![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Difference between _________ and _________ is the s shape spine. |
hominids, humans |
|
|
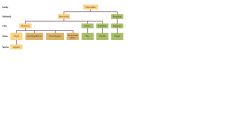
Hominoids are divided into 3 familys : |
Hominidae( hominids/humans) , Pongidae (pongids aka gorillas or great apes), and Hylobatidae (gibbons)
|
|
|
taxonomic classification placed below subfamily and above genus |
tribe |
|
|
member of the subfamily homininae, which includes the African Apes and humans |
Hominine |
|
|
condition in which the lower first premolar is somewhat sharpened or flattened from rubbing against the upper canine as the mouth closes |
shearing complex |
|
|
Disadvantages of Bipedalism |
Less Speed Less Agility Less Stability more stress on joints child birth is much more difficult and risky because of the skeletal structure required of bipedalism |
|
|
boundary between the pilocene and pleistocene epochs about 1.8 mya |
Pilo-Pleistocene |
|
|
The first homonins were found principally in _______. |
Africa (Afropithecus, Kenyapithecus, and Samburupithecus) |
|
|
d |
|
|
|
|
|
prognathism |
condition in which the jaw projects behind the upper parts of the face |
|
|
first lower premolar that exhibits its lateral (side to side) compression due to its role as a shearing surface for the upper canine tooth; related to the shearing complex |
sectorial premolar |
|
|
Differences between Australopithecines and Earlier Hominins |
Austra: Bipedal Anatomy, Thick molar anatomy, small canines and reduced shearing complex Early Hominins- possibly bipeds, thin and thick molar enamel, reduced canines |
|
|
From Australopithecines to recent humans |
increase in brain size increase in body size increasing use of and sophistication in tools increasing tooth size decreasing skeletal robustness |
|
|
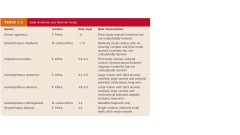
Orrorin Tugenesis Fossil Location: Date: Characteristics |
E. Africa , 6 Mya ; thick molar enamel hominine but not undoubtedly hominin |
|
|
Sahelanthropus Tchadensis Fossil Location: Date: Characteristics |
N. Central Africa 7-6 Mya Relatively small canines with no shearing complex and thick molar enamel, hominine but not undoubtedly hominin |
|
|
*Ardi(Floor)pithecus Ramidus Fossil Location: Date: Characteristics |
E. Africa 5.8-4.4 Mya Walked Upright, Thin molar enamel, reduced canines, forward placed foramen magnum, hominine but not undoubtedly hominin |
|
|
*Australopithecus anamensis Fossil Location: Date: Characteristics |
E. Africa 4.5 - 3.9 Mya Chimp like characteristics, Large molars with thick enamel, relatively large canines and semisectorial premolar, bipedal anatomy, long arms |
|
|
*Australopithecus Afarensis Location: Date: Characteristics |
DIscovered by Donald Johnson (1974) E. Africa 3.9-3.0 Mya Thought to be ancestral to both homo, and austropithecus. Large molars with thick enamel, relatively large canines and semisectorial premolar, bipedal anatomy, long arms |
|
|
Australopithecus bahrelghazali Fossil Location: Date: Characteristics |
N. Central Africa 3.3 Mya Mandible fragment only |
|
|
Kenyanthropus Platyops Fossil Location: Date: Characteristics |
E. Africa 3.5 mya single cranium, relatively small teeth, thick molar enamel |
|
|
Dates are formed by : |
1. Discovery 2. Publication/ Acceptance 3. Stratigraphic Record |
|
|
Discovered by Ramond Dart in 1924 South Africa Cave Sit Child 3-5 Years old 410 cc brain case canine teeth which were small not ape like position of foramen magnum |
Taung Child |
|
|
epoch that occured between 5.0 and 1.8 mya |
Pliocene |
|
|
evolutionary change and adaptation through both somatic (biological) and extrasomatic (material/cultural) means |
biocultural evolution |
|
|
epoch dating from 1.8 million to 10,000 years ago |
pleistocene |
|
|
area that consists of two or more habitat types |
mossaic habitat |
|
|
the hominin genus to which humans belong ; characterized by bipedal locomotion, large brains, and biocultural evolution |
homo |
|
|
a ridge running between the parietal bones along the top of the cranium, usually representing increased bone area for the attachment of chewing muscles |
saggital crest |
|
|
the characteristic of having larger postcanine teeth than would be expected for body size, measured as MQ |
Megadontia |
|
|
cheekbones; arches created by the meeting of extensions of the temporal and _______bones in the cranium |
zygomatic arches |
|
|
measure of premolar/ molar tooth area relative to body size |
megadontia quotient (MQ) |
|
|
ability to grip objects forcefully with the phalanges of the hand and yet exert fine tuned control of the movement of the objects; includes the ability to grip items between the thumb and any of the fingers |
precision grip |
|
|
a robust projection at the front of the frontal bone on the cranium |
supraorbital torus |
|
|
relating to the first stone tools in the archaeological record , dating to about 2.5 mya and consisting of relatively simple flakes and choppers |
olduwan |
|
|
raised area , much less pronounced than a sagittal crest , where the parietals meet on top of the cranium |
