spinal cord, Peripheral nerves |
|
|
Endocrine System |
Secretes hormones, regulates bodily processes |
Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Pancreas, Adrenal Glands and Testes/Ovaries |
|
|
Cardiovascular System |
Delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues. Equalizes temperature in the body |
Heart, Blood vessels |
|
|
Lymphatic System |
Returns fluid to blood and defends against pathogens |
Thymus, Lymph Nodes, Spleen and Lymphatic Vessels |
|
|
Digestive System |
Processes food used by the body and removes waste from the undigested food |
Stomach, Liver, Gall Bladder, Large intestine and Small intestine |
|
|
Urinary System |
Controls water balance in the body and removes waste from blood and excretes them |
Kidneys and urinary bladder |
|
|
Male Reproductive system |
Produces sex hormones and gametes and deliver gametes to female |
Epididymus and Testes |
|
|
Female Reproductive System |
Produce sex hormones and gametes also supports embryo/fetus until birth and produces milk for an infant. |
Mammary Glands, Ovaries and Urterus |
|

What system is this? |
Integumentary System |
|
|
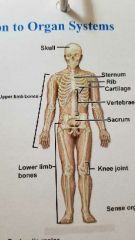
What system is this? |
Skeletal System |
|
|
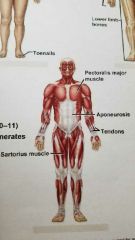
What system is this? |
Muscular System |
|
|
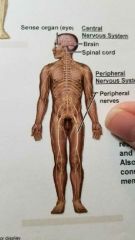
What system is this? |
Nervous |
|
|
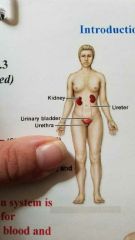
What system is this? |
Urinary System |
|
|
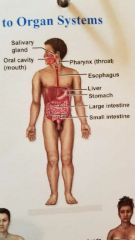
What system is this? |
Digestive system |
|
|
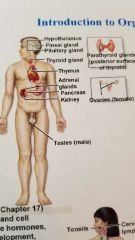
What system is this? |
Endocrine System |
|
|
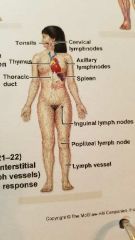
What system is this? |
Lymphatic System |
|
|
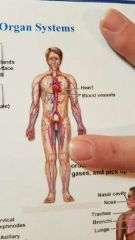
What system is this? |
Cardiovascular System |
|
|
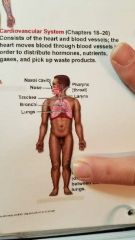
What system is this? |
Respiratory System |
|
|
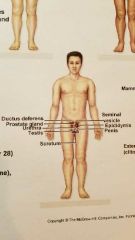
What system is this? |
Male Reproductive system |
|
|
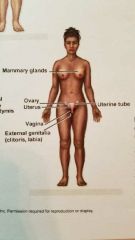
What system is this? |
Female Reproductive system |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
The sum of all chemical reactions that occur with in the body; composed of anabolism and catabolism, both occurring simultaneously and continually to keep us alive. |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Small molecules joined to form larger ones |
Utilizes energy |
|
|
Anabolic reactions |
Building reactions and they consume(utilize) energy |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
Large molecules broken down into smaller ones |
Releases energy |
|
|
Catabolic reaction |
Breaks materials down and release energy |
|
|
|
Properties of all Organisims |
Organization and order Metabolism (anabolism&catabolism) Grow and develop Responsiveness Regulation Homeostasis Reproduce |
|
|
|
Cranium |
Anterior Cranial |
Skull |
|
|
Frons |
Anterior Frontal |
Forehead |
|
|
Oculus |
Anterior Orbital/Ocular |
Eye |
|
|
Bucca |
Anterior Buccal |
Cheek |
|
|
Facies |
Anterior Facial |
Face |
|
|
Auris |
Anterior Otic |
Ear |
|
|
Nasus |
Anterior Nasal |
Nose |
|
|
Oris |
Anterior Oral |
Mouth |
|
|
Mentis |
Anterior mental |
Chin |
|
|
Front Cervicis |
Anterior Cervical |
Neck |
|
|
Thorcis/thorax |
Anterior thoracic |
Chest |
|
|
Axilla |
Anterior Axillary |
Armpit |
|
|
Mamma |
Anterior Mammary |
Breast |
|
|
Antecubitis |
Anterior Antecubital |
Front of elbow |
|
|
Abdomen |
Anterior Abdominal |
|
|
|
Antebrachium |
Anterior Antebrachial |
Front of forearm |
|
|
Umbilicus |
Anterior Umbilical |
Naval |
|
|
Carpus |
Anterior Carpal |
Wrist |
|
|
Hip |
Anterior Coxal |
|
|
|
Pelvis |
Anterior Pelvic |
|
|
|
Pollex |
Thumb |
|
|
|
Palma |
Anterior Palmar |
Palm |
|
|
Digits/ phalanges |
Anterior Digital or Phalangeal |
Fingers |
|
|
Inguen |
Anterior Inguinal |
Groin |
|
|
Pubis |
Anterior Pubic |
|
|
|
Patella |
Anterior Patellar |
Kneecap |
|
|
Femur |
Anterior Femoral |
Thigh |
|
|
Crus |
Anterior Crural |
Front of Leg |
|
|
Tarsus |
Anterior Tarsal |
Ankle |
|
|
Pes |
Anterior Pedal |
Front of foot |
|
|
Digits/ Phalanges |
Anterior Digital/Phalangeal |
Toes |
|
|
Cephalon |
Posterior Cephalic |
Head |
|
|
Shoulder |
Posterior Acromial |
|
|
|
Dorsum |
Posterior Dorsal |
Back |
|
|
Brachium |
Posterior brachial |
Back of Arm |
|
|
Olecranon |
Posterior Olecranal |
Back of Elbow |
|
|
Lumbus |
Posterior Lumbar |
Loin |
|
|
Sacrum |
Posterior Sacral |
|
|
|
Antebrachium |
Posterior Antebrachial |
Back of forearm |
|
|
Manus |
Posterior Manual |
Back of Hand |
|
|
Gluteus |
Posterior Gluteal |
Buttock |
|
|
Femur |
Posterior Femoral |
Back of thigh |
|
|
Sura |
Posterior Sural |
Calf |
|
|
Calcaneous |
Posterior Calacaneal |
Heel of Foot |
|
|
Planta |
Posterior Plantar |
Sole of Foot |
|
|
Dorsum |
Anterior, top of the arch |
|
|
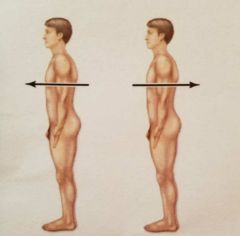
What are the relative postions? |
Anterior and Posterior |
|
|
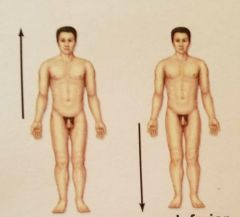
What are the relative postions? |
Superior and Inferior |
|
|
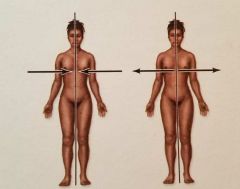
What are the relative positions? |
Medial and Lateral |
|
|
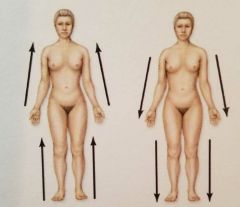
What are the relative positions? |
Proximal and Distal |
|
|

