![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
163 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
non-insulin medications for DM
3 main categories |
1-oral for DM -II
2-injectable for DM II
3-injectable for DM I |
|
|
|
oral medications for DM II categories # 7 |
1-Biguanide = metformin
2-insulin secretagogous ((SFU / non-SFU))
3-DPP-IV
4-TZDs = pioglitazone
5-a-glucosidase inhibitors
6-bile acid sequestrant
7-dopamine receptors agonist |
|
|
|
biguainide |
metformin |
|
|
|
SFUs secretagogues |
(Glyb)uride / (gli)penclimide |
|
|
|
non-SFUs secretagogues |
Nate(glinide) |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors |
acarbose |
|
|
|
thia-zolidin-diones |
pio-glita-zone |
|
|
|
DPP-4 |
sita-gliptin |
|
|
|
bile acid sequestrant |
cole-seve-lam |
|
|
|
dopamine receptor agonist |
bromocriptine mesylate |
|
|
|
2-injectable for DM II |
GLP agonist |
Liraglutide |
|
|
2-injectable for DM II + I |
amylin analog |
pramlinitide |
|
|
************** |
***************88 |
************** |
|
|
Biguanide
example |
metformin |
|
|
|
metformin
doses forms / tab |
500
850
1000 |
|
|
|
metformin
dose / day
|
start by 500-850 once
increase every days - wks
|
start
500 X2
850 X1 |
|
|
meformin extended release |
Glucophage XR
500 X1 then increase up to 2000/d |
|
|
|
metformin
max dose |
max 2000 mg / day
? 200 - 2550 |
|
|
|
metformin
mechanism of action |
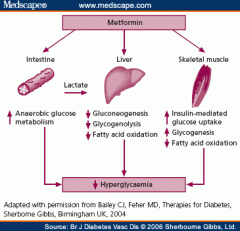
1-inhibits hepatic glucose output
2-decrease GI glucose absorption
2-stimulate periphral glucose uptake/ sensitivity |
|
|
|
metformin
advantages |
wt loss
no hypoglycemia |
|
|
|
metformin
administration |
with food |
|
|
|
metformin
side effects |
1-GI
2-lactic acidosis
3-asthenia /weakness |
|
|
|
metformin
contraindications |
1-CHF
2-M.acidosis
3-DKA
4-cr > 1.5 male / > 1.4 fem
5-contrast within 48 hrs before / after
6-lactation
7-shock
|
|
|
|
metformin
when to D/C during hospitalization |
-trauma
-fever
-stress
-avoid with alcohol
-infection |
|
|
|
metformin
pregnancy |
B |
|
|
|
metformin
uses / |
montherapy / 1st line
as combination |
|
|
|
meformin
brand names |
-glucopahge
-Diamet
-formit
-metforal
-Mystro |
|
|
|
metformin combination available |
meformin + Glmepride
metformin + glibenclimide
metformin + vildagliptin
metformin + sitagliptin
metformin + saxaglibtin _____________________
metformin + pioglitazone
|
|
|
|
metformin + glimepride |
amaryl M
500 / 2 |
|
|
|
metformin + glibenclimide |

Glucovance
500 / 2.5
500 / 5 |
|
|
|
metformin + vildagliptin |
Galvusmet
1000 / 50
850 / 50 |
|
|
|
metformin + sitagliptin |
janumet
500 / 50
1000 / 50
1000 / 100 (ER) |
|
|
metformin + saxaglibtin |

