![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of the lower extremity
|
-weight bearing
-locomotion -maintenance of equilibrium |
|
|
Composition of Pelvis (bones)
|
-2 innominate/coxal bones (ilium, ischium, pubis)
-sacrum -coccyx |
|
|
Sex differences of pelvic girdle
|
-subpubic angle: male=70deg., female=90-100deg.
-females have wider sacral width and iliac flare -females tend to have less thigh muscle development |
|
|
Joints of the pelvic girdle
|
-sacroiliac joint
-hip joint -pubic symphysis |
|
|
SI joint stabilizer ligaments
|
-sacrospinous ligament (dorsal sacrum to ischial spine)
-sacrotuberous ligament (dorsal sacrum to ischial tuberosity) |
|
|
Boundaries of the greater sciatic foramen
|
-anterior sacroiliac lig. (sup)
-sacrotub (post) -sacrospin (inf) -greater sciatic notch (ant) |
|
|
Boundaries of lesser sciatic foramen
|
-spine of ischium (sup/posterior)
-sacrotuberous (post/inf) -tuberosity of ischium (inf) -lesser sciatic notch (ant) |
|
|
Contents of greater sciatic foramen
|
-piriformis
-sciatic nerve -internal pudendal bv/n. -sup./inf. gluteal nerve/bv -posterior femoral cutaneous nerve |
|
|
Contents of the lesser sciatic foramen
|
-obturator internus
-internal pudendal vessels -pudendal nerve |
|
|
Hip joint
|
-acetabulum articulates with the head of the femur
-lunate lines inside of acetabulum but is incomplete -ligament of the head of the femur attached to inferior aspect -fibrous joint capsule w/deep synovial membrane |
|
|
Diagnostic measurements of the lower extremity
|
-angle of inclination
-quadriceps angle -angle of torsion |
|
|
Angle of inclination/normal measurement
|
-angle between median axis of femoral head and axis of femoral shaft
-normal=125deg. |
|
|
Coxa valga
|
-angle of inclination > 125 deg.
-leads to genu varum ("bowed-legs") -lengthens the lower extremity -increases load on femoral head, decreases load on femoral neck |
|
|
Coxa varum
|
-angle of inclination <125 deg.
-leads genu valga ("knocked-knees") -shortens lower extremity -reduces load on femoral head, increases load on femoral neck |
|
|
Quadriceps angle/normal measurement
|
-angle between axis that connects ASIS-patella midpoint and axis between patella midpoint-tibial tubercle
-men: 12 deg. -women: 17 deg. -estimates degree of genu valgum--part of basis of sex differences |
|
|
Sex differences in lower extremity function
|
-females: less muscular thigh development, less-developed VMO, increased flexibility in knee joint/genu valgum
-females: more muscular thigh development, VMO hypertrophy, less knee flexibility/genu varum |
|
|
Angle of torsion/normal measurement
|
-angle between axis of femoral condyles at knee and axis of femoral head
-normal=8-15 deg. |
|
|
Abnormal angles of torsion
|
-anteversion=increased angle-->pigeon-toed
-retroversion=decreased-->duck feet -abnormal angle causes the natural femur/extremity position to shift so as to maximize femoral head articulation with acetabulum |
|
|
Capsular ligaments and purpose
|
-iliofemoral
-ischiofemoral -pubofemoral -restrict extension of the hip |
|
|
Hip disolaction (posterior)
|
-most common, often MVC
-displacement/tearing of ischiofemoral ligament, ligament of femoral head -critical because possibility of disruption of sciatic nerve |
|
|
Fascia lata
|
-extension of inguinal ligament
- |
|
|
Femoral sheath
|
-continuation of iliacus/transversalis fascia inferior to inguinal ligament
-contains femoral a. v. |
|
|
Anterior fascia
|
-area of venous drainage
-saphenous opening: allows for passage of femoral a. and v. |
|
|
Muscles of the gluteal region
|
-gluteus maximus
-gluteus medius -gluteus minimus |
|
|
Gluteus maximus function & innervation
|
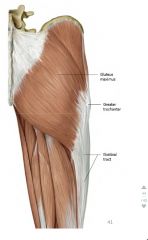
-extends, laterally rotates the thigh
-inferior gluteal nerve |
|
|
Gluteus medius location
