![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Chart |
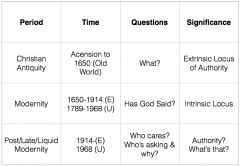
|
|
|
From The Chart: When was Christian Antiquity? What was the main question of the period? What was the significance? |
When: Ascension to 1650 (Old World) Question: "What?" Significance: Extrinsic Locus of Authority |
|
|
From The Chart: When was Modernity? What was the significance? |
When: 1650-1914 (E), 1789-1968 (U) Question: Has God said? Significance: Intrinsic Locus |
|
|
From The Chart: When was Post/Late/Liquid Modernity? What was the main question of the period? What was the significance? |
When: 1914- (E), 1968- (U) Question: Who cares? Who's asking and why? Significance: Authority? What's that? |
|
|
What is history? |
History is telling the truth about the past as best we can Truth can be known, though with difficulty and imperfectly |
|
|
Why is historical truth known imperfectly? |
Missing records Dead witnesses Lies Illiteracy Confused Historians Bad Theory (a priori, experience) By Praxis (mistakes) |
|
|
What are the types of history? |
|
|
|
Why study history? |
|
|
|
How do we study history? |
|
|
|
How should the study of history be done? |
|
|
|
When was the period of the ancient church? |
100AD - 500AD
|
|
|
What was the ancient church's view of ancient church historiography? |
|
|
|
What was the Golden Age view of ancient church historiography? |
|
|
|
What was the Reformation's view of ancient church historiography? |
|
|
|
What was the Tridentine Roman view of ancient church historiography? |
ANACHRONISTIC |
|
|
What was the Modern view of ancient church historiography? |
|
|
|
Adolph von Harnack |
|
|
|
What comes to mind considering Bauer, Bousset, Reitzenstein, and Bultmann? |
Moves to make Gnosticism normative (the standard) |
|
|
Walter Bauer, Orthodoxy & Heresy In Earliest Christianity |
|
|
|
What are works that follow the explosion of Gnostic studies post 1950's? |
|
|
|
Gnosticism Thesis: Gnosticism was a corruption of Christianity |
Gnosticism is mostly associated with the thought of salvation (from this evil world) through secret knowledge A Variety of Loosely Related Movements & Persons w/Common Themes & Interests |
|
|
What is alleged evidence and problems of pre-Christian Gnosticism? |
|
|
|
What is the problem with the thesis that Gnosticism preceded Christianity? (That Christianity emerged from Gnosticism) |
|
|
|
What are some attributes of Gnosticism in the 2nd century? |
|
|
|
Canon Thesis: The formation of the canon was neither a mechanical nor magical process - it was gradual |
Canon is derived from the rule or measure and refers to the collection of writings determined to be of religious and spiritual authority |
|
|
What supports the thesis of the canon formation? |
|
|
|
Tatian's Diatesseron |
|
|
|
Melito of Sardis (on topic of the canon) |
|
|
|
Origen (on topic of canon) |
|
|
|
What is the Sinaiticus? |
|
|
|
What are the Codex Vaticanus (4th c.) and Codex Alexandrinus (5th c.)? |
The oldest extant, nearly complete, manuscripts of the Greek Bible - Septuagint (OT) and NT |
|
|
Jerome (on topic of canon) |
|
|
|
Council of Laodicea |
|
|
|
When were the Regional Councils in Carthage? |
AD 393, 397 |
|
|
When were non-canonical and apocryphal books included? |
|
|
|
Describe the process of canonization |
|
|
|
What are some of the OT Pseudepigrapha? |
|
|
|
Describe/Name (some) the OT Apocrypha |
|
|
|
What are some of the NT Apocrypha and Pseudopigrapha? |
Gospels of... - Thomas - Ebionites - Peter - Judas |
|
|
What is a heresy? |
Broad: doctrinal or moral error Narrow: that which contradicts the catholic faith as defined by the catholic creeds (Apostles’, Nicene, Chalcedon, Athanasian) - Distinct from mere error |
