![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The epidermis is ____ in origin.
|
ectodermal
|
|
|
The epidermis has what epithelial characteristics?
|
stratified squamous, keratinized epithelium
|
|
|
What are 5 types of layers found in the epidermis?
|
Layers (strata)
1. Stratum germinativum 2. Stratum spinosum 3. Stratum granulosum 4. Stratum lucidum 5. Stratum corneum (comes off on keyboards) |
|
|
Stratum Germinativum
also called stratum basale is a single layer of ___ or ____ which rest on the basal lamina. |
cuboidal or columnar
|
|
|
How are the basal cells of the straum germinativum attached to the basal lamina? How are these cells attached to adjacent cells?
|
by hemidesmosomes; then to other cells by desmosomes.
|
|
|
This cell layer is made up of polygonal cells that have spiny projections that form “intercellular bridges”. These bridges were once believed to represent sites of cytoplasmic continuity between cells. They are now known to be locations of desmosomes that contribute to the cohesiveness of the epidermis. Mitoses seen in this layer as well
|
epidermis - straum spinosum
|
|
|
The stratum germinativum and stratum spinosum are frequently referred to as the____.
|
malpighian layer. This region of keratinocyte proliferation is named after the Italian histologist Marcello Malphigi.
|
|
|
This layer is characterized by basophilic granules, keratohyaline granules, which are not membrane bound. There are also membrane bound granules called membrane-coating granules. These granules contain glycosaminoglycans and phospholipids that are extruded out into the extracellular space to form a barrier to micro-organisms, foreign substances and most importantly water.
|
Stratum Granulosum
|
|
|
It is most prominent in thick skin. In thin skin, this layer is often not identifiable. It is a translucent layer of normally very acidophilic cells that are devoid of nuclei and organelles.
|
Stratum Lucidum
|
|
|
What is the name of the epidermal layer that contains flattened keratin-filled cells devoid of any organelles including the nucleus? (They are also called horny cells or squams.)
|
Stratum Corneum
|
|
|
What is the characteristic of a 1st degree burn?
|
Damage to superficial epidermis
Cells of stratum germinativum remain viable and regenerate epidermis |
|
|
What is the characteristic of a 2nd degree burn?
|
Epidermis completely destroyed
Remnants of sweat glands and hair follicles in the dermis are able to regenerate the epidermis |
|
|
What is the characteristic of a 3rd degree burn?
|
Full-thickness burn
Destroys epidermis and dermis Skin grafts are typically necessary Loss of body fluids can cause hypovolemia and shock - With 15% of body area in adults - With 10% of body area in children |
|
|
what are four Cells types Found in Epidermis?
|
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes Langerhans cells Merkel Cells |
|
|
What is the origin of Melanocytes?
|
neural crest
|
|
|
what is the origin of keratinocytes?
|
ectodermal origin
|
|
|
What are Langerhan's cells?
|
Dendritic, antigen presenting cells
|
|
|
What are Merkel Cells? and what is their origin?
|
Specialized keratinocyte that is involved in touch.
must be ectodermal if it is a keratinocyte deriviative. |
|
|
what do keratinocytes produce?
|
the protective dead cell layer, the stratum corneum.
|
|
|
What are 70% of skin cancers?
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Where do basal cell carcinomas arise?
|
arise in regions of skin containing sebaceous glands.
typically on eyelids and bridge of nose in fair-skinned 40-yr-olds. |
|
|
True /False: Basal Cell carcinomas typically metastasize.
|
false, they rarely do this.
|
|
|
in basal cell carcinoma - what is different about the basal cell?
|
Histologically basal cell carcinoma cells form discrete nests or islands of cells that resemble normal basal cells
|
|
|
What makes up 20% of skin cancers?
|
squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Fair-skinned blonds with outdoor occupations are particularly prone to this form of cancer
|
what is squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
in squamous cell carcinoma, Histologically, there is a complete replacement of normal epithelium with ____ cells.
|
pleomorphic (capable of assuming different shapes )
|
|
|
What is the metastasis rate of squamous cell carcinomas?
|
Relatively few squamous cell carcinomas (2-5%) metastasize to regional lymph nodes.
|
|
|
These dendritic cells are mainly found in the stratum spinosum.
