![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lumbar Lordosis |
The ventral curvature of the lumbar portion of the vertebral column that positions the center of gravity over the hind limbs so that the body does not fall forward. |
|
|
Ilium Broad and Bowl-Shaped |
The human ilium is shorter and broader than that of the apes Additionally, instead of being positioned primarily posteriorly, the "bowl" shape of the ilium provides stability during phases of walking where only one foot is on the ground. |
|
|
Long Hindlimb |
Gives a longer stride and makes bipedalism more energetically efficient. |
|
|
Valgus Angle |
The "knock-kneed" posture of humans to improve balance during walking when only one foot is on the ground. |
|
|
Arched Foot |
The human feet have a "double arched" structure. The bottom side (plantar) with reinforced connective tissue maintains this arch, like the string of a bow. The tissue then acts as a spring that stores energy for more efficient walking and provides "spring-back" during the toe-off phase of the stride. |
|
|
Long Feet with Short Toes |
The metatarsals are lengthened to increase stride length and make the gait more efficient. The phalanges are shortened as a consequence of them no longer being used to grasp organs. |
|
|
Adducted Big Toe |
The hallux of human feet is in line with the other digits, versus abducted like apes' hallux. |
|
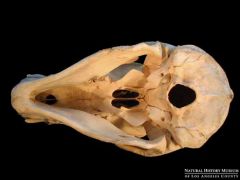
Baboon Foramen Magnum |
Anterior |
|
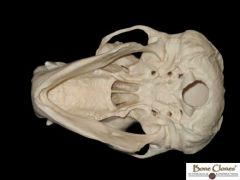
Ape Foramen Magnum |
Posterior |
|
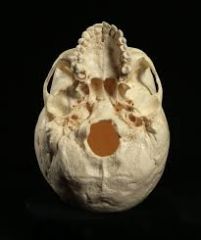
Human Foramen Magnum |
Anterior |
|
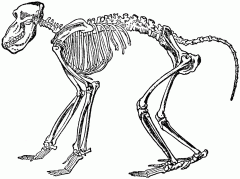
Baboon Vertebral Column Curvature |
"C" |
|
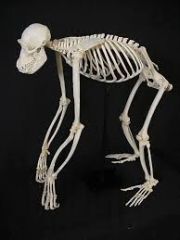
Ape Vertebral Column Curvature |
"C" |
|
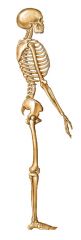
Human Vertebral Column Curvature |
"S" |
|
|
What age during development would you expect the lordosis to appear? |
12-18 months old |
|

Baboon Valgus Angle |
~85 degrees |
|
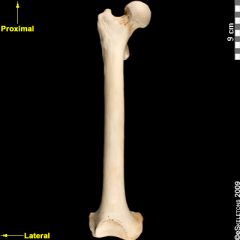
Ape Valgus Angle |
~90 degrees |
|

Human Valgus Angle |
~85 degrees |
|
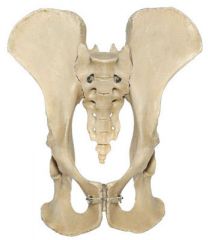
Ape Pelvic Shape |
Narrow and Long |
|
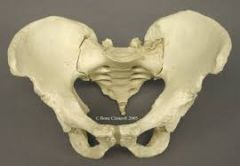
Human Pelvic Shape |
"Bowl-Shaped" |
|
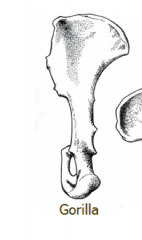
Ape Position of Iliac Blades |
Posteriorly |
|
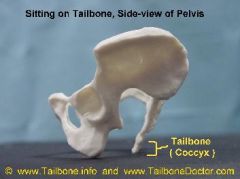
Human Position of Iliac Blades |
Anteriorly |
|
|
What are the consequences for human birth of the shape of the pelvic inlet and outlet? |
Human babies must complete a corkscrew maneuver during birth. |
|
|
When comparing the pelves of different eutherian species, why would you expect to see a relationship between pelvic anatomy and brain size? |
A smaller pelvis can only accommodate smaller-brained infants, while a larger pelvis can accommodate lager-brained infants. |
|
|
What are the consequences of the differences between male and female pelvic anatomy? |
Women are able to give birth easier, the center of gravity for women is in the hips, while men's is higher and they cannot give birth. |

