![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
165 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What main artery is located underneath the pterion?
|
anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
If the thin bones of the pterion were fractured, what might this cause?
|
rupture of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery can result in a hematoma with increasing pressure on the underlying cortex, death in a few hours.
|
|
|
What type of suture would be needed to save the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery after a blow to the pterion fractured the cranium?
|
Sphenoparietal suture
|
|
|
The bones of the cranium are joined by interlocking _____ suture joints, except for the mandible which articulates at the synovial temporomandibular joint.
|
fibrous
|
|
|
what are the Sphenoid and occipital bone are united by during childhood?
|
hyaline cartilage (synchondrosis)
|
|
|
what are the 8 bones of the neurocranium?
|
frontal, 2 parietal, 2 temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid
|
|
|
What part of the cranium Contains the proximal parts of the cranial nerves and the vasculature of the brain?
|
neurocranium (brain box)
|
|
|
Bones of the calvaria are flat bones derived from ___ ___ tissue that becomes head mesenchyme
|
neural crest
|
|
|
Flat bones of the calvaria are formed by ____ ossification
|
intramembranous
|
|
|
the cranium can be divided into which two parts?
|
neurocranium and viscerocranium
|
|
|
Bones of the cranial base are primarily irregular with significant flat portions, they are formed by ____ ossification or both methods
|
endochondral (or both includes intramembranous)
|
|
|
What are the bones of the viscerocranium?
|
Viscerocranium has 14 bones: 2 lacrimal, 2 nasal, 2 maxillae, 2 zygomatic, 2 palatine, 2 inferior nasal conchae, mandible, and vomer
|
|
|
what part of the cranium Contains the orbits (eye sockets) and nasal cavities, upper and lower jaws?
|
viscerocranium
|
|
|
in the dura, Notice that the ____ _____ protrude cranially and leave impressions on the interior superior aspect of the calvaria.
|
arachnoid granulations
|
|
|
What can be seen between the inner and outer tables of the calvaria?
|
Diploë
|
|
|
what is the Pericranium?
|
(periosteum of the cranium)
|
|
|
what are the inner and outer tables?
|
of the calvaria, the compact bone layers are frequently referred to as the inner and outer tables
|
|
|
what is the cancellous bone between 2 layers of compact bone referred to as in the center?
|
diploë
|
|
|
What transmits the diploic veins that communicate with the cranial dural sinuses via emissary veins - AND also contains red marrow in vivo?
|
Diploë
|
|
|
What is seen in the anterior view of the skull?
|
frontal bones, nasal bones and internasal sutures, zygomatic bones, maxillae, mandible and orbit
|
|
|
from the anterior view of the skul, What forms the skeleton of the forehead (develops as 2 bones)?
|
Frontal bone (squamous part)
|
|
|
Inferior to the nasal bones is the _____ (pear shaped) aperture, which is the anterior nasal opening of the cranium
|
piriform
|
|
|
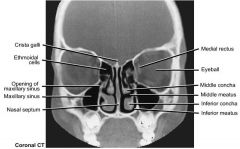
Nasal septum divides nasal cavity in two halves and is predominantly made up of the perpendicular plate of the ____ bone and the ____ , but also includes the palatine bone.
|
ethmoid ; vomer
|
|
|
What are the (curved bony plates) occupy lateral wall of nasal cavity?
|
Nasal conchae
|
|
|
Superior and middle conchae are part of the _____ bone. The inferior nasal conchae are individual bones.
|
ethmoid
|
|
|
which bones make up the prominence of the upper cheek ?
|
Zygomatic bones
|
|
|
what bone forms the upper jaw and contain the alveolar process which include the tooth sockets (alveoli)?
|
Maxillae
|
|
|
Paired maxillae unite at the ____ suture.
|
intermaxillary
|
|
|
What is the lower jaw bone called?
|
Mandible
|
|
|
Which bone is easily injured by a sharp upward blow to the nose, causing bone fragments to pass through the ciribiform plate? What does this cause?