|
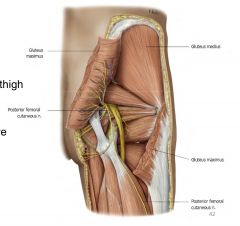
-deep/superior to maximus
|
|
|
Gluteus medius/minimus action/innervation
|
-abducts/medially rotates the thigh
-superior gluteal nerve |
|
|
Gluteus minimus location
|
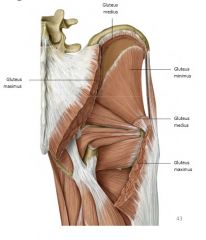
-deep to gluteus medius
|
|
|
Clinical presentation of hip abductor weakness
|
-trendelengurg gait
-pelvis tilts away from affected side while walking -gluteals (med/min) are abductors and help to keep pelvis level (tends to sink during leg swing); if they are weak, pelvis on opposite side will sink |
|
|
Lateral rotators of the hip (5/6), general attachments, innervation
|
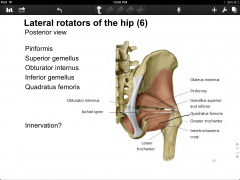
-piriformis
-superior gemellus -obturator internus -inferior gemellus -quadratus femoris -general attachments: posterior hip--greater trochanter/ intertrochanteric crest -innervation? |
|
|
Lateral rotator of hip (6/6), attachment, innervation
|
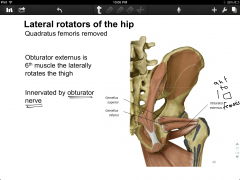
-obturator externus (anterior quadratus femoris)
|
|
|
Adductor longus attachments/action/innervation
|
-pubic crest to midshaft posterior femur
-adducts, flex thigh; also internal rotation due to anterior bowing of femur making distal attachment anterior to axis of femoral head -obturator nerve |
|
|
Compartments of the thigh
|
-anterior
-posterior -medial |
|
|
Fascia of thigh
|
-lateral intermuscular septum separates anterior/posterior compartments
-medial intermuscular septum separates anterior/medial compartments |
|
|
Muscles of anterior compartment of the thigh
|
-rectus femoris*
-vastus medialis* -vastus lateralis* -vastus intermedius* *make up "quads" -sartorius |
|
|
Action of the muscles of anterior thigh
|
-flex hip
-extend knee |
|
|
Innervation of the muscles of anterior compartment of thigh
|
femoral nerve
|
|
|
Bloody supply of the muscles of anterior compartment of thigh
|
femoral artery
|
|
|
Muscles of medial compartment of thigh
|
-adductor longus
-adductor brevis (deep to adductor longus) -adductor magnus -gracilis |
|
|
Action of muscles of medial compartment of thigh
|
-adduct thigh
-medially rotate thigh |
|
|
Innervation of muscles of medial compartment of thigh
|
obturator nerve
|
|
|
Blood supply of muscles of medial compartment of thigh
|
obturator artery
|
|
|
Adductor magnus attachments, action, innervation
|
-hamstring part: ischial tuberosity-adductor tubercle of distal femur, extends thigh, tibial division of sciatic nerve
-adductor part: ischial tuberosity-posterior femur, adducts thigh, obturator nerve |
|
|
Muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh
|
-"hamstrings"
-biceps femoris (long & short heads) -semimembranous -semitendinosus |
|
|
Action of muscles of posterior compartment of thigh
|
-extend hip
-flex knee |
|
|
Innervation of muscles of posterior compartment of thigh
|
tibial division of the sciatic nerve
|
|
|
Blood supply of muscles of posterior compartment of thigh
|
-profunda femoris artery
|
|
|
Lateral "aspect" of thigh
|
-iliotibial tract: thickening of the fascia lata
-attaches to gluteus maximus and tensor fasciae latae -runs alongside of thigh muscles and attaches at knee |
|
|
Femoral nerve (spinal nerve) origin
|
L2-L3-L4
|
|
|
Femoral nerve course
|
-saphenous branch descends through femoral triangle
-enters adductor canal -posterior/deep to inguinal ligament |
|
|
Obturator nerve (spinal nerve) origin
|
L2, L3, L4
|
|
|
Obturator nerve course
|
-emerges inferior to superior pubic ramus
-splits into anterior/posterior branch |
|
|
Sciatic nerve course
|
-between greater trochanter and ischial tuberosity
-splits (@biceps femoris?) into common fibular nerve and tibial nerve |
|
|
Borders/contents of femoral triangle
|
-inguinal ligament, adductor longus, sartories
-contains femoral nerve, a. and v. |
|
|
Joints of the knee
|
-tibiofemoral
