![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nodal Agents – “Rate Control”
ABCD |
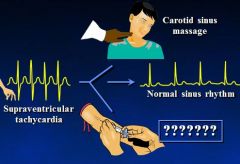
Adenosine
Beta Blockers (class II) Ca++ Channel Blockers (class IV) Digoxin |
|
|
adenosine
|
|
|
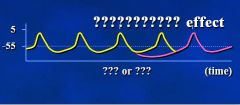
Acetylcholine/adenosine effect
|
|
|
adenosine MOA in the heart
|
Activates IKAch channels via Gβγ ⇨ hyperpolarizing force slows down AV nodal rate
↓ cAMP via Ga → decreased DAD’s, EAD’s |
|
|
Where is the A1 receptor found in the heart?
|
SA/AV Nodal Cells >> Cardiocytes
|
|
|
what is an adenosine antagonist found in many beverages?
|
caffeine
|
|
|
adenosine pharmacology
|
Extensive first pass metabolism
Re-uptake blocked by Dipyridamole Methylxanthines block A1 receptor |
|
|
adenosine S/E
|
Chest Discomfort, Bronchospasm
|
|
|
Beta 1 Selectivity
|
Metoprolol, Atenolol and Esmolol >>>>
Propranolol, Nadolol and Carvedilol |
|
|
adverse effects and toxicity of Ca++ blockers
|
Dizziness, headache, flushing, hypotension, edema, constipation, GERD, CHF, bradycardia and heart block (greater with verapamil)
|
|
|
lipid soluble beta blockers
|
Propranolol and Metoprolol
|
|
|
water soluble beta blockers
|
Nadolol, Atenolol, Esmolol
|
|
|
metoprolol metabolism
|
CYP2D6
|
|
|
propranolol metabolism
|
high first pass metabolism
|
|
|
Which β blockers would you ↓dose in renal dysfunction?
|
Atenolol and Nadolol
|
|
|
mechanism of Ca++ channel blockers
|
block voltage-gated “L-type” Ca++ channels --> ↓iCa++ in cardiac and vascular smooth muscle --> ↓HR and contractility and relax blood vessels
|
|
|
Which β blockers would you ↓dose in liver dysfunction?
|
Metoprolol and Propranolol
|
|
|
Dihydropyridines
|
Nifedipine
Amlodipine |
|
|
non-Dihydropyridines
|
Diltiazem
Verapamil |
|
|
digoxin MOA
|
Digoxin ┤Na+/K+ ATPase → ↑intracellular Na+ → ↑ Na+/Ca++ pump → ↑ intracellular Ca++
|
|
|
digoxin and contractility
|
↑Ca++ → +inotropic action
|
|
|
digoxin and HR
|
digoxin ↑vagal impulses and ↓sinus rate
|
|
|
How does digoxin act on atria at toxic levels?
|
increases sympathetic tone and Ca2+ loading leading to increased automaticity and DAD’s (delayed afterdepolarizations)
|
|
|
Why would you avoid digoxin in Wolf-Parkinson White syndrome?
|
It may improve conduction in some accessory pathways
|
|
|
What does P-glycoprotein have to do with digoxin?
|
It excretes absorbed digoxin back into gut lumen (also controls renal elimination)
|
|
|
Quinidine + digoxin =
|
Increases digoxin levels by displacing from binding sites and inhibiting P-glycoprotein system
|
|
|
Amiodarone, Propafenone, or Verapamil + digoxin =
|
decreases digoxin renal and non-renal clearance
|
|
|
cyclosporine, anti-fungals, benzodiazepines + digoxin =
|
inhibit P-glycoprotein so ↑digoxin
|
|
|
non cardiac symptoms with digoxin toxicity
|
anorexia, nausea, vomiting, changes in color vision including scotoma, halo vision and altered color perception
|
|
|
cardiac digoxin toxicity
|
Delayed afterdepolarizations (DADs)
|
|
|
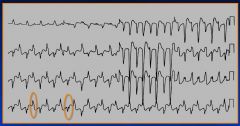
Bidirectional Ventricular tachycardia (think digoxin toxicity → Ca++ overload)
|
|
|
What are some drugs that cause INCREASED Digoxin?
|
Amiodarone
Cyclosporin Erythromycin Quinidine Tetracycline Verapamil |
|
|
What drugs cause DECREASED Digoxin?
|
Cholestyramine
Neomycin Rifampin |
|
|
Why do you have to push adenosine so quickly?
|
T1/2 < 10 sec
|
|
|
Adenosine + Verapamil
|
⇧risk of VF (Ventricular fibrillation)
|
|
|
adenosine + theophylline≈(caffeine)
|
decreased efficacy
|
|
|
Why would a patient on metoprolol or propranolol get depressed?
|
they are lipid soluble beta blockers
|
|
|
β blockers % protein bound
|
Esmolol (55%) > Nadolol (30%) > Metoprolol/Atenolol (10%)
|
|
|
Why does % protein bound matter in pharmacology?
|
if ↓liver function then ↓albumin
|
|
|
Elimination Half Life for beta blockers
|
Nadolol (20 hours) >>> Atenolol (6-7 hours)/Metoprolol (3-7 hours)/Propranolol (4 hours) >>> Esmolol (10 min)
|
|
|
Only true once a day β blocker?
|
Nadolol
|
|
|
Which β blockers are renally excreted?
|
Atenolol and Nadolol
|
|
|
Which Ca++ channel blockers are used for HR control?
|
Diltiazem
Verapamil |
|
|
Verapamil metabolism
|
CYP3A4
|
|
|
Antidote for digoxin?
|
Digoxin Immune Fab (Digibind®)
|