|
ethmoid bone. Fragments through cribriform plate into the meninges or brain tissue. This can cause leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the nasal cavity and maybe followed by the spread of infection from the nasal cavity to the brain
|
|
|
If the ehtmoid bone is fractured, fragments might pierce what plate? (causing damage to the meninges and brain tissue - and leading to a brain infection)
|
ciribiform plate
|
|
|
if the ciribiform plate is pierce by bone fragments , as in a collision, what might leak into the nasal cavity?
|
This can cause leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the nasal cavity and maybe followed by the spread of infection from the nasal cavity to the brain
|
|
|
What foramina transmit terminal sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve?
|
"anterior foramina (4) - 1) Supraorbital notch/foramen transmits the supraorbital nerve and vessels 2) Zygomaticofacial foramen transmits the zygomaticofacial nerve 3) Infraorbital foramen transmits the infraorbital nerve and vessels. 4) Mental foramen transmits the mental nerve and vessels
|
|
|
____ _____ are relatively sharp ridges and a blow here, such as during a boxing match or fist fight, may lacerate the skin and cause bleeding. Tissue fluid and blood can accumulate around the orbit and into the thin skin of the eyelids leaving a “black eye” (echymosis).
|
Superciliary arches
|
|
|
____ are fibrous joints between the bones of the skull
|
Sutures
|
|
|
When do sutures of the calvaria eventually disappear?
|
At ages 30-40 the sutures of the calvaria begin obliteration on the internal surface and about 10 years later on the external surface
|
|
|
what disease is the premature closure of the cranial sutures? (causing cranial malformations 1/2000 births)
|
Craniosynostosis
|
|
|
which suture lies between the frontal bone and the 2 parietal bones ?
|
Coronal
|
|
|
which suture lies between the 2 parietal bones?
|
Sagittal
|
|
|
which suture lies between the parietal bone and the squamous part of the temporal bone?
|
Squamous
|
|
|
which suture lies between the two parietal bones and the occipital bone?
|
Lambdoid suture (resembles Greek letter λ)
|
|
|
There is also a highest nuchal line, which provides attachment for the ___ ____.
|
galea aponeurotica
|
|
|
what are Sutural bones occurring along the lambdoid suture, or on the lateral aspect, also known as?
|
Wormian bones
|
|
|
What bone has superior and inferior temporal lines
|
parietal
|
|
|
what bone has mastoid and styloid processes, zygomatic arch, external acoustic meatus, and a squamous part?
|
Temporal
|
|
|
what bone is in the medial wall of the orbit?
|
Lacrimal
|
|
|
what bone has an angle, mental protuberance, body, and ramus?
|
Mandible
|
|
|
what is the junction of lambdoid and sagittal sutures known as?
|
Lambda
|
|
|
what is the junction of the sagittal and coronal sutures known as?
|
Bregma
|
|
|
what is the junction of frontal, parietal, temporal bones, and greater wing of the sphenoid on the lateral aspect of the skull known as?
|
Pterion
|
|
|
what is a thin part of the calvaria overlying anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery?
|
Pterion
|
|
|
what is the intersection of the frontal and 2 nasal bones known as?
|
Nasion
|
|
|
what is the highest point of the superior aspect of the skull?
|
Vertex
|
|
|
what is the prominence of frontal bone above root of nose (depression between the supercilliary arches) known as?
|
Glabella
|
|
|
A fracture at the pterion, the thinnest part of the calvaria may lacerate the anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery causing what?
|
a epidural hematoma.
|
|
|
what can cause a hematoma that may compress the lateral part of the cerebral hemisphere and result in herniation of the medial part of the temporal lobe through the tentorial notch of dura?
|
pterion fracture with damage to middle meningeal a.
|
|
|
what kind of fracture can cause limb weakness, dilated pupil from compression of the oculomotor nerve, and deterioration of cardiovascular and respiratory function?
|
pterion fracture with damage to middle meningeal a.
|
|
|
A pterion fracture may casue neurological signs up to several ____ after the initial injury, as blood accumulates to the point at which pressure on the brain reaches a critical value.
|
hours
|
|
|
what are 3 cranial fossae?
|
ant, mid, post
|
|
|
which cranial fossa is the Shallowest of the 3 fossae?
