![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Parkinson disease cause |
Death of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, accompanied by misfolding and aggregation of α-synuclein |
|
|
When do symptoms of parkinson appear? |
When neuronal loss is such that itcauses an 80% reduction of dopamine in thestriatum (part of the basal ganglia of the brain) |
|
|
Familial form of Parkinsonism |
Autosomal Dominant pattern of inheritance |
|
|
Other forms of Parkinsonism due to specific entities |
Viral Inflammation Brain Trauma, Stroke, and by poisoning by Manganese Intoxication with MPTP Idiopathic (loss of dopamine neurons with age) |
|
|
Iatrogenic Parkinsonism |
Complication of antipsychotic therapy especially following the use of butyrophenone and phenothiazine drug classes |
|
|
Levodopa |
Dopamine precursor (L-dopa), converted to DA by Dopa-decarboxylase. Crosses BBB On and off phenomena, due the to the decrease in number of dopamine neutrons with time. |
|
|
Levodopa Pharmacokinetics |
Orally Proteins interfere with its absorption Taken 45 minutes before a meal Short half-life (1 to 2 hours) |
|
|
Carbidopa |
does not cross BBB inhibits L-amino acid DOPA-carboxylase in the periphery |
|
|
Levodopa + Carbidopa |
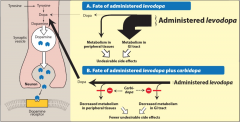
fewer adverse effects in the periphery and GIT |
|
|
Tolcapone |
COMT inhibitor, an enzyme that converts Levodopa to 3OMD, which competes with Levodopa for transport into the CNS
Extend the duration of action of Levodopa Causes acute hepatic failure |
|
|
Levodopa adverse effects |
Emesis Postural Hypotension Mydriasis Fluctuations Dyskinesia (reflects the overactivity of dopamine receptors) Contraindicated in angle-closure glaucoma |
|
|
Ropinirole Pramipoxole Rotigotine Apomorphine |
Dopamine receptor agonists Longer duration of action than levodopa (No fluctuations Pramipexole depends on renal function for its elimination |
|
|
Dopamine Receptor Agonists adverse effects |
Sedation Hallucination Confusion Nausea Hypotension |
|
|
Amantadine |
Enhances DA neurotransmission by increasing synthesis or release of DA orinhibition of reuptake of DA Also antimuscarinic actions lasts only for few weeks |
|
|
Selegiline |
Selective inhibitor of MAO type B enzyme that metabolises dopamine Therefore, increases Dopamine levels in the brain. Metabolised to amphetamine |
|
|
Rasagilin |
Irreversible inhibitor of MAO Type B 5 times more potent than Selegiline Not metabolised to amphetamine |

