![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Relations of Production |
Ways humans organize themselves to get work done, products distributed & used No just physical products, but also classes and social structure Marxist theory |
|
|
Mode of Production |
Activities and tools used by society to satisfy its material needs
The political economic "social order" |
|
|
Economy = |
Natural Resources + labor + tools + knowledge/skill + "capital" (in some form) |
|
|
3 Phases of Economy |
1 - Production 2 - Distribution 3 - Consumption |
|
|
Production |
Economic phase where raw materials are turned into human "social or cultural" goods
|
|
|
Distribution |
Economic phase where goods are moved from the producers to the consumers
|
|
|
Consumption |
Economic phase where products are used.
|
|
|
Systems of Production |
1 - Foraging 2 - Pastoralism 3 - Horticulture 4 - Intensive Agriculture |
|
|
Autochthonous |
Belief that the people/culture arose directly from the earth
|
|
|
Swidden Agriculture |
"Slash-and-burn" agriculture Field rotation: after depletion (2-3 yrs) let plot return to nature & clear new area Not in the large commercial sense |
|
|
Intensive Agriculture |
High-input, high-yield farming techniques Uses plows, irrigation, fertilizer & draft animals. Lead to more "permanent farmlands" |
|
|
Civilization |
Form of society based around cities & typically dependent on intensive agriculture
|
|
|
Market |
A place & practice for exchanging value based goods
|
|
|
Types of Distribution Systems |
1 - Reciprocity 2 - Redistribution 3 - Market exchange |
|
|
Forms of Reciprocity |
1 - Generalized 2 - Balanced 3 - Negative Reciprocity has no hub/center for distribution |
|
|
General Reciprocity |
Goods given without determining value and without expectation for "return" goods It's understood people will share |
|
|
Balanced Reciprocity |
Goods have estimated value and have expectation of equal value return in reasonable time |
|
|
Negative Reciprocity |
Goods given with calculated value with an expectation or intent of receiving more value than one gives Most closely resembles the "modern market" |
|
|
Redistribution |
Exchange of wealth or surplus collected by a hub group that controls distribution and use Controlled hub/center is key characteristic |
|
|
Market Exchange |
Distribution using a specific location, & impersonal principles of supply & demand, to pursuit profit |
|
|
Two principles in Marx's view on the importance of society's material basis |
1 - it is NOT equivalent to socialists or communists 2 - Capitalism is NOT the same as 'the market' or 'market economy' |
|
|
Anthropological view of economy |
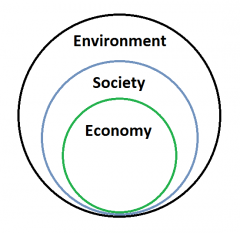
|
|
|
6 initial domesticate crops |
1 - Wheat 2 - Barley 3 - Rice 4 - Millet 5 - Tubers 6 - Maize |
|
|
Social Control
|
Process of directing members of the group to perform their duties, follow norms & "do the right thing" ad defined by society
|
|
|
Externalized Control
|
Creation & enforcement of appropriate behavior by others, such as parents, teachers, police, etc.
|
|
|
Agents of Social Control
|
Those who instill the social norms in an individual. Ex: Parents, teachers, peers, etc. |
|
|
Internalized Control
|
Process by which a person conforms to the societal standards |
|
|
Sanctions
|
Tools the agents of social control can use when people violate the norms
|
|
|
Formal Sanction
|
Punishments that are explicit & well known Often written down & administered by a specific authority |
|
|
Informal Sanction
|
Reward or punishment that is understood by the society, but not written or truly defined
|
|
|
Authority
|
Legitimate power of person, group or institution to enforce norms
|
|
|
Office
|
More or less formal social position with specific rights & duties
|
|
|
Persuasion
|
Intermediate power based on one's ability to influence or manipulate people to comply
|
|
|
Symbolic Capital
|
Resources that can be used for influence Ex: Knowledge, social relationships, flags, myths, etc. |
|
|
Integration typologies as stated by Elman Service in Primitive Social Organization |
BAND TRIBE CHIEFDOM STATE <---------------------------------------------------------------> Least Most Integrated Integrated |
|
|
Band
|
Small, autonomous, & typically leaderless group
|
|
|
Leveling Mechanism
|
Practice used to establish or re-establish social equality
|
|
|
Tribe
|
Multiple local communities organized into a single system, with informal power |
|
|
Chiefdom
|
Multiple local communities under a central office with formal political power & redistributive control over surplus |
|
|
State
|
Formal centralized government with power over a defined territory. Establishes laws, collects taxes, maintains army, etc. |
|
|
Diffusion
|
Spread of a cultural trait - objects, ideas, practices, etc. |
|
|
Secondary Innovation
|
Combination of already existing principles or objects |
