![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Risk factors for aortic dissection |
Inherited Diseases - Marfan's - Ehlers-Danlos - Turner syndrome - Family history
Aortic Wall Stress - Chronic HTN - Previous CV Surgery - Bicuspid aortic valve - Syphillis - Arteritis (Takayasu's) - Cocaine - Weightlifting - Valsalva
Decreased wall resistance - Older age - Pregnancy
Other - PCKD - IABP use |
|
|
Physiological Factor favoring continued dissection
|
(1) higher SBP
(2) Slope of pulse wave (dP/dT) |
|
|
Chronic aortic dissetion |
Present greater than 2 weeks |
|
|
Mechanisms of aortic dissection |
(1) Intimal tear (2) Degeneration of vasa vasorum of aorta (3) Penetrating Aortic Ulcer |
|
|
Stanford classification of aortic aneurysms |
Type A: Involve Ascending Aorta Type B: Involve only descending aorta |
|
|
Ascending aorta |
From Left ventricle to left subclavian branch point |
|
|
Debakey classification system of aortic dissection |
I - Ascending aorta to descending II - Confined to ascending aorta III - Originate and confined to descending a - Thoracic aorta only b - Extends to abdominal aorta |
|
|
Likelihood ratio for various findings in TAD |
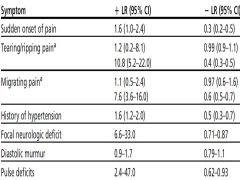
|
|
|
Most common MI pattern in TAD |
Inferior MI secondary to right coronary artery involvement |
|
|
Chest xray findings traumatic aortic rupture |
Wide mediastinum Displaced intimal calcification |
|
|
Sensitivity and Specificity of Advanced Imaging Options for TAD |
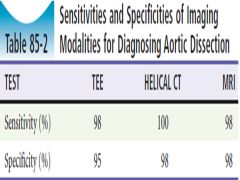
|
|
|
Recommended imaging modality for TAD |
CT-A unless contraindications or too unstable -->
Then TEE |
|
|
Heart and SBP target in management of TAD |
HR <60 SBP <120 |
|
|
Indications for surgery in Type B Aortic Dissections |
- Persistent/recurrent pain - Frank aortic leak or rupture - Visceral, renal, or limb malperfusion syndrome - Uncontrolled HTN - Development of a localized aneurysm |
|
|
Complications of TAD |
CVS - AI - MI - CHF - Cardiogenic shock - Tamponade
Neurological - CVA - Cord ischemia/infarction
ENT - Tracheal compression - Horner's syndrome - Hoarseness do to recurrent laryngeal nerve compression
Resp - Hemoptysis - Hemothorax
GI - Mesenteri ischemia
Renal - AKI |