|
|
What are some Scriptural proofs of heresy in the apostolic age? |
Acts 5:17 - sects 2 Peter 2:1 - false teachers |
|
|
Vincent of Lerins |
d.c. 450 Vincentian Canon ubique, semper, et ad omnibus believed "everywhere, always, by everyone" |
|
|
What is a Patristic? |
A theologian or writer from the 2nd century to the end of the 5th:
Eastern (Greek), Western (Latin) |
|
|
Platonism |
- One, Nous, World Soul |
|
|
Aristotle |
c. 384-322 BC
|
|
|
Zeno |
Stoicism (c. 300 BC) Physis of things Logos Universal Rational Principal |
|
|
Epicureanism |
Epicurus (d. c. 270 BC) Existential ---> sublime sense experience Atomism Skepticism |
|
|
Simon of Samaria |
- The "first heretic" mentioned by Irenaeus and Justin Martyr - Ontological Dualist - Arguments end before 200 AD |
|
|
Menander |
- Samaritan - Taught Gnostic Basilides - OD |
|
|
Ebionites |
- Jewish Christians in Trans-Jordan post 70 AD - Believed Jesus was adopted by God - 613 Mitzvoth (Ceremonial Law) - Ascetics - Rejected Paul |
|
|
Cerinthus |
fl. c. 100 - Regarded as early gnostic - World created by demiurge - Eternality of matter - Adoptionist Christology |
|
|
Basilides |
fl. 124-140 - Influential gnostic - Alexandria - Emanations: Nous, Logos, Phronesis, Sophia, Dynamis, Principalities & Angels, Salvation of souls to a select few |
|
|
Valentinus |
c. 115-165 - Most important 2nd cent Gnostic - Alexandrian - In Rome c. 135-165 - Elaborate hierarchical theology - Nag Hammadi Text |
|
|
Marcion |
d. c. 160 (Mvt till 450) - Son of bishop - Influenced by Gnosticism - Excommunicated - Starts Sect - Gospel = love & no wrath (no law) - No OT & NT connection - Docetic Christology - Only accepted Pauline Epistles (own canon) |
|
|
Montanus |
c. 156 - Visions of the end (continued rev) - Proto-Pentacostal (glossologia) - Two type of Christians (w/ and w/out gifts) - Chiliast - anticipating literal millennia reign - Rigorist - opposed lax church discipline - Either claimed to be HS or Mediator of HS - Reaction to Institutionalized church |
|
|
Sabellius |
3rd cent Monarchian Modalism: One God and different appearances/manifestation - Successive modes of being - Reduces the ontology of the Son |
|
|
Paul of Samosata |
3rd cent - Dynamic Monarchianism: powers of God, not person - Adoptionist - Bishop of Antioch/Deposed 268 AD |
|
|
Novatian |
d. 257 - Roman presbyter - Led schism when Cornelius was ordained Bp of Rome - Rigorist discipline = no re-admission to those that denied Christ in face of Roman pers - Opposed by Cyprian |
|
|
Arius |
c. 336 - Ascetic presbyter of Alexandria - c. 319 Subordinationism - "There was when the Son was not" |
|
|
When was the Council of Nicea? |
325 AD |
|
|
When was the Nicene Creed drafted? |
381 AD Nicene-Constanopolitan Creed |
|
|
Nestorius |
c. 351-451 - Monk in Antioch - Accused of teaching that Christ was two person (a divine and human) not two natures - Reaction to monophysite error - Condemned by Celestine & Roman cnl in 430 - Deposed in Ephesus in 431 & Banished |
|
|
Eutychus |
c. 378-454 - Contra Nestorius - Monophysite: Christ only divine nature (confused/conflated natures) - Denies consubstantiality of Christ humanity with ours - Deposed then Acquitted in 449 - Deposed and Exiled by Chalcedon in 451 |
|
|
Pelagius |
c. 380-410 - British ascetic and moralist - Drawn to Rome by Jerome's strong moralist teaching (c. 342-420) - Declared heretic by Carthage (412, 416, 418) - Opposed by Augustine |
|
|
Pelagianism |
- Adam = example (posse pecare, posse non pecare) - Denies Adams federal headship - Conflated Nature and Grace - Sinless perfection theoretically possible in this life |
|
|
What is the Pelagian fallacy? |
We have free will to choose to sin and to choose not to sin |