-patellofemoral -superior (proximal) tibiofibular |
|
|
Movements of the leg at the knee joint
|
-flex (heel towards butt)/extension
|
|
|
Function of the popliteus/attachment
|
-tibia laterally rotates as the knee reaches full extension b/c of large medial condyle of femur
-popliteus attaches to lateral condyle of femur and posterior tibia; medially rotates the tibia to allow for initiation of flexion -i.e. "unlocks" the knee |
|
|
Patellofemoral joint
|
-posterior surface of patella covered w/thick hyaline cartilage
-patella slides w/in trochlear groove of the femur |
|
|
Patella (sesamoid) bony landmarks
|
-base (superior)
-rounded anterior surface -apex (inferior) -flat posterior w/two articular surfaces: lateral (larger) and medial (smaller) |
|
|
Purpose/location of patellar ligament
|
-anterior to sesamoid;lying overtop
-resists knee flexion |
|
|
Bursae of knee/function
|
-suprapatellar bursa: lubrication for patellar tendon; articularis genu prevents bursa from collapsing into joint
-several other bursa (infrapatellar;subpopliteal recess) w/in joint |
|
|
Fibrous capsule of knee joint attachment
|
-margins of femoral condyle to margins of tibial condyles
|
|
|
Major ligaments of the knee
|
-Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
-Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) -Medial collateral ligament (MCL) -Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) -Medial meniscus -Lateral meniscus |
|
|
ACL attachments
|
-intercondylar fossa/posteromedial aspect of lateral femoral condyle (proximal)
-anterior intercondylar area (medial to anterior attachment of lateral mensicus) (distal) -lateral to PCL |
|
|
PCL attachments
|
-intercondylar fossa; posterolateral aspect of medial femoral condyle (proximal)
-posterior interondylar area (distal) -medial to ACL |
|
|
ACL function
|
resists anterior displacement of tibia
|
|
|
PCL function
|
prevents posterior displacement of tibia
|
|
|
MCL function/attachment
|
-resists genu valgus stress (knock-kneed)
-can be injured from blow to outside of knee -closely applied to joint capsule/medial meniscus |
|
|
LCL function
|
-resists genu varus stress
-injured from blow to inside of knee -lateral condyle to origin to distal attachment of biceps femoris |
|
|
Muscles that provide knee support
|
-"pes anserine"=goose's foot (b/c attachments looks like goose foot)
-sartorius -gracilis -semitendinosus |
|
|
Menisci purpose
|
-medial & lateral
-medial="C" shaped and larger; attached to MCL -lateral="O" shaped and smaller -absorb shock, decrease friction, increase contact area for joint |
|
|
tibiofibular joints
|
-proximal/distal ends articulate at notches
-crural interosseus membrane between the shafts of the bones provides stability |
|
|
Movements of the foot at the ankle joint
|
-plantar flex (toes point down); dorsiflexion
-inversion (medial edge rotate towards midline); eversion -flexion (towards sole of foot)/extension of toes -abduction (big toe away from others)/adduction of toes |
|
|
Joints of the ankle/foot
|
-talocrural
-talocalcaneal joint/subtalar joints -tarsometatarsal joints -metatarsalphalangeal joints -proximal interphalangeal joints -distal interphalangeal joints |
|
|
Talocrural joint
|
-"mortise" joint
-talus fits into section formed by lateral malleolus, distal tibia, and medial malleolus |
|
|
Compartments of the leg
|
-anterior
-lateral -posterior superficial -posterior deep |
|
|
Deep fascia that surrounds anterior compartment of the leg?
|
Anterior intermuscular septum
|
|
|
Deep fascia that surrounds lateral compartment of the leg?
|
Posterior intermuscular septum
|
|
|
Deep fascia that surrounds posterior superficial compartment of the leg?
|
transverse intermuscular septum
|
|
|
Deep fascia that surrounds posterior deep compartment of the leg?