|
|
Cultural Loss
|
Process of losing cultural traits over time Syn: Deculturation |
|
|
Acculturation
|
Process of acquiring a second culture
|
|
|
Ethnocide
|
Destruction of a group's culture without killing the people
|
|
|
Directed Change
|
Planned, coordinated & sustained efforts to change part or all of a culture
|
|
|
Colonies of Settlement
|
Colonies where many foreigners immigrate, sometimes to the point they become the majority |
|
|
Colonies of Exploitation
|
Colonies where few foreigners immigrate, but territory is used for resources or strategic location |
|
|
Internal Colonialism
|
When a society penetrates a territory with in its borders, but people in this area do not relate to occupying society Ex: Pre-Civil War northern societal influence over the south |
|
|
Goals of Colonialism
|
1 - Wealth 2 - Resources 3 - Land 4 - Labor |
|
|
Methods of Colonialism
|
1 - Taxation 2 - Markets 3 - Geopolitics |
|
|
Doctrine of Discovery
|
European colonial principle that whoever arrived first had the right to occupy & administer without interference
|
|
|
Terra nullis
|
Doctrine that "empty land" (without inhabitants) could be claimed & settled
|
|
|
Geopolitics
|
Use of territory for maintenance & projection of power
|
|
|
Plural Society
|
Group of cultures that occupy same area by do not interact except in limited ways
|
|
|
Identity Politics
|
Politics of identity Ex: Prussia splitting into two cultures, Germany & Austria |
|
|
Communal Representation
|
Practice of setting aside representation for the various cultures within the government
|
|
|
Self-determination
|
Concept that groups have the right to choose their own political arrangements & their collective destiny |
|
|
Nation
|
Corporate group that shares a political identity
|
|
|
Country
|
Territory that a society inhabits
|
|
|
Multinational State
|
Contains some or all of two or more cultures Ex: Iraq |
|
|
Multi-state Nation
|
Cultural group that spans two or more state borders Ex: Kurds |
|
|
Prenational Group
|
Social group that has yet to achieve mobilization & self-awareness of a nation
|
|
|
Potential Nation
|
Group in the process of becoming a nation
|
|
|
Offshoot Nation
|
Group that emerges as a local or historical branch of an older group, eventually pursuing its own culture
|
|
|
Diaspora
|
Dispersion of a social group from its homeland
|
|
|
State Terrorism
|
Use of force & terror by a government against a portion or all of its people
|
|
|
Separatism
|
Movement with goal of cultural/political disengagement of two groups
|
|
|
Primary Production
|
Production of raw materials in form of farming, mining, etc.
|
|
|
Gross National Product GNP |
Total value of goods & services provided by a society or state |
|
|
Gross Nation Product per Capita
|
GNP divided by population
|
|
|
Relative Poverty
|
Possession of less money than others in the same society
|
|
|
Absolute Poverty
|
Level of income below what is required to have a decent standard of living
|
|
|
Development
|
Form of directed change where a state tries to change its internal economy & society or foreign state tries
|
|
|
Development Policy
|
General priorities & decisions set by a state to achieve goals
|
|
|
Import Substitution
|
Policy to produce internally what the nation is currently importing
|
|
|
Structural Adjustment
|
Changes required of a government that is receiving outside developmental aid |
|
|
Social Impact Analysis
|
Fieldwork study of consequences of a development project on affected peoples |
|
|
Sociocultural Appraisal
|
Study of appropriateness of a development or social change project, its impact on affected groups, & distribution of benefits
|
|
|
Multilateral Development Institutions
|
Organizations that are funded & operated by more than one government for the purpose of development Ex: World Bank & International Monetary Fund |
|
|
Modernization Theory
|
Theory that improvement of socioeconomic conditions in poor states entails the creation of "modern" institutions
|
|
|
Dependency Theory
|
Theory that Third World underdevelopment is caused by their dependence on First World countries for key economic resources
|
|
|
World Systems Theory
|
Theory that Third World underdevelopment is caused by external arrangements with global economics set up by the First World countries for their advantage, and the disadvantage of the underdeveloped country
|
|
|
Core
|
States that make up the center of the world system Mostly rich industrial states & former colonialists |
|
|
Periphery
|
Societies & states with least wealth, power & influence |
|
|
Semi-periphery
|
States that are not as dependent as periphery states, but are not influential enough to be core states
|
|
|
Market-dominant Minority
|
Ethnic minorities that tend to dominate economically under market conditions |
|
|
Overurbanization
|
Growth of large cities without the infrastructure to handle it
|