Name the 3 most commonly used planes? |
Sagittal, Frontal(coronal) and Transverse |
|
|

Name the planes |
Blue-Coronal Green-Transverse Yellow-Midsagittal |
|
|
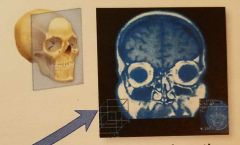
|
Coronal Section |
|
|
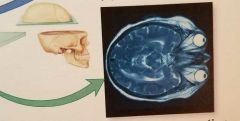
|
Transverse section |
|
|
|
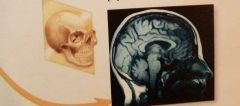
Midsagittal |
|
|
|
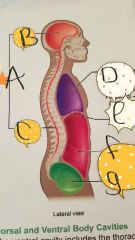
A- Dorsal cavity B- Cranial cavity C- Vertebral cavity D- Thoracic cavity E- Diaphragm F- Adominal cavity G- Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
A- Cranial cavity B- Vertebral cavity C- Ventral body cavity D- Adomino-pelvic cavity E- Pelvic cavity F- Abdominal cavity G- Diaphragm H- Pericardial cavity within the Mediastinum I- Thoracic cavity J- Pleural cavity K- Superior Mediastinum |
|
|
|
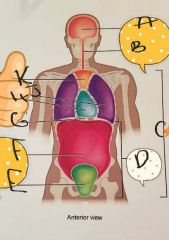
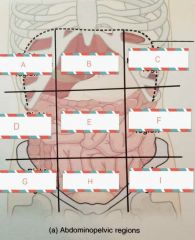
A- RIGHT HYPOCHONDRIAC REGION B- EPIGASTRIC REGION C- LEFT HYPOCHONDRIAC REGION D- RIGHT LUMBAR REGION E- UMBILICAL REGION F- LEFT LUMBER REGION G- RIGHT ILIAC REGION H- HYPOGASTRIC REGION I- LEFT ILIAC REGION |
|
|
|
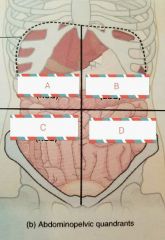
A- Right Upper Quadrant B- Left Upper Quadrant C- Right Lower Quadrant D- Left Lower Quadrant |
|
|
|
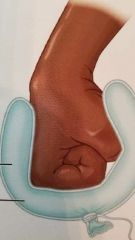
Serous Membrane |
Lines the Pericardial cavity and reflects back to cover the heart |
|
|
|
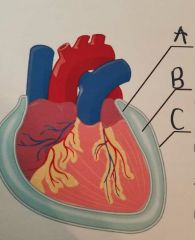
A- Visceral Pericardium B- Pericardial Cavity C- Parietal Pericardium |
|