kombiglyza XR
500 / 5
1000 / 2.5
1000 / 5 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1111 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
DDP-IV ??? |
dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhib
=gliptins |
|
|
|
DDP-IV
mechanism of action |
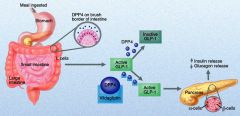
1-L-cells in intestine
2-L-cells secreates the enzyme DPP-IV
3-DPP4 breaks down GLP
4-GLP is an (incretin) that secraeted from L-cells
5-GLP act ti inhibit glucagon and stimulate insulin |
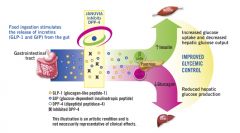
GLP = incretin |
|
|
GLP ?? |
Glucagon-like-peptide
is an incretin |
|
|
|
incretin ?? |
group of gastrointestinal hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels by : 1-inhibiting glucagon 2-stimulating insulin
|
|
|
|
incretin examples ?? |
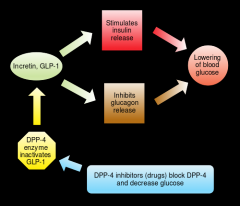
only 2 : ______________________ 1-GLP : glucagon-like-peptide
2-GIP :gastric inhibitory peptide |
|
|
|
DPP- IV ?? |
is the enzyme that inhibits incretin and breaks them |
|
|
|
DPP-IV
side effects |
-pancreatitis مهم مهم مهم / نادر
-angioedema
-Steven Johnson synd |
|
|
|
DPP-IV
Examples #4 |
1-sitagliptin = jinuvea
2-saxagliptin = Ongelyza
3-linagliptin
4-vildaglibtin = |
|
|
|
Sitagliptin
generic name
|
JANUVIA |
|
|
|
Sitagliptin
administration |
once daily |
|
|
|
Sitagliptin
dose |
100 mg
|
|
|
|
Sitagliptin
renal impairment |
renal elimenation
if GFR < 50
dose 50 mg |
|
|
|
Saxagliptin
generic name
|
Onglyza |
|
|
|
Saxagliptin
dose |
once daily
2.5 mg
5 mg |
|
|
|
Saxagliptin
renal imparment |
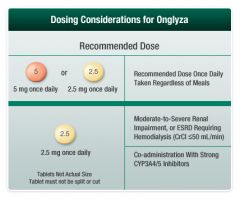
renal elimination
2.5 mg / day |
|
|
|
Saxagliptin
side effects |
urticaria
angioedema |
|
|
|
Vildagliptin
generic name |
Galvus |
|
|
|
Vildagliptin
dose |
once daily
50 100 mg |
|
|
|
Vildagliptin renal impairment |
not approved |
|
|
|
linagliptin
dose |
once daily
5 mg |
|
|
|
linagliptin
renal imparment |
fecal excreation
no adjustment |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
11 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
111 |
1 |
11 |
|
|
1 |
111 |
11 |
|
|
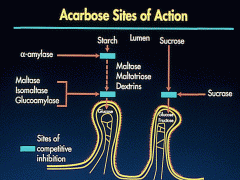
a-glucosidase inhibitors
mechanism of action |
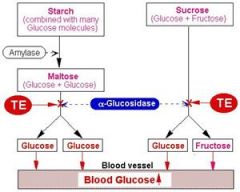
acts by inhibition of : -polusaccharides
-disacchardides breakdown to glucose so decreasing postprandial hyperglycemia |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
administration |
with meals |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
examples |
1-Acarbose
2-Miglitol |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
dose / initial
max |
300 mg / day |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
main side effect |
GI 25 - 50 % ____________________ bloating cramps diarrhea flatulance |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
HbA1c reduction |
modest
0.4 - 0.7 % |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
risk of hypoglycemia |
no |
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors acarbose
|
1 |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
acarbose
specific side effect |
elevated liver enzymes |
|
|
|
a-glucosidase inhibitors
if hypoglycemia while in regimen |
treat with glucose not sucrose |
|
|
|
***** |
*** |
|
|
|
*** |
**** |
*** |
|
|
*** |
*** |
**** |
|
|
*** |
********** |
******* |
|
|
**** |
***** |
*** |
|
|
TZDs ?? |
thia-zolidine-diones |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
mechanism of action?? |
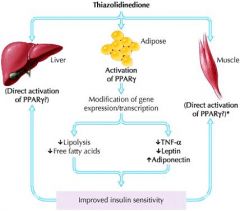
increased insulin sensitivity in : -,uscles
-adipose
-liver |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
examples |
only one : _____________________
Pioglitazone |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone
brand name |

Actos |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone
use |
as single agent
in combination
in pt early in DM , still have endogenous insulin |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone frequency of use |
once daily |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone dose |

15 - 30 mg daily
up to 45 /day |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone max dose |
45 mg daily
30 mg daily if used with insulin |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone contraindications |
combromized heart function NYHA III-IV
every pt must be assessed regarding cardiac function
active bladder CA |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone side effects |
- edema / CHF
-hepatotoxicity - rare
-bladder CA ?? still
-subclinical BM suppression (((with possible pancytopenia due to volume expansion))
-inhib. osteoblast : risk of fx in females
-ovulation in women with anovulatory cycles
-interactions / cyto-p450 |
|
|
|
TZDs thia-zolidine-diones
pioglitazone risk factors for precipitating heart failure |
-previous CHF -IHD -HTN -long-standing DM -left vent. hypertropthy -pre-existing edema -edema after TZDs therapy -insulin therapy -aging -renal failure -aortic stenosis -mitral valve disease |
|
|
|
actos u have to monitor >>>> |
liver enzemes |
|
|
|
actos and bladder CA ?? |
still under-study |
|
|
|
**** |
** |
** |
|
|
*88 |
88 |
88 |
|
|
88 |
88 |
88 |
|
|
88 |
88 |
88 |
|
|
88 |
88 |
88 |
|
|
dopamin rec agonist |
bromocriptin |
|
|
|
22 |
22 |
|
|
|
2222 |
22 |
222 |
|
|
22 |
22 |
22 |
|
|
22 |
11 |
|
|
|
Bile acid sequestrant
example
mech. of action |
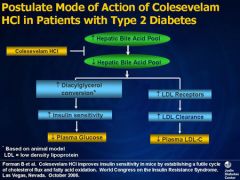
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride |
|
|
|
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride
use |
as monotherapy
combination |
|
|
|
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride
dose |

