![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
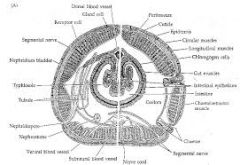
Phylum Annelida |
segmented worms=metamerism hydrostatic skeleton closed circulatory system has coelomate=cavity excritory system (kidney like structures) circular and longitudal muscles protosomes |
|
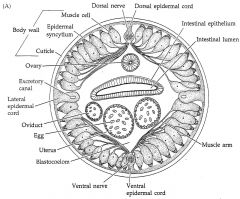
Phylum Nematoda |
Round worms Male= coiled end female= larger flat end have complete digestive tract has pseudocoelom which comes from blastoceoel just longitudal muscles(also move using hydrostatic skeleton) protosomes |
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda |
high level of cephalization (brain development, organs) open circulatory system Tagmatization(head and thorx that can fuse also abdomen) nostrils along abdomen protosomes |
|
|
Diff between metamerism and tagmatization |
Meta= segmentation Tag= specialization of those segmants |
|

Phylum Echinodermata |
Sea star radial bilateral hard exoskeleton deuterosomes |
|
|
Phylum Chordata |
has spinal cords some have backbones some do not(metameric) Special features 1.notochord 2. pharengial gil slits 3.post anal tail 4.dorsal hollow nerve chord Closed circulatory system heart chambers 2-fish 3-frogs 4-mammalls |
|
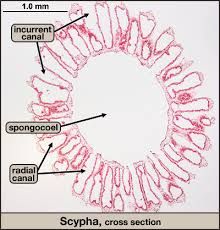
Phylum Porifera |
Sponges -choanocytes – flagelated for creating streamof water for feeding kinds of cells -amoebocytes moves nutrientsbetween cells Intracellular digestion (within cells) Spicules for support (made by amoebocytes) |
|
|
Phylum Cnidaria |
Stingers diploblastic radial symmetry polymorphic(two life cycle stages -polyps-sessile - Medusal-motile stinger cells on tenetacles are called( Cnidocytes) |
|
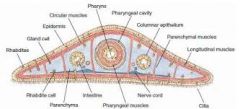
Phylum Platyhelminthes |
Flat worms tripoblastic no coelome cephalised longitudal and circular muscles |
|
|
Phylum Molusca |
Snails clams tripoblastic protosome development true coloeme |