They are NOT attached to adjacent keratinocytes by desmosomes. They are similar to dendritic cells seen in lymphoid tissues. They are responsible for engulfing invading micro-organisms in the epidermis and presenting antigens to lymphoid cells. |
langerhans cells
|
|
|
How are langerhans cell samples prepared?
|
Langerhans cells cannot be distinguished easily in H and E stained tissue. One must use gold impregnation techniques to visualize Langerhans cells.
|
|
|
What type of cell can act as a resevoir for HIV that is found in the epidermis?
|
langerhans cells
|
|
|
What type of cell can migrate out of the epidermis, enter lymphatics in the underlying dermis and travel to local lymph nodes.
|
langerhans cell
|
|
|
Where are melanocytes located?
|
stratum germinativum
|
|
|
True/False: Melanocytes cannot replicate.
|
false. Melanocytes can replicate slowly throughout life, thereby maintaining epidermal-melanin units (one melanocyte associates with a fixed number of keratinocytes).
|
|
|
What is not determined by race or gender?
|
among other things, Epidermal-melanin units
|
|
|
Melanocytes have which, hemidesmosome or desmosomes?
|
Melanocytes are NOT connected to surrounding keratinocytes by desmosomes, but can be attached to the basal lamina by hemidesmosomes
|
|
|
melanocytes contain a large amount of what substance, and what does it do?
|
Melanocytes contain large amount of the enzyme, tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is responsible for conversion of tyrosine through a series of steps to melanin.
|
|
|
What is cytocrine secretion?
|
A process in which Melanin granules are injected into keratinocytes.
|
|
|
Melanin granules take position above the nuclei of keratinocytes in the ____ and ____.
|
strata germinativum
spinosum |
|
|
Melanin granules eventually fuse with lysosomes in the keratinocytes and are degraded by the time the keratinocytes reach the ____.
|
stratum granulosum
|
|
|
______ of melanin granules is slower in darker-skinned races and melanin granules may be evident in the upper strata of the epidermis.
|
Lysosomal degradation
|
|
|
What are 2% of skin cancers?
|
malignant melanomas
|
|
|
what type of skin cancer, Because of the neural crest origin (i.e. highly migratory cells), are very metastatic?
|
malignant melanoma; Melanoma appears as nests of pigmented melanocytes that penetrate the epidermis.
|
|
|
Melanoma appears as nests of pigmented melanocytes that penetrate the epidermis. The cells also invade the dermis where they have access to ____ and ____.
|
blood vessels and lymphatics.
|
|
|
Where are merkel cells typically found?
|
They are primarily found in thick skin where touch is acute.
|
|
|
What type of cell in the epidermis contain 80nm neurosecretory granules?
|
merkel cells
|
|
|
What type of cell cannot be distinguished from keratinocytes in H and E preparations?
|
merkel cells, a specialized keratinocyte.
|
|
|
What are two distinc cell layers in the dermis?
|
papillary and reticular
|
|
|
which layer of the dermis has loose CT containing fibroblasts, mast cells and macrophages as well as some leukocytes - major part of the dermal papillae or pegs
|
papillary
|
|
|
which layer has dense irregular CT - composed of collagen fibers (type I) and fewer cells than the papillary layer
|
reticular layer
|
|
|
Where can you find thick (glaborous) skin?
|
Found in areas exposed to greater wear and abrasion.
The palms of the hands and the soles of the feet have classic examples of thick skin. |
|
|
What layers does thick skin have?
|
Thick skin has all five epidermal layers with a prominent stratum lucidum and a thick stratum corneum.
|
|
|
Does thick skin have sebaceous glands?
|
Thick skin is hairless and, as such, has no sebaceous glands.
|
|
|
Where can you find thin (hairy) skin?
|
Anywhere but the palms of hands and soles of feet.
|
|
|
thin hairy skin is missing what epidermal layer, and which layer is especially thin?
|
It typically has no distinct stratum lucidum and a thin stratum corneum
|
|
|
What lies deep to the dermis, but not considered part of the skin?
|
hypodermis;It is also called superficial fascia or subcutaneous CT.
|
|
|
What does the hypodermis contain?
|
loose CT with varying numbers of fat cells. The fat cells vary in size according to the degree of obesity of the individual
|
|
|
what are five appendages of the skin?
|
Hair follicles
Sweat glands Sebaceous glands Mammary glands nails |
|
|
Hair follicles are invaginations of epidermis which during periods of growth have what?