3 tabs X 2
((625 mg X2)) |
|
|
|
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride
administration |
empty stomach
not with other medications / not to interfere with their absorptions |
|
|
|
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride
HbAic lowering effect |
0.4 - 0.8 % |
|
|
|
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride
other benefit |
LDL lowering effect
can be used in pregnancy
can be used in renal + hepatic disease |
|
|
|
Cole-Sevelam hydrochloride
side effects |
constipation
Increases TG : triglecyrides |
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
11 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
insulin secretagogus
SFU
mechanism of action |
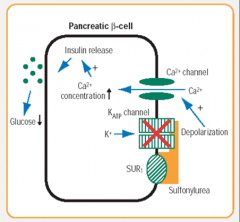
- increasing insulin secreation by binding to specific receptor at B-cells |
|
|
|
SFUs
administration |
before meals by 30-60 min
never to fasting |
|
|
|
SFU
frequency of pills |
once ( esp. lomg acting)
twice daily |
|
|
|
SFUs main side effects |
-hypoglycemia\\wt gain |
|
|
|
SFUs
examples #4 |
1-Gli(b)enclimide = Daonil= Glibil
2-Gli(m)epride = Amaryl / Glemax
3-Gli(c)lazide = Dimicron
4-Gli(p)izide |
|
|
|
Glibenclamide
other name |
Glyburide |
|
|
|
Glibenclamide
trade name |
Daonil
Glibil |
|
|
|
Glibenclamide
dose |
1.25 - 20
5 mg X2
10 mg X2 max |
|
|
|
Glibenclamide
renal impairment |
avoid
also in elderly
high risk of hypoglycemia |
|
|
|
Glibenclimide + metformin
brand name |
Glucovance
Diamet |

|
|
|
11 |
11 |
11 |
|
|
11111111 |
11 |
11 |
|
|
Glipizide |
short action 2-3 X once if ling acting |
|
|
|
1111 |
11 |
1111 |
|
|
11 |
11 |
1111111111 |
|
|
Gli(M)epride
administration
|
longest duration
once daily |
|
|
|
Gli(M)epride
brand name |
Amaryl
Glemax |
|
|
|
Gli(M)epride
doses |
1 mg >>>>> 8 mg |
|
|
|
Gli(M)epride + glucophage
brand |
Amaryl M |
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
Gli(c)lazide brand name |
Di-mi(c)ron
dimicron |
|
|
|
11 |
11111 |
1111 |
|
|
11 |
11 |
111111 |
|
|
non-SFUs segreatagogus
examples ((-glinide grop)) |
-meglitinide
-Repaglitinide
-nateglitinid
_________________________________- X3 with meals |
|
|
|
meglitinide
?? |
short acting secretagogus
5-20 X 3 (meals) |
|
|
|
Repaglitinide
|
short action / half life
within 30 min before meals
0.5 - 4 mg X 3 (meals)
hypoglycemia / wt.gain |
|
|
|
Natiglinide |
D-phenylalanine derevatives
within 10 mino of meals
low hypoglycemia risk
to control postprandial hyperglycemia
18- - 320 X 3 |
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
1111 |
|
|
11 |
11 |
1111 |
|
|
11 |
1 |
|
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
111111 |
1 |
|
|
|
injectable drugs for Type 2 DM |
GLP agonist |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
mechanism |
similar to endogenous GLP 1 = incretin
resistant to degradation by DPP-IV enzyme |
|
|
|
GLP agonist administration |
SC
|
|
|
|
GLP agonist
advantages |
- improved satiety
-wt loss |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
examples |
Exenatide
Liraglutide |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
Exenatide
doses/admin |
-daily doses (X3 meals)
-weekly dose |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
Exenatide
daily dose |
5 - 10 micg X3 |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
Exenatide
weekly dose |
2 mg / wk |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
Exenatide
side effects |
-pancreatitis
-renal impairment |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
Exenatide
advantages wt HbA1c |
-wt loss = 4 Kgg
-Hba1c 0.6 - 1.2 % |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
leraglutide |
SC
Once daily
0.6 ..... 1.2......1.6 |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
leraglutide
side effects |
-nausea
-vomitting
-dizziness
-headach |
|
|
|
GLP agonist
leraglutide
possible side effects in animal models |
increased calcitonin and thyrois]d medullary cancer |
|
|
|
injectable medication for type 1+2 |
Amylin analogues |
|
|
|
amylin analogue
mechanism |
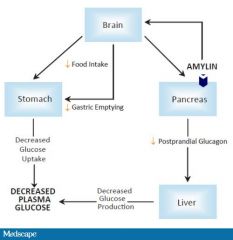
blunting postprandial BG |
|
|
|
amylin analogue
example |
pram-lintide
SC
15 - 120 mic
before meals |
|