sagittal keel (ridge) |
|
|
prounounced ridge at the rear most point on the occipital bone |
occipital torus (nuchal) |
|
|
incisor teeth with a shovel like grooved inner surface |
shovel shaped incisors |
|
|
relating to the type of stone tool that follows the olduwan in the archaeological record dating to about , 1.5 mya and consisting of bifaced tools (flaked on both sides) that are more complex to make and allow more kinds of manipulation than the earlier types |
Acheulean |
|
|
- Found in south africa -Discovered in 1947 by __________ at Sterkfontein in south africa. -Well preserved cranium of an adult -best specimen of africanus -Brain size is about 485 cc. |
Australopithecus Africanus, Robert Broom |
|
|
Who made fundamental contributions to our knowledge of humanity's early ancestor? |
Louis Leakey and Mary Leakey |
|
|
-Discovered by ___________ in 1959 at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania -Estimated age: 1.8 mya -Brain size is about 530 cc - First specimen of this species and Leaky briefly considered this a human ancestor |
Paranthropus Boisei, Mary Leakey |
|
|
- Discovered by the _________, in the early 1960's at Olduvai Gorge -A number of fragments were found including, a mandible(13 teeth), 2 parietal bones; 21 fingers, hand and wrist bones -Estimated age 1.8 mya -brain size of this child is about 363 cc (extrapolated to 590-710 for an adult) |
Homo habilis ( Olduvai hominid7), The leakey's |
|
|
- Discovered by ________, in 1972 at kaobifora in Kenya -Estimated age: 1.9 mya - Most complete habilis skull known -Brain size is 750 cc, large for habilis -Is perhaps a different species: Rudolfensis |
KNM-ER 1470, H.habilis, Bernard Ngeneo |
|
|
- Discovered by _________, in mid 1980's -Called "Turkena Bay" or " Nariokotome Bay" -12 years old, 5'3, 100 lbs - Close relative of modern humans - More rounded skull than earlier species, with higher "vaulting" -850 cc brain size -estimated age: 1.8 mya -Possible ancestor of both erectus and heidelbergenisis |
Homo ergaster, KNM WT 15000 , by Richard Leakey's group |
|
|
What are the three dates? |
1. Discovery 2. Stratigraphy 3. Publication/ Acceptance |
|
|
What are the three names used for naming the ancestors? |
1. Scientific name (linnaus name) 2.popular name 3. Accession #/name |
|
|
What are the new speculations on the cave? |
1. Fire appears natural, not human 2. Faces destroyed, supra-orbital torus eaten away 3. not man the hunter, man the hunted 4. Greater hyenas |
|
|
- Discovered on the islands of Java -"Java Man" 1891 -originally Pithecanthropus erectus -900 cc brain size - Now homo erectus |
Eigore Dubois |
|
|
-Discovered by _________, in 1975 at kaobi Fora - Estimated age 1.7 mya - almost complete cranium -brain size 850 cc -whole skull similar to Peking Man fossils - H- erectus (possibily ergaster) |
KNM-ER 3733, by Bernard Nganeo |
|
|
- In 1921, swedish geologist __________, finds molars of extinct __________ at Chou- Koutien, 25 miles south of Peking (Beijing) -In 1926, it was proved that it was a human -Project given to ___________, canadian Anatomist -More Molars found |
J Aummon Anderson, anthropoids, and given to Davidson Black ( The discovery and loss of peking man) |
|
|
In 1927, ___________, with chinese paleoanthropologist _________, announced that the molars are a new prehistoric genus called _____________. |
Davidson Black, Pei Wengkong, Sinanthropus Pekinensis aka Peking man |
|
|
In 1939, remaining of __ individuals in association with fire and tools |
37 |
|
|
How did they name the species that were found? and who named them? |
Scientist such as Marcellin Boute shortened the name of Sinothropus Pekinensis to Peking man and Pitheconthropus erectus to Java Man. |
|
|
How did the name Peking man became H. erectus? |
They were in the same species group so the peking man was reassigned to P. erectus and later discovered that p.erectus was in the same genus as homo sapiens so the species became homo erectus.
|
|
|
4 steps to abstract a discovery |
1.What looking for 2. How gonna find it 3. What did you find 4. Why is it important |
|
|
- Discovered by ____________ - Was the first hominid ancestor - discovered in Africa - Supported darwins ideas that closest living relatives of humans are African apes - Fiercely apposed by European establishment, especially by ____________, who claimed that it was indisputably an ape. |
discovered by Raymond Dart, and apposed by Sir Arthur Keith |
|
|
In 1947, ____________ visited south africa to examine ___________. - Left south africa convinced that his discovery was part of human family tree - Conclusion paved the way for acceptance of this discovery as human. - He later expose Piltdown man as a _______. |
Sir Wilfrid Le Gros Clark, Taung Child, Hoax |
|
|
How was the Taung Child Killed? |
First they thought it was killed by another hominid then thought that it was killed by a big carnivore like a leopard then they found specific marks on the taung child's skull and came to the conclusion that it was killded by a large bird |

