![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|
|
What is a heterogenous affective disorder that manifests itself in disturbances in emotion, cognitive, behavioral, and somatic regulation? |
Depression |
|

Which are considered core syndromes? Which are "vital" signs? |

|
|

Identify the depression type: |
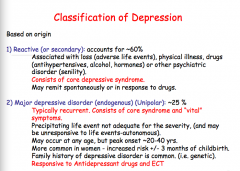
|
|

Identify the depression type: |

|
|
|
Functional deficits of which two neurotransmitters is though the be involved in the pathophysiology of depression?
|
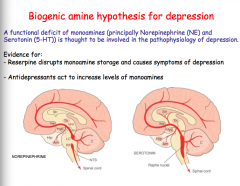
|
|
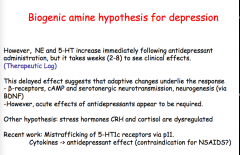
|
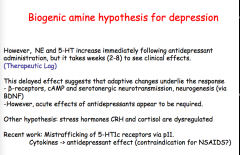
|
|
|
What are the four major classes of antidepressants? |

|
|
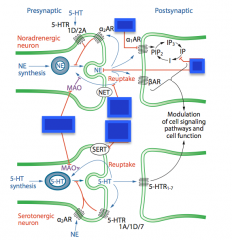
Identify where MAOIs, TCAs, SNRIs, SSRIs, and Li act. |
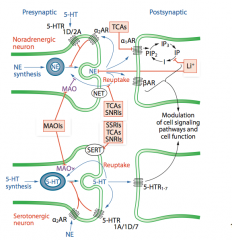
|
|
|
What is a black box warning in children and adolescents taking antidepressants? |

Suicide |
|
|
Which antidepressants are substrates for MDR1?
Which drugs are not substates for MDR1?
Why do some antidepressants limited in their ability to accumulate in the brain? Which nucleotide polymorphism tended to have depression that did not remit in response to drugs that were substrates of MDR1? |

|
|
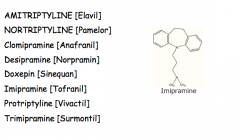
What type of antidepressant? |
Tricyclic (TCAs) |
|
|
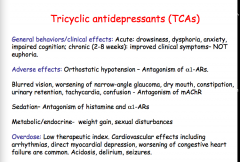
What is the mechanism of action of TCAs? What other three receptors do they also block? |
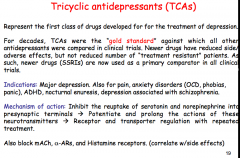
|
|
|
Antagonism of alpha-1 causes what two side effects in TCAs? What side effects are caused through antagonism of mAChR? Any weight gain or sexual disturbances?
High or low therapeutic index?
|
|
|
|
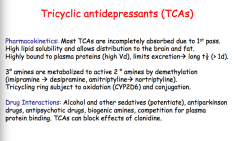
Are most TCAs completely absorbed? High or low lipid solubility? High or low binding to plasma proteins?
How are tertiary amines metabolized to secondary amines?
What are some possible drug interactions? |
|
|

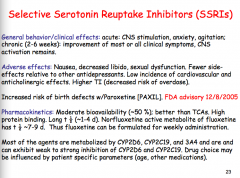
What type of antidepressants? What are they the first line therapy for?
Any activity at mACh, H1, and alpha1 receptors? Selective inhibition of what? |

|
|
|
Do SSRIs have lower or higher incidence of CV and anticholinergic effects? Higher or lower TI? Which SSRI has an increased risk of birth defects? Which SSRI has the longest half-life?
|
|
|
|
Which drug class is contraindicated with SSRIs? What could result if taken together?
What other two drug classes can cause 5-HT release? |

|
|

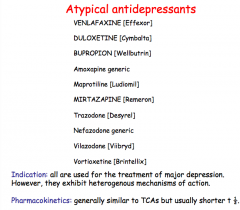
What class of antidepressants?
What AD class are they similar to but just have a short half-life? |
|
|

Identify the drugs. |

|
|
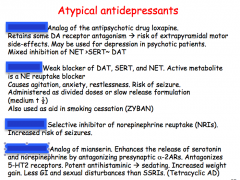
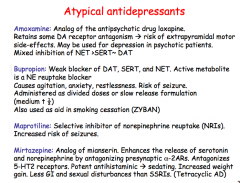
Identify the atypical antidepressants. |
|
|
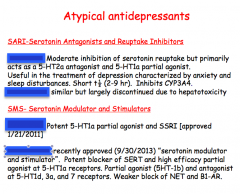
|
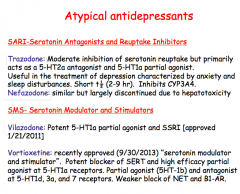
|
|

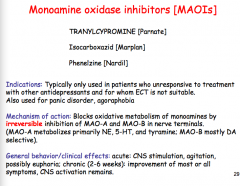
What class of drugs?
Which patients get them? What is the mechanism?
|
|
|
|
How long do the drug effects of MAOIs persist?
What foods should you avoid? What drug class can cause an acute hypertensive reaction?
What two drugs when used with MAOIs can cause hyperpyrexia, delirium, convulsions, coma, and death? |

|
|

What are these drugs used in the maintenance of? What is acute mania typically treated with? |

|
|
|
What is the hypothesized MOA of lithium? What is the half-life? Speed and completeness of absorption?
High or low therapeutic window?
Neuro, glandular, renal, cardia, and other AEs?
What two drug classes is lithium sensitive to? |

|
|
|
What are two anticonvulsants used to manage bipolar disorder?
What can they be used with? What are the advantages and disadvantages compared to lithium? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of valproic acid? Which two channels does it act on?
Effects on its own metabolism and the metabolism of other drugs?
What dangerous side effect can be common? |

|
|
|
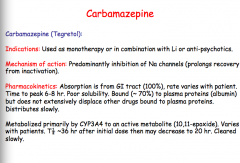
What is the MOA of carbamazepine? Primarily metabolized by which CYP? What is the half-life after initial dose and how does it vary? |
|
|
|
Carbamazepine is a CYP inducer. True or false.
What are some AEs? |

|
|
|
Melancholy, more withdrawn, irritable, late for work, suspected drug abuse. Diagnosed with major depressive disorder => placed on sertraline.
Common side effect or illness (loss of sexual function)? What can he do? Any pharmacological treatments that may work? |
Common side effect Viagra (Sildenafil)
Offer up another class possibly, atypicals.
|
|
|
20 year old college student, depression, previously attempted suicide, citalopram did not help. Venlafaxine did not help. Fluoxetine. Second suicide attempt.
Did this medication fail? Any tests to perform? Was the choice of fluoxetine appropriate? What processes control the responsiveness of patients to antidepressant therapy? What additional instructions should the second clinician have included? |
Who knows...Tavalin just rambled |
|
|
History of mood swings, nausea, vomiting, ataxia, tremor, confusion in hot weather.
What medication caused this (in patients who lost a lot of fluid)? |
Serotonin syndrome (SSRIs), Lithium (polyuria, nephrotoxic) Hyperthermia |