|
Anterior Cranial Fossa
|
|
|
which fossa is Made up of frontal bone, ethmoid, body and lesser wings of sphenoid?
|
Anterior Cranial Fossa
|
|
|
which fossa is Butterfly shaped?
|
Middle Cranial Fossa
|
|
|
which cranial fossa Contains the sella turcica?
|
Middle Cranial Fossa
|
|
|
which cranial fossa is the Largest and deepest, comprised mostly of occipital bone?
|
Posterior Cranial Fossa
|
|
|
which fossa Holds cerebellum, pons, and medulla?
|
Posterior Cranial Fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Foramen cecum
|
Anterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Olfactory foramina of cribriform plate
|
Anterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina
|
Anterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Optic canal
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Superior orbital fissure
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Foramen rotundum
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Foramen ovale
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Foramen spinosum
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Carotid canal
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Hiatuses and canals for the greater and lesser petrosal nerves
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Foramen lacerum (only a foramen in a preserved skull, in life it is filled with cartilage)
|
Middle cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Internal acoustic meatus
|
Posterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Jugular foramen
|
Posterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Hypoglossal canal
|
Posterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Foramen magnum
|
Posterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
which fossa has the following?: Condylar canal
|
Posterior cranial fossa
|
|
|
What passes through the optic canal?
|
1. Optic nerve (CN II) 2. Opthalamic a.
|
|
|
the Optic nerve (CN II) passes through which opening in the cranial fossa?
|
middle cranial fossa - optic canal
|
|
|
Ophthalmic artery passes through which opening in the cranial fossa?
|
middle cranial fossa - optic canal
|
|
|
what passes through the Superior orbital fissure?
|
ALTOS! Abducent nerve (CN VI), Lacrimal frontal and nasociliary branches of opthalamic nerve, Trochlear nerve (CN IV), Occulomotor nerve (CN III), Superior opthalamic vein
|
|
|
Oculomotor nerve (CN III) passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
Trochlear nerve (CN IV) passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
Lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
Abducent nerve (CN VI) passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
Superior ophthalmic vein passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
what passes through the Foramen rotundum?
|
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
|
|
|
Maxillary nerve (CN V2) passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - foramen rotundum
|
|
|
what passes through the Foramen ovale?
|
MAL - Mandibular nerve (V3), Accessory meningeal a. , Lesser petrosal nerve
|
|
|
Mandibular nerve (CN V3) passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - foramen ovale
|
|
|
Accessory meningeal artery passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - foramen ovale
|
|
|
Lesser petrosal nerve passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - foramen ovale
|
|
|
what passes through Foramen spinosum?
|
4M's! Middle Meningeal artery and vein, Meningeal branch of Mandibular nerve (V3)
|
|
|
Middle meningeal artery and vein passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - foramen spinosum
|
|
|
Meningeal branch of mandibular nerve V3 passes through which opening and cranial fossa?
|
Middle cranial fossa - foramen spinosum
|
|
|
Foramen lacerum contains what structures?
|
It is filled with cartilage. The greater petrosal nerve passes horizontally across foramen lacerum and traverses the cartilage. (carotid artery and plexus passes over this)
|
|
|
petrosal nerve traverses cartilage of what cranial structure, and in what fossa?
|
middle cranial fossa - foramen lacerum (filled with cartilage)
|
|
|
what structures pass through the Internal acoustic meatus?
|
FLV flash file! Facial nerve (CN VII), Labryinthe Artery, Vestibulocochlaear nerve (CN VIII)
|
|
|
Facial nerve (CN VII) passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
Posterior Cranial Fossa - internal acoustic meatus
|
|
|
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
Posterior Cranial Fossa - internal acoustic meatus
|
|
|
Labyrinthine artery passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
Posterior Cranial Fossa - internal acoustic meatus
|
|
|
what structures pass through the Jugular foramen?