|
interosseus membrane
|
|
|
Muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg
|
-tibialis anterior
-extensor hallucis longus -extensory digitorum longus -fibularis teritius |
|
|
Action of muscles of anterior compartment of the leg
|
-dorsiflexion
-inversion -toe extension |
|
|
Innervation of muscles of anterior compartment of the leg
|
deep fibular nerve
|
|
|
Blood supply of muscles of anterior compartment of the leg
|
anterior tibial artery
|
|
|
Muscles of lateral compartment of the leg
|
-fibularis longus (most superficial)
-fibularis brevis |
|
|
Action of muscles of lateral compartment of the leg
|
-eversion
-plantar flexion |
|
|
Innervation of muscles of lateral compartment of the leg
|
superficial fibular nerve
|
|
|
Blood supply of muscles of lateral compartment of the leg
|
fibular artery
|
|
|
Muscles of the posterior superficial compartment of the leg
|
-gastrocnemius (two heads, medial and lateral) + soleus (deep to gastro) = triceps surae
-plantaris (mostly tendon alongside medial edge of soleus) |
|
|
Actions of the posterior superficial compartment of the leg
|
-plantar flexion
-knee flexion (only gastro and plantaris) |
|
|
Innervation of the posterior superficial compartment of the leg
|
tibial nerve
|
|
|
Bloody supply of the posterior superficial compartment of the leg
|
posterior tibial artery
|
|
|
Muscles of the posterior deep compartment of the leg
|
-popliteus (exception--very superior to others)
-flexor digitorum longus -flexor hallucis longus -tibialis posterior |
|
|
Actions of the posterior deep compartment of the leg
|
-plantar flexion
-toe flexion -inversion -knee flexion (popliteus) |
|
|
Innervation of the posterior deep compartment of the leg
|
tibial nerve
|
|
|
Blood supply of the posterior deep compartment of the leg
|
posterior tibial artery
|
|
|
Causes/symptoms/treatment of compartment syndrome
|
-trauma, burns, intense use may produce edema or hemorrhage w/in compartments
-compression of nerves/vessels compromises fxn -fasciotomy may be performed |
|
|
Symptoms of anterior compartment syndrome
|
-weakness in dorsiflexion or toe extension
-parathesias (tingling) over dorsum of foot |
|
|
Symptoms of deep posterior compartment syndrome
|
-weakness in toe flexion and inversion
-parasthesias (tingling) in plantar aspect |
|
|
Symptoms of superficial posterior compartment syndrome
|
-weakness in plantar flexion
-dorsolateral foot hypoesthesia (partial/total loss of sensation) |
|
|
Course of the common fibular nerve
|
-branches from sciatic nerve
-deep to proximal fibularis longus -curves lateral to neck of fibula -splits deep to fibularis longus |
|
|
Course of superficial fibular nerve
|
-begins at bifurcation of common fibular n.
-innervates fibularis longus and brevis m. -emerges as cutaneous branch -innervates lateral compartment of leg |
|
|
Course of deep fibular nerve
|
-approaches interosseus membrane
-between tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus -descends with anterior tibial artery -innervates anterior compartment of leg |
|
|
Course of tibial nerve
|
-joins with popliteal a. v.
-continues with posterior tibial artery -gives off sural n. (posterior cutaneous) -splits into lateral and medial plantar n. in foot -innervates posterior superficial compartment of leg |
|
|
Major ligaments of the ankle
|
-medial collateral (deltoid) ligament
-lateral ligament complex |
|
|
Medial collateral (deltoid) ligament attachments/function
|
-medial malleoulus to talus, navicular, sustentaculum tali of calcaneous
-stabilizes joint -resists eversion -much stronger than lateral collateral ligaments |
|
|
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
|
-tibial n. and posterior tibial a. v. are w/in tarsal tunnel
-entrapment/compression of tibial n. -edema, tightness of ankle -pain, tingling, numbness in plantar -weakness of intrinsic foot muscles |
|
|
Function/attachments of lateral ligament complex of angle
|
-lateral malleolus to talus and calcaneous
-stabilize joint -resist inversion -much weaker than medial |
|
|
Typical ankle sprain
|
-90% of ankle spains are inversion
-b/c ligaments of lateral complex are weaker/less able to resist inversion than the medial are able to resist eversion |
|
|
Plantar ligaments of the foot
|
-long plantar ligament
-short plantar (calcaneocuboid) ligament (deep to long) -plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring) |
|
|
What covers plantar surface of foot
|
-plantar fascia/plantar apoeneurosis
|
|
|
First layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
-flexor digitorum brevis
-abductor hallucis -abductor digiti minimi |
|
|
Innervation of first layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
lateral/medial plantar nn.
|
|
|
Second layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
-quadratus plantae
-lumbricals (from flex digitorum longus) |
|
|
Innervation of second layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
lateral/medial plantar nn.
|
|
|
Third layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
-adductor hallucis
-flexor hallucis brevis -flexor digiti minimi brevis |
|
|
Innervation of third layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
lateral/medial plantar nn.
|
|
|
Fourth layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
-plantar interossei (3)
-dorsal interossei (4) |
|
|
Innervation of fourth layer of muscles on plantar surface of foot
|
lateral plantar nerve
|
|
|
Muscles of dorsal aspect of foot
|
-extensor hallucis brevis
-extensor digitorum brevis |
|
|
Innervation of muscles of dorsal aspect of foot
|
deep fibular nerve
|
|
|
Arterial supply of the foot (plantar)
|
pic
|
|
|
Nerve supply of the foot
|
pic
|
|
|
Arterial supply of foot (dorsal)
|
pic
|
|
|
Arterial supply to leg
|
pic
|

