![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
WHat are three components of the autonomic nervous system?
|
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic enteric |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE: preganglionic cell bodies are found in the PNS.
|
FALSE. Preganglionic neurons are still in the CNS.
|
|
|
where are postglanglionic sympathetic neuronal cell bodies located?
|
in ganglia
|
|
|
where are postglanglionic parasympathetic neuronal cell bodies located?
|
in visceral wall or ganglia close to organ
|
|
|
The sympathetic nervous system has preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord in what vertebral levels?
|
the sympathetic nervous system is also known as the thoracolumbar division, because of its location from T1 - L2 or L3
|
|
|
sympathetic motor fibers will synpase in ___vertebral ganglia or travel via ____ nerves to ____vertebral ganglia.
|
para;
splanchnic ; pre |
|
|
preganglionic sympathetic motor fibers use ____ as a neurotransmitter.
|
acetylcholine as neurotransmitter; cholinergic
|
|
|
postganglionic sympathetic neurons use ___ neurotransmitters except where?
|
for the most part - epinephrine or norepinephrine. THE EXCEPTION is sweat glands, where acetylcholine is used, (and adrenal glands, where a preganglionic fiber innervates this)
|
|
|
The cells of the intermediolateral cell column use acetylcholine as their transmitter. Their axons leave the spinal cord via the ___ roots.
|
ventral; intermediolateral cell column is the pathway in the lateral horn from T1 - L2 or L3, and is therefore the presynaptic/thoracolumbar division of the sympathetic nervous system.
|
|
|
the sympathetic chanin is comprised of ___ pairs of ganglia.
|
31
|
|
|
The prevertebral ganglia receive preganglionic axons via what?
|
the splanchnic nerves.
|
|
|
The preganglionic neurons that have their axons in the splanchnic nerves are found within the intermediolateral cell column of the spinal cord at which levels?
|
Greater T5-T9 (working nerve) 9 to 5!
Lesser T10-T11 Least (T11)-T12 |
|
|
The greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves arise in the thorax, but innervate what?
|
abdominal viscera.
|
|
|
The prevertebral (collateral) ganglia contain ____ sympathetic neurons that receive _____ axons via the _____.
|
postganglionic
preganglionic thoracic/abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves |
|
|
The white ramus communicans contains (pre/post?)ganglionic neurons, that (ARE/ARE NOT) unmyelinated.
|
PREganglionic; they are myelinated (are not)
|
|
|
the gray rami communicantes contains unmyelinated ___ganglionic axons.
|
post
|
|
|
Injury to any of the neurons or axons in what pathway can result in a Horner’s syndrome?
|
The superior cervical ganglion is the sympathetic ganglion of the head. Postganglionic axons leave the ganglion and travel along blood vessels to reach their targets in the head.
|
|
|
Horner's syndrome has what two characteristics?
|
1. Ptosis (drooping eyelid)
2. Miosis (small pupil) |
|
|
where are preganglionic neurons for the parasympathetic nervous system found?
|
Located in brainstem nuclei or sacral spinal cord
|
|
|
preganglionic neurons for the parasympathetic nervous system use what neurotransmitter?
|
acetyl choline
|
|
|
postganglionic neurons for the parasympathetic nervous system use what neurotransmmitter?
|
acetyl choline
|
|
|
postganglionic neurons for the parasympathetic nervous system are found where?
|
in the wall of viscera
|
|
|
the enteric nervous system is formed by neural ___ cells that move to gut wall during development.
|
crest
|
|
|
what are the plexuses of the enteric nervous system?
|
Submucosal or Meissner’s plexus
AND Myenteric or Auerbach’s plexus |
|
|
what does the Myenteric or Auerbach’s plexus do?
|
Regulates peristalsis and sphincters
|
|
|
Submucosal or Meissner’s plexus do?
|
Regulates secretion by glandular epithelial cells
Regulates motility of muscularis mucosa Some may be sensory neurons that help signal presence of material in lumen |
|
|
True/False - the enteric nervous system works in the absence of input from the brain and spinal cord
|
true
|
|
|
What are four steps in peristaltic reflex?
|
Bolus of material distorts mucosa
Enterochromaffin cells release serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT stimulates nerve endings in lamina propria Cell bodies of these sensory neurons in the submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus Sensory neurons activate motor neurons in myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus |
|
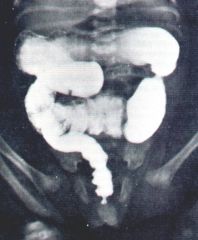
Describe this disease.
|
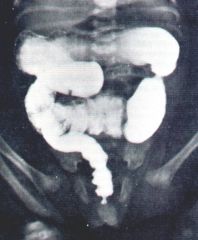
Hirschsprung’s Disease
Also known as congenital aganglionic MEGAcolon There is a failure of neural crest cells to migrate into the distal colon 1:5000 births Males affected more than females 4:1 |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of the disease in which there is a Loss of myenteric neurons (Auerbach’s plexus) in lower the esophagus?
|
Achalasia
Formerly called cardiospasm Onset 25-60 years Men=women Loss of myenteric neurons (Auerbach’s plexus) in lower the esophagus Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) paralyzed in constricted state Esophagus dilated |
|
|
in visceral afferents:
Pain afferents travel With the _____. Stretch afferents travel With the _____. |
sympathetics
parasympathetics |
|
|
What is the reason for referred pain?
|
Pain associated with visceral disease and inflammation is referred to the abdominal wall.
This is because visceral nociceptive (pain) afferents enter the spinal cord with somatic afferents. All pain fibers run with the sympathetic system and enter the spinal cord at the same segment that gives rise to the preganglionic efferents. |
|
|
what is a common type of referred pain caused by heart problems?
|
Angina pectoralis is most well known
|
|
|
Case Presentation: A 65-year-old man comes to his physician complaining of pain in upper back on the right side. During the history, the physician notes that the man’s right eyelid is drooping. During the examination, the physician notices that the man’s right pupil is small and unresponsive to light. In addition, the man’s facial skin on the right side is dry and appears flushed as compared to that on the left side of his face. A thoracic MRI reveals a right posterior wall mass between the 1st and 2nd ribs.
What is the most likely cause of this man’s problems? Where are the preganglionic neurons that are affected? Where are the postganglionic neurons that are affected? |
What is the most likely cause of this man’s problems?
Compression of the sympathetic chain or T1 white ramus communicantes. Where are the preganglionic neurons that are affected? T1 level of the intermediolateral cell column. Where are the postganglionic neurons that are affected? Superior cervical ganglion. |

