![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
anatomical preventions |
• skin • ciliary clearance, e.g. lung, trachea • lower stomach pH |
|
|
risks for infection |
• young & elderly • immunocompromised • immunization hx • prior illnesses • nutrition • pregnancy • coexisting illness • emotional status • severe burns • cancer • HIV • indwelling catheters • corticosteroids |
|
|
gram (+) v. (-) |
gram (+)-- • retain color in cell wall • thick outer peptidoglycan cell wall • cocci, e.g. staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci • bacilli
gram (-)-- • does not retain cell wall • thin outer peptidoglycan cell wall • thick outer lipid membrane • coccobacilli, cocci, bacilli |
|
|
pathogens & age group |
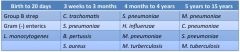
|
|
|
diagnostic tests |
• gram stain • cultures • serology- titers/antibodies measured, esp. relevant in viruses • CBC |
|
|
CBC bacteria v. viruses |
(+) bacteria (-) or stays the same in viral infection |
|
|
antibiotic susceptibilities |
sensitive-- • eradication of pathogens
intermediate-- • may not eradicate @ certain doses; need higher dose >> you wouldn't use unless you really have to
resistant-- • cannot eradicate
|
|
|
mean inhibitory concentration (MIC) |
**how to determine sensitivity
• the lowest concentration that antimicrobial agents must achieve to effectively prevent further growth of bacteria in specified medium • predicts bacteriological response to therapy • (+) MIC to agent means it may be resistant • MIC creep- broad spectrum antibiotics causing MIC (+) |
|
|
time v. concentration dependent kinetics |
time dependent-- • relies on amount of time serum concentration remains above MIC • used in general infections • no serum monitoring
concentration dependent-- • relies on highest concentration in serum reached; must greatly exceed MIC |
|
|
post antibiotic effect (PAE) |
• delayed regrowth of bacteria following antibiotic exposure • (+) resistance; those that grow back are the toughest |
|
|
What are the considerations for which antibiotics to prescribe? |
• allergies • combination therapy >> synergy • cost • antibiotic resistance • formulary agents that vary across institutions • patient response to antibiotics |
|
|
T/F. Two antibiotics from the same class should not be used at the same time. |
True |
|
|
beta-lactams |
**cross-sensitivity across a class of abx **broad spectrum
• PCN • extended spectrum PCN • b-lactam/b-lactamase inhibitors • cephalosporin • carbapenems • monobactam |
|
|
beta-lactams MOA |
• bactericidal • binds to cell wall & inactivates PCN binding proteins • interferes w/ last step of bacterial wall synthesis >> enzymes will leak out >> cell death |
|
|
PCN |
• natural PCN • aminoPCN • PCNase-resistant synthetic PCN • extended-spectrum PCN • beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitors |
|
|
natural PCN |
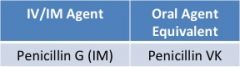
clinical use-- • pneumococcal & streptococcal infections • DOC for syphilis |
|
|
aminoPCNs |
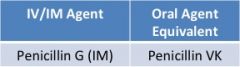
**mainly gram (+), minimal activity against gram (-)
clinical use-- • DOC for enterococcal infections • community-acquired respiratory infections • otitis media • listeria monocyogenes- meningitis risk <3 mos; if patient is 2 y/o & have listeria >> aminoPCNs |
|
|
PCNase-resistant synthetic PCN |
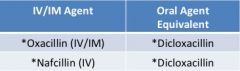
**do not require renal adjustment **no enterococcal coverage **no MRSA coverage
clinical use-- • DOC for beta-lactamase (+) staphylococcal infections, e.g. oxacillin sensitive staph aureus (OSSA) • preferred over vancomycin due to rapid bactericidal activity |
|
|
extended spectrum PCN |
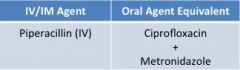
**enterococcal activity **good anaerobic activity
clinical use-- • pseudomonas aeruginosa, usually w/ aminoglycoside • monotherapy for UTI |
|
|
b-lactam/b-lactamase inhibitors |

**restores activity of b-lactam component in presence of b-lactamase **no effect on non-b-lactamase mediated resistance
clinical use-- • broad spectrum, e.g. respiratory, abdominal, skin/soft tissue, bite wounds, resistant UTIs |
|
|
selected b-lactamase producing organisms |
• staph aureus • h. influenza • most anaerobes • many gram (-) bacilli |
|
|
PCN ADEs |
• rash, usually delayed • seizures, rare • abdominal discomfort • neutropenia • fever • (+) LFTs; oxacillin & nafcillin |
|
|
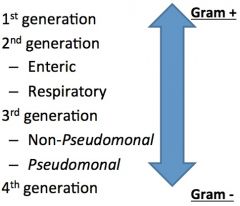
cephalosporins |
|
|
|
1st generation cephalosporins |
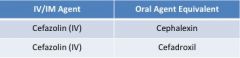
clinical use-- • primarily GPC infections EXCEPT enterococcus • garden-variety gram (-) bacillary infections • surgical prophylaxis & skin infections |
|
|
garden-variety gram (-) bacillary infections |
PECK • proteus • e. coli • klebsiella |
|
|
2nd generation cephalosporins: enteric |
clinical use-- • anaerobic coverage • enhanced GNR activity, but not GPC • surgical prophylaxis
NO ORAL AGENTS, ONLY IV/IM** • cefoxitin • cefotetan |
|
|
2nd generation cephalosporins: respiratory |
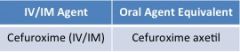
SAME IV/IM & ORAL! YAY!