|
Pedantic GLOSSy VAGinas Assaulted SIGfreid's Manhood - petrosal sinus (inferior), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), Vagus nerve (CN X), Accessory nerve (CN XI), Sigmoid sinus, Posterior meningeal artery
|
|
|
Inferior petrosal sinus passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa - jugular foramen
|
|
|
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa - jugular foramen
|
|
|
Vagus nerve (CN X) passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa - jugular foramen
|
|
|
Accessory nerve (CN XI) passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa - jugular foramen
|
|
|
Sigmoid sinus passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa - jugular foramen
|
|
|
Posterior meningeal artery passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa - jugular foramen
|
|
|
what are the contents of the Hypoglossal canal?
|
Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
|
|
|
Hypoglossal nerve (XII) passes through which opening and in what fossa?
|
posterior cranial fossa hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
what are the structures within the Foramen magnum?
|
medulla oblongota, meninges, meningeal branches of vert arteries, vert arteries, spinal roots of accessory nerves.
|
|
|
Spinal roots of accessory nerves is in what fossa and in what foramen?
|
posterior cranial fossa foramen magnum
|
|
|
The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the ____ bone anteriorly and the horizontal plates of the ____ bone posteriorly
|
maxillae; palatine
|
|
|
Superior to the posterior edge of the palate are 2 large openings, the _____ (posterior nasal apertures)
|
choanae
|
|
|
Incisive foramen transmits which nerve?
|
the nasopalatine nerve. It is posterior to the central incisor teeth (front teeth)
|
|
|
TRUE FALSE - Greater & lesser palatine foramina transmit the greater & lesser palatine nerves and vessels and the nasopalatine nerve.
|
FALSE - only because the nasopalatine nerve passes through the incisve foramen (anterior part of palate).
|
|
|
Stylomastoid foramen transmits which nerve?
|
the facial nerve (VII)
|
|
|
what transmits the internal carotid artery and accompanying sympathetic plexus?
|
Carotid canal
|
|
|
The ____ fontanelle is the largest and easiest to palpate
|
anterior
|
|
|
what are Regions of membrane between skull bones that are not yet ossified in the infant skull?
|
fontanelles
|
|
|
what allows deformation of the calvaria during the birth process?
|
Fibrous sutures and fontanelles
|
|
|
_____ ____ of the calvaria permit the cranium to enlarge through childhood (15-16 years) and there after enlargement is due to bone thickening for 3-4 years.
|
Fibrous sutures
|
|
|
The membrane of a fontanelle is blended with the ____ externally, and the ______ _____ internally.
|
pericranium , dura matter
|
|
|
What allows skull deformation during birth and allow the continued growth of the brain.
|
fontanelles
|
|
|
The fontanelles are usually closed by the ____ year.
|
2nd
|
|
|
in the birthing process, one ____ bone slightly overrides the other.
|
parietal
|
|
|
The Mandibular symphysis between the 2 developing parts of the mandible closes during the ___ year. Intermaxillary suture can be identified in the adult, there are 2 maxillae
|
2nd
|
|
|
The Metopic suture between 2 developing frontal bones allows skull deformation and closes during the ____ year leaving 1 frontal bone in the adult (there is short remnant of the metopic suture superior to the nasion)
|
6th
|
|
|
what is contained within: Ant Cranial fossa - Foramen Cecum?
|
nasal emissary vein (1% of pop)
|
|
|
what is contained within: Ant Cranial fossa - ciribriform foramina in cribriform plate?
|
axons of olfactory cells in olfactory epithelium that form olfactory nerves, (CN I)
|
|
|
what is contained within: Ant Cranial fossa - ant and post ethmoidal foramina?
|
vessels and nerves with same names as foramina
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - optic canals?
|
optic nerves CN II, and opthalamic arteries
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure?
|
ophthalamic veins, ophthalamic nerve (CN V1) CN III,IV, VI. And sympathetic fibers
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - foramen rotundum?
|
maxillary nerve (CN V2)
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - foramen ovale?
|
mandibular nerve (CN V3) and acessory meningeal artery
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - foramen spinosum?
|
middle meningeal artery and vein, and meningeal branch of CN V3.