|
bulbous terminal dilations -the hair bulb.
|
|
|
the hair bulb of a hair follicle rests upon a dermal papilla that contains what?
|
the capillaries that nourish the hair follicle.
|
|
|
The cells of the hair bulb are like those of which epidermal cell layer?
|
the stratum germinativum.
|
|
|
Apocrine or Eccrine?
simple, coiled tubular glands - secrete a non-viscous fluid. Evaporation of the fluid cools skin. Sweat glands are also excretory. Sweat contains catabolites. |
Eccrine
|
|
|
Apocrine or Eccrine?
have lightly staining, simple cuboidal secretory acini (arrows) and darker staining, stratified cuboidal ducts (arrowheads) |
eccrine
|
|
|
What are myoepithelial cells?
|
specialized cells that squeeze the secretions from the sweat acini.
They are epithelial, not smooth muscle cells. They are acidophilic because they contain actin filaments. |
|
|
why are myoepithelial cells acidophilic?
|
they contain actin
|
|
|
Apocrine or Eccrine?
Specialized glands located in the axillary, areolar and anal regions. |
apocrine
|
|
|
Apocrine or Eccrine?
The ducts open into hair follicles and secrete a viscous, odorless fluid. The secretion attains a distinctive odor by the action of bacteria that reside on the skin. |
apocrine
|
|
|
The mammary gland is believed to be a highly modified what?
|
apocrine sweat gland
|
|
|
What do sebaceous glands develop in association with?
|
hair follicles; They are not found, therefore, on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet. (thick skin)
|
|
|
What locations do sebaceous glands exist without hair follicles?
|
They are found, however, in the skin of the lips, the glans penis and the clitoris where they are not associated with hair follicles.
|
|
|
what secrete sebum by holocrine secretion.
|
sebaceous glands
|
|
|
what sweat gland makes for good pimples? especially at puberty?
|
sebaceous glands
|
|
|
The cells at the base of a sebaceous gland are germinal cells. what happens to these cells As the cells fill with sebum?
|
their nuclei become pyknotic (irreversibly condensed) and eventually are lost.
|
|
|
blue nails indicate what?
|
Blue indicates poor oxygenation (cyanosis).
|
|
|
nails are plates of what?
|
keratinized epithelial cells
|
|
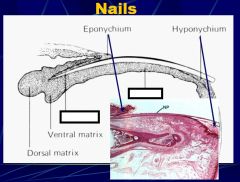
which part has the stratum germinativum and stratum spinosum only (the malpighian layer) ?
|
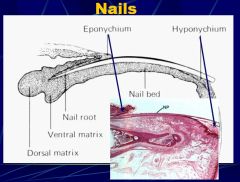
nail bed; this layer does not contribute to the nail plate.
|
|
|
Case Presentation: A 24-year-old blond, blue eyed woman has moved to Sarasota from Alaska. She finds Siesta Beach irresistible and spends 4-5 hours per day sunbathing using only coconut butter to get a deep, dark tan.
One year later, a darkly-pigmented, irregular lesion appears on her right upper pectoral region. On a visit to her dermatologist, the lesion was surgically excised and sent to a pathologist. The pathology report came back 4 days later and the lesion is malignant. What type of cancer does she have? What is the embryological origin of the cells that gave rise to the cancer? Is the risk of metastases high or low? |
melanoma;
neural crest; high |
|
|
Describe free nerve endings in the skin.
|
Unmyelinated axons that penetrate the basal lamina of the epidermis to enter the stratum germinativum and spinosum.
Ramify among the epithelial cells. Involved in temperature and pain perception. May also function in crude touch as evidenced by the fact that they are the only type of receptor found in the cornea. |
|
|
What are meissner's corpuscles?
|
most abundant in thick (glabrous) skin as well as in the skin of the lips and nipples.
These specialized encapsulated receptors can be found within the dermal papillae of thick skin. Involved in discriminative touch, ability to discriminate two points. |
|
|
What are Pacinian Corpuscles?
|
This encapsulated receptor is found in the dermis and often, the hypodermis, of both thick and thin skin.
Pacinian corpuscles are especially abundant in the skin of the fingertips. The corpuscle is traditionally described as a pressure sensor, but its rapid adaptation has lead some to believe the pacinian corpuscle signals a vibratory sense, i.e. it responds to a tuning fork placed against the skin. |