clinical use-- • activity against h. influenzae • lower respiratory tract infections, e.g. h. influenza, s. pneumonia |
|
|
3rd generation cephalosporins: non-pseudomonal |
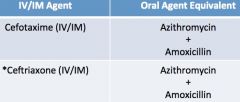
**no renal adjustment needed
clinical use-- • enhanced gram (-) activity • activity against PCN-resistant pneumococci • community acquired pneumonia • meningitis • gonorrhea |
|
|
3rd generation cephalosporins: pseudomonal |
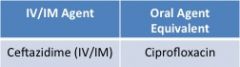
**least coverage of GPCs of all cephalosporins
clinical use-- • additional coverage of p. aeruginosa |
|
|
4th generation cephalosporins |
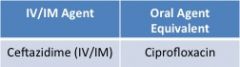
clinical use-- • best for GNR • exhibits excellent gram (+) & (-) activity • covers staph, strep, p. aeruginosa • can be used if isolate is resistant to 3rd generation cephalosporins |
|
|
cephalosporins ADEs |
• rash, delayed • seizure, rare • abdominal discomfort • neutropenia • fever • biliary sludging, ceftriaxone >> breaks up bile >> unable to excrete |
|
|
T/F. There is cross-sensitivity between cephalosporins and PCN. |
True; 10% |
|
|
carbapenems |
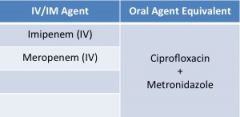
**broadest spectrum of all antibiotics
clinical use-- • serious infections w/ multi-resistant bacteria • pseudomonas infections • febrile neutropenia • mono therapy for polymicrobial infections |
|
|
carbapenem ADEs |
• rash, delayed • seizure; most common b/c it crosse BBB • abdominal discomfort • neutropenia • fever |
|
|
T/F. There is cross-sensitivity between carbapenems and PCN. |
True; 13% |
|
|
organisms resistant to carbapenems |
• ORSA • e. faecium • stenotrophomonas • burkhoderia • chlamydia • mycoplasma • corynebacterium |
|
|
monobactam |
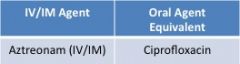
• no activity against gram (+) or anaerobes; only gram (-) • no cross-reactivity w/ B-lactam |
|
|
aminoglycosides |
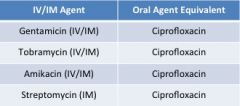
**not generally used as monotherapy **poor penetration into abscesses
clinical use-- • gram (-) • synergy for gram (+) |
|
|
aminoglycosides MOA |
• bactericidal • concentration dependent killing • inhibits protein synthesis |
|
|
aminoglycoside ADEs |
• nephrotoxicity; most common • ototoxicity, esp. if long term |
|
|
sulfonamides |
**sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim **bacteriostatic **inhibits cell growth by interfering w/ folic acid synthesis
clinical use-- • DOC for stenotrophomonas, nocardia, pneuocystitis jiroveci pneumonia • alternate therapy for systemic g(+) infections & g(-) skin infection • UTI, respiratory & abdominal infections |
|
|
T/F. Dosing for sulfonamides is based on the sulfamethoxazole component. |
False; trimethoprim |
|
|
sulfonamide ADEs |
• rash • photosensitivity • nephrotoxic • obstructive uropathy; stones may develop • neutropenia • thrombocytopenia • hyperkalemia |
|
|
fluoroquinolones MOA |
• broad spectrum against g(-) • poor anti-anaerobic activity • bactericidal • inhibits topoisomerase & DNA gyrase |
|
|
fluroquinolones |
**ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin
clinical use-- • variable anti-pseudomonal/streptococcal activity • covers OSSA but not ORSA reliably • UTIs, STDs, GI infections, osteomyelitis, mycobacterial infections |
|
|
fluroquinolones ADEs |
• photosensitivity • seizures • abdominal discomfort • QTC interval prolongation • CNS stimulation • tendon ruptures |
|
|
T/F. Fluroquinolones is safe to use during pregnancy. |