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - foramen lacerum?
|
internal carotid artery, with its sympathetic and venous plexus.
|
|
|
what is contained within: Middle Cranial fossa - groove or hiatus of greater petrosal nerve?
|
greater petrosal nerve and petrosal branch of middle meningeal artery.
|
|
|
what is contained within: Posterior Cranial fossa - foramen magnum?
|
medulla and meninges, vert arteries, CN XI, dural veins, ant and post spinal arteries
|
|
|
what is contained within: Posterior Cranial fossa - jugular formaen?
|
CN IX, X, and XI, sup bulb of internal jugular vein, inf petrosal and sigmoid sinuses, and meningeal branches of ascending pharyngeal and occipital arteries
|
|
|
what is contained within: Posterior Cranial fossa - hypoglossal canal?
|
hypoglossal nerve CN XII
|
|
|
what is contained within: Posterior Cranial fossa - condylar canal?
|
emissary vein that passes from sigmoid sinus to vertebral veins in neck
|
|
|
what is contained within: Posterior Cranial fossa - mastoid foramen?
|
mastoid emissary vein from sigmoid sinus and meningeal branch of occipital artery.
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: nasal emissary vein (1% of pop)
|
Ant Cranial fossa - Foramen Cecum
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: axons of olfactory cells in olfactory epithelium that form olfactory nerves, (CN I)
|
Ant Cranial fossa - ciribriform foramina in cribriform plate
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: ethmoidal vessels and nerves
|
Ant Cranial fossa - ant and post ethmoidal foramina
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: optic nerves CN II, and opthalamic arteries
|
Middle Cranial fossa - optic canals
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: ophthalamic veins, ophthalamic nerve (CN V1) CN III,IV, VI. And sympathetic fibers
|
Middle Cranial fossa - superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: maxillary nerve (CN V2)
|
Middle Cranial fossa - foramen rotundum
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: mandibular nerve (CN V3) and acessory meningeal artery
|
Middle Cranial fossa - foramen ovale
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: middle meningeal artery and vein, and meningeal branch of CN V3.
|
Middle Cranial fossa - foramen spinosum
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: internal carotid artery, with its sympathetic and venous plexus.
|
Middle Cranial fossa - foramen lacerum
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: greater petrosal nerve and petrosal branch of middle meningeal artery.
|
Middle Cranial fossa - groove or hiatus of greater petrosal nerve
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: medulla and meninges, vert arteries, CN XI, dural veins, ant and post spinal arteries
|
Posterior Cranial fossa - foramen magnum
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: CN IX, X, and XI, sup bulb of internal jugular vein, inf petrosal and sigmoid sinuses, and meningeal branches of ascending pharyngeal and occipital arteries
|
Posterior Cranial fossa - jugular formaen
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: hypoglossal nerve CN XII
|
Posterior Cranial fossa - hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: emissary vein that passes from sigmoid sinus to vertebral veins in neck
|
Posterior Cranial fossa - condylar canal
|
|
|
what foramen do the following structures pass through?: mastoid emissary vein from sigmoid sinus and meningeal branch of occipital artery.
|
Posterior Cranial fossa - mastoid foramen
|
|
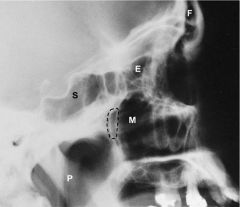
Sinuses Lateral Photograph
|
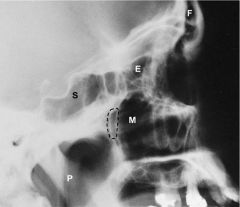
Sinuses Lateral Photograph
Frontal Ethmoid Maxillary Sphenoid Pharynx |
|
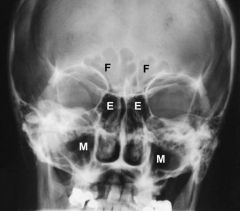
Sinuses PA Radiograph
|
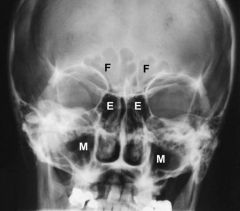
Sinuses PA Radiograph
Frontal sinus Ethmoid sinus Maxillary sinus |
|
|
|