False; avoid in pregnancy |
|
|
When should fluroquinolones be taken? |
**2 hours before or after meals Avoid taking foods/medication w/ metallic cations, e.g. maalox, leafy green vegetables. |
|
|
T/F. Fluroquinolones are ideal agents for broad spectrum oral antibiotics. |
True |
|
|
tetracyclines MOA |
• bacteriostatic • inhibits ribosomal subunits in susceptible bacteria |
|
|
tetracyclines |
**tetracycline, minocycline, doxycycline
clinical use-- • community-acquired respiratory tract infection • STDs • lyme & rickettsial diseases • malaria prophylaxis • acne |
|
|
tetracycline ADEs |
• photosensitivity • abdomina discomfort • stained teeth |
|
|
T/F. Tetracycline absorption is increased with foods and metallic cations. |
False; decrease |
|
|
T/F. Doxycycline does not require renal adjustment. |
True |
|
|
macrolides MOA |
• bacteriostatic • binds to ribosomal subunits to inhibit RNA synthesis |
|
|
macrolides |
ezythromycin, azithromycin
clinical use-- • respiratory infection, i.e. legionella, mycoplasma, chlamydia pneumoniae • skin & soft tissue infections • STDs • h. pylori |
|
|
macrolide ADEs |
• abdominal discomfort • ototoxicity • taste disturbances, esp. metallic dry mouth |
|
|
T/F. Macrolides cause decreased clearance of many drugs via CYP450 inhibition. |
True; exception is azithromycin |
|
|
T/F. Macrolides should be avoided in pregnancy. |
False; only clarithromycin due to its category C rating |
|
|
T/F. Macrolides may also be used as an intestinal motility agent. |
True; has pro-kinetic effects |
|
|
lincosamides MOA |
• bacteriostatic & bactericidal • inhibits protein synthesis
|
|
|
lincosamides |
**clindamycin does not need renal adjustment
clinical use-- • anaerobic infections, esp. polymicrobial • aerobic g(+) • inhibits toxin release
ADEs-- • abdominal discomfort >> pseudomembranous colitis |
|
|
metronidazole |
**renal adjustment not needed
MOA-- • bactericidal • interacts w/ DNA >> loss of helical structure >> strand breakage
clinical use-- • anaerobic • protozoal infections • STDs • c. diff |
|
|
metronidazole ADEs |
• peripheral neuropathy • taste disturbances • disulfiram reaction; alcohol >> emesis • seizures • abdominal discomfort |
|
|
vancomycin |
MOA-- • bactericidal • glycopeptide inhibits cell wall synthesis
clinical use-- • ORSA & MRSA • empiric therapy for pneumococcal meningitis • oral therapy for c.diff |
|
|
vancomycin ADEs |
• ototoxicity • nephrotoxicity; not common--synthetic production has (-) ADEs • red-man syndrome • neutropenia |
|
|
linezolid |
**renal adjustment not needed
MOA-- • bactericidal in vivo, bacteriostatic in vitro • inhibits cell wall synthesis
clinical use-- • vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE) • systemic oral gram(+) |
|
|
linezolid ADEs |
**caution in liver failure
• thrombocytopenia • peripheral neuropathy • optic neuropathy • lactic acidosis |
|
|
daptomycin |
**surfactant deactivates daptomycin >> avoid in pneumonia
MOA-- • bactericidal • depolarizes cell wall
clinical use-- • VRE • ORSA • VRSA |
|
|
daptomycin ADEs |
• CPK elevations >> muscle/structural problems • myopathies >> avoid in combination w/ statins |
|
|
switching from IV to PO |
• WBC < 15,000 • ANC > 1000 • Tmax < 38 °C for 48 hours • functional GI tract • (-) blood cultures for 48 hours • (-) CSF cultures for 10 days • non ICU status, clinically responding to current treatment |

